Spaces:
Runtime error
Runtime error
Upload 141 files
Browse filesThis view is limited to 50 files because it contains too many changes.
See raw diff
- .gitattributes +1 -0
- smolagents/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug_report.md +26 -0
- smolagents/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/custom.md +10 -0
- smolagents/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/feature_request.md +23 -0
- smolagents/.github/workflows/build_documentation.yml +27 -0
- smolagents/.github/workflows/build_pr_documentation.yml +22 -0
- smolagents/.github/workflows/quality.yml +31 -0
- smolagents/.github/workflows/tests.yml +43 -0
- smolagents/.github/workflows/trufflehog.yml +18 -0
- smolagents/.github/workflows/upload_pr_documentation.yml +16 -0
- smolagents/.gitignore +155 -0
- smolagents/.pre-commit-config.yaml +13 -0
- smolagents/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md +133 -0
- smolagents/CONTRIBUTING.md +127 -0
- smolagents/LICENSE +201 -0
- smolagents/Makefile +17 -0
- smolagents/README.md +262 -0
- smolagents/SECURITY.md +9 -0
- smolagents/docs/README.md +271 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/en/_config.py +14 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/en/_toctree.yml +42 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/en/conceptual_guides/intro_agents.mdx +104 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/en/conceptual_guides/react.mdx +48 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/en/examples/multiagents.mdx +174 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/en/examples/rag.mdx +136 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/en/examples/text_to_sql.mdx +197 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/en/examples/web_browser.mdx +213 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/en/guided_tour.mdx +498 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/en/index.mdx +38 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/en/reference/agents.mdx +54 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/en/reference/models.mdx +230 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/en/reference/tools.mdx +96 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/en/tutorials/building_good_agents.mdx +420 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/en/tutorials/inspect_runs.mdx +178 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/en/tutorials/memory.mdx +134 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/en/tutorials/secure_code_execution.mdx +414 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/en/tutorials/tools.mdx +332 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/hi/_config.py +14 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/hi/_toctree.yml +36 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/hi/conceptual_guides/intro_agents.mdx +100 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/hi/conceptual_guides/react.mdx +29 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/hi/examples/multiagents.mdx +184 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/hi/examples/rag.mdx +141 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/hi/examples/text_to_sql.mdx +188 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/hi/guided_tour.mdx +345 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/hi/index.mdx +39 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/hi/reference/agents.mdx +151 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/hi/reference/tools.mdx +76 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/hi/tutorials/building_good_agents.mdx +420 -0
- smolagents/docs/source/hi/tutorials/inspect_runs.mdx +86 -0
.gitattributes
CHANGED
|
@@ -34,3 +34,4 @@ saved_model/**/* filter=lfs diff=lfs merge=lfs -text
|
|
| 34 |
*.zst filter=lfs diff=lfs merge=lfs -text
|
| 35 |
*tfevents* filter=lfs diff=lfs merge=lfs -text
|
| 36 |
smolagents-main/tests/data/000000039769.png filter=lfs diff=lfs merge=lfs -text
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 34 |
*.zst filter=lfs diff=lfs merge=lfs -text
|
| 35 |
*tfevents* filter=lfs diff=lfs merge=lfs -text
|
| 36 |
smolagents-main/tests/data/000000039769.png filter=lfs diff=lfs merge=lfs -text
|
| 37 |
+
smolagents/tests/data/000000039769.png filter=lfs diff=lfs merge=lfs -text
|
smolagents/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug_report.md
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
---
|
| 2 |
+
name: Bug report
|
| 3 |
+
about: The clearer your bug report, the faster it will be fixed!
|
| 4 |
+
title: "[BUG]"
|
| 5 |
+
labels: bug
|
| 6 |
+
assignees: ''
|
| 7 |
+
|
| 8 |
+
---
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
**Describe the bug**
|
| 11 |
+
A clear and concise description of what the bug is.
|
| 12 |
+
|
| 13 |
+
**Code to reproduce the error**
|
| 14 |
+
The simplest code snippet that produces your bug.
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
**Error logs (if any)**
|
| 17 |
+
Provide error logs if there are any.
|
| 18 |
+
|
| 19 |
+
**Expected behavior**
|
| 20 |
+
A clear and concise description of what you expected to happen.
|
| 21 |
+
|
| 22 |
+
**Packages version:**
|
| 23 |
+
Run `pip freeze | grep smolagents` and paste it here.
|
| 24 |
+
|
| 25 |
+
**Additional context**
|
| 26 |
+
Add any other context about the problem here.
|
smolagents/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/custom.md
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
---
|
| 2 |
+
name: Custom issue template
|
| 3 |
+
about: Describe this issue template's purpose here.
|
| 4 |
+
title: ''
|
| 5 |
+
labels: ''
|
| 6 |
+
assignees: ''
|
| 7 |
+
|
| 8 |
+
---
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
|
smolagents/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/feature_request.md
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
---
|
| 2 |
+
name: Feature request
|
| 3 |
+
about: Suggest an idea for this project
|
| 4 |
+
title: ''
|
| 5 |
+
labels: enhancement
|
| 6 |
+
assignees: ''
|
| 7 |
+
|
| 8 |
+
---
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
**Is your feature request related to a problem? Please describe.**
|
| 11 |
+
A clear and concise description of what the problem is. Ex. I'm always frustrated when [...]
|
| 12 |
+
|
| 13 |
+
**Describe the solution you'd like**
|
| 14 |
+
A clear and concise description of what you want to happen.
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
**Is this not possible with the current options.**
|
| 17 |
+
Make sure to consider if what you're requesting can be done with current abstractions.
|
| 18 |
+
|
| 19 |
+
**Describe alternatives you've considered**
|
| 20 |
+
A clear and concise description of any alternative solutions or features you've considered.
|
| 21 |
+
|
| 22 |
+
**Additional context**
|
| 23 |
+
Add any other context or screenshots about the feature request here.
|
smolagents/.github/workflows/build_documentation.yml
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
name: Build documentation
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
on:
|
| 4 |
+
push:
|
| 5 |
+
branches:
|
| 6 |
+
- main
|
| 7 |
+
- doc-builder*
|
| 8 |
+
- v*-release
|
| 9 |
+
- use_templates
|
| 10 |
+
paths:
|
| 11 |
+
- 'docs/source/**'
|
| 12 |
+
- 'assets/**'
|
| 13 |
+
- '.github/workflows/doc-build.yml'
|
| 14 |
+
- 'pyproject.toml'
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
jobs:
|
| 17 |
+
build:
|
| 18 |
+
uses: huggingface/doc-builder/.github/workflows/build_main_documentation.yml@main
|
| 19 |
+
with:
|
| 20 |
+
commit_sha: ${{ github.sha }}
|
| 21 |
+
package: smolagents
|
| 22 |
+
languages: en
|
| 23 |
+
notebook_folder: smolagents_doc
|
| 24 |
+
# additional_args: --not_python_module # use this arg if repository is documentation only
|
| 25 |
+
secrets:
|
| 26 |
+
token: ${{ secrets.HUGGINGFACE_PUSH }}
|
| 27 |
+
hf_token: ${{ secrets.HF_DOC_BUILD_PUSH }}
|
smolagents/.github/workflows/build_pr_documentation.yml
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
name: Build PR Documentation
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
on:
|
| 4 |
+
pull_request:
|
| 5 |
+
paths:
|
| 6 |
+
- 'docs/source/**'
|
| 7 |
+
- 'assets/**'
|
| 8 |
+
- '.github/workflows/doc-pr-build.yml'
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
concurrency:
|
| 11 |
+
group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.head_ref || github.run_id }}
|
| 12 |
+
cancel-in-progress: true
|
| 13 |
+
|
| 14 |
+
jobs:
|
| 15 |
+
build:
|
| 16 |
+
uses: huggingface/doc-builder/.github/workflows/build_pr_documentation.yml@main
|
| 17 |
+
with:
|
| 18 |
+
commit_sha: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha }}
|
| 19 |
+
pr_number: ${{ github.event.number }}
|
| 20 |
+
package: smolagents
|
| 21 |
+
languages: en
|
| 22 |
+
# additional_args: --not_python_module # use this arg if repository is documentation only
|
smolagents/.github/workflows/quality.yml
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
name: Quality Check
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
on: [pull_request]
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
env:
|
| 6 |
+
UV_SYSTEM_PYTHON: 1
|
| 7 |
+
|
| 8 |
+
jobs:
|
| 9 |
+
check_code_quality:
|
| 10 |
+
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
| 11 |
+
env:
|
| 12 |
+
UV_HTTP_TIMEOUT: 600 # max 10min to install deps
|
| 13 |
+
|
| 14 |
+
steps:
|
| 15 |
+
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
| 16 |
+
- name: Set up Python
|
| 17 |
+
uses: actions/setup-python@v2
|
| 18 |
+
with:
|
| 19 |
+
python-version: "3.12"
|
| 20 |
+
|
| 21 |
+
# Setup venv
|
| 22 |
+
- name: Setup uv
|
| 23 |
+
run: |
|
| 24 |
+
pip install --upgrade uv
|
| 25 |
+
|
| 26 |
+
- name: Install dependencies
|
| 27 |
+
run: uv pip install "smolagents[quality] @ ."
|
| 28 |
+
|
| 29 |
+
# Equivalent of "make quality" but step by step
|
| 30 |
+
- run: ruff check examples src tests # linter
|
| 31 |
+
- run: ruff format --check examples src tests # formatter
|
smolagents/.github/workflows/tests.yml
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
name: Python tests
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
on:
|
| 4 |
+
pull_request:
|
| 5 |
+
push:
|
| 6 |
+
branches:
|
| 7 |
+
- ci-*
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
env:
|
| 10 |
+
UV_SYSTEM_PYTHON: 1
|
| 11 |
+
|
| 12 |
+
jobs:
|
| 13 |
+
build-ubuntu:
|
| 14 |
+
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
| 15 |
+
env:
|
| 16 |
+
UV_HTTP_TIMEOUT: 600 # max 10min to install deps
|
| 17 |
+
|
| 18 |
+
strategy:
|
| 19 |
+
fail-fast: false
|
| 20 |
+
matrix:
|
| 21 |
+
python-version: ["3.10", "3.12"]
|
| 22 |
+
|
| 23 |
+
steps:
|
| 24 |
+
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
| 25 |
+
- name: Set up Python ${{ matrix.python-version }}
|
| 26 |
+
uses: actions/setup-python@v2
|
| 27 |
+
with:
|
| 28 |
+
python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }}
|
| 29 |
+
|
| 30 |
+
# Setup venv
|
| 31 |
+
- name: Setup uv
|
| 32 |
+
run: |
|
| 33 |
+
pip install --upgrade uv
|
| 34 |
+
|
| 35 |
+
# Install dependencies
|
| 36 |
+
- name: Install dependencies
|
| 37 |
+
run: |
|
| 38 |
+
uv pip install "smolagents[test] @ ."
|
| 39 |
+
|
| 40 |
+
# Run tests
|
| 41 |
+
- name: Test with pytest
|
| 42 |
+
run: |
|
| 43 |
+
pytest ./tests/
|
smolagents/.github/workflows/trufflehog.yml
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
on:
|
| 2 |
+
push:
|
| 3 |
+
|
| 4 |
+
name: Secret Leaks
|
| 5 |
+
|
| 6 |
+
permissions:
|
| 7 |
+
contents: read
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
jobs:
|
| 10 |
+
trufflehog:
|
| 11 |
+
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
| 12 |
+
steps:
|
| 13 |
+
- name: Checkout code
|
| 14 |
+
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
| 15 |
+
with:
|
| 16 |
+
fetch-depth: 0
|
| 17 |
+
- name: Secret Scanning
|
| 18 |
+
uses: trufflesecurity/trufflehog@main
|
smolagents/.github/workflows/upload_pr_documentation.yml
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
name: Upload PR Documentation
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
on:
|
| 4 |
+
workflow_run:
|
| 5 |
+
workflows: ["Build PR Documentation"]
|
| 6 |
+
types:
|
| 7 |
+
- completed
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
jobs:
|
| 10 |
+
build:
|
| 11 |
+
uses: huggingface/doc-builder/.github/workflows/upload_pr_documentation.yml@main
|
| 12 |
+
with:
|
| 13 |
+
package_name: smolagents
|
| 14 |
+
secrets:
|
| 15 |
+
hf_token: ${{ secrets.HF_DOC_BUILD_PUSH }}
|
| 16 |
+
comment_bot_token: ${{ secrets.COMMENT_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
smolagents/.gitignore
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,155 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Logging
|
| 2 |
+
logs
|
| 3 |
+
tmp
|
| 4 |
+
wandb
|
| 5 |
+
|
| 6 |
+
# Data
|
| 7 |
+
data
|
| 8 |
+
outputs
|
| 9 |
+
data/
|
| 10 |
+
|
| 11 |
+
# Apple
|
| 12 |
+
.DS_Store
|
| 13 |
+
|
| 14 |
+
# VS Code
|
| 15 |
+
.vscode
|
| 16 |
+
|
| 17 |
+
# Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files
|
| 18 |
+
__pycache__/
|
| 19 |
+
*.py[cod]
|
| 20 |
+
*$py.class
|
| 21 |
+
|
| 22 |
+
# C extensions
|
| 23 |
+
*.so
|
| 24 |
+
|
| 25 |
+
# Distribution / packaging
|
| 26 |
+
.Python
|
| 27 |
+
build/
|
| 28 |
+
develop-eggs/
|
| 29 |
+
dist/
|
| 30 |
+
downloads/
|
| 31 |
+
eggs/
|
| 32 |
+
.eggs/
|
| 33 |
+
lib/
|
| 34 |
+
lib64/
|
| 35 |
+
parts/
|
| 36 |
+
sdist/
|
| 37 |
+
var/
|
| 38 |
+
wheels/
|
| 39 |
+
share/python-wheels/
|
| 40 |
+
node_modules/
|
| 41 |
+
*.egg-info/
|
| 42 |
+
.installed.cfg
|
| 43 |
+
*.egg
|
| 44 |
+
MANIFEST
|
| 45 |
+
|
| 46 |
+
# PyInstaller
|
| 47 |
+
*.manifest
|
| 48 |
+
*.spec
|
| 49 |
+
|
| 50 |
+
# Installer logs
|
| 51 |
+
pip-log.txt
|
| 52 |
+
pip-delete-this-directory.txt
|
| 53 |
+
|
| 54 |
+
# Unit test / coverage reports
|
| 55 |
+
htmlcov/
|
| 56 |
+
.tox/
|
| 57 |
+
.nox/
|
| 58 |
+
.coverage
|
| 59 |
+
.coverage.*
|
| 60 |
+
.cache
|
| 61 |
+
nosetests.xml
|
| 62 |
+
coverage.xml
|
| 63 |
+
*.cover
|
| 64 |
+
*.py,cover
|
| 65 |
+
.hypothesis/
|
| 66 |
+
.pytest_cache/
|
| 67 |
+
cover/
|
| 68 |
+
uv.lock
|
| 69 |
+
|
| 70 |
+
# Translations
|
| 71 |
+
*.mo
|
| 72 |
+
*.pot
|
| 73 |
+
|
| 74 |
+
# Sphinx documentation
|
| 75 |
+
docs/_build/
|
| 76 |
+
|
| 77 |
+
# PyBuilder
|
| 78 |
+
.pybuilder/
|
| 79 |
+
target/
|
| 80 |
+
|
| 81 |
+
# Jupyter Notebook
|
| 82 |
+
.ipynb_checkpoints
|
| 83 |
+
|
| 84 |
+
# IPython
|
| 85 |
+
profile_default/
|
| 86 |
+
ipython_config.py
|
| 87 |
+
|
| 88 |
+
# pyenv
|
| 89 |
+
# .python-version
|
| 90 |
+
|
| 91 |
+
# pipenv
|
| 92 |
+
#Pipfile.lock
|
| 93 |
+
|
| 94 |
+
# UV
|
| 95 |
+
#uv.lock
|
| 96 |
+
|
| 97 |
+
# poetry
|
| 98 |
+
#poetry.lock
|
| 99 |
+
|
| 100 |
+
# pdm
|
| 101 |
+
.pdm.toml
|
| 102 |
+
.pdm-python
|
| 103 |
+
.pdm-build/
|
| 104 |
+
|
| 105 |
+
# PEP 582
|
| 106 |
+
__pypackages__/
|
| 107 |
+
|
| 108 |
+
# Celery stuff
|
| 109 |
+
celerybeat-schedule
|
| 110 |
+
celerybeat.pid
|
| 111 |
+
|
| 112 |
+
# SageMath parsed files
|
| 113 |
+
*.sage.py
|
| 114 |
+
|
| 115 |
+
# Environments
|
| 116 |
+
.env
|
| 117 |
+
.venv
|
| 118 |
+
env/
|
| 119 |
+
venv/
|
| 120 |
+
ENV/
|
| 121 |
+
env.bak/
|
| 122 |
+
venv.bak/
|
| 123 |
+
|
| 124 |
+
|
| 125 |
+
# mkdocs documentation
|
| 126 |
+
/site
|
| 127 |
+
|
| 128 |
+
# mypy
|
| 129 |
+
.mypy_cache/
|
| 130 |
+
.dmypy.json
|
| 131 |
+
dmypy.json
|
| 132 |
+
|
| 133 |
+
# Pyre type checker
|
| 134 |
+
.pyre/
|
| 135 |
+
|
| 136 |
+
# pytype static type analyzer
|
| 137 |
+
.pytype/
|
| 138 |
+
|
| 139 |
+
# Cython debug symbols
|
| 140 |
+
cython_debug/
|
| 141 |
+
|
| 142 |
+
# PyCharm
|
| 143 |
+
.idea/
|
| 144 |
+
|
| 145 |
+
# Interpreter
|
| 146 |
+
interpreter_workspace/
|
| 147 |
+
|
| 148 |
+
# Archive
|
| 149 |
+
archive/
|
| 150 |
+
savedir/
|
| 151 |
+
output/
|
| 152 |
+
tool_output/
|
| 153 |
+
|
| 154 |
+
# Gradio runtime
|
| 155 |
+
.gradio/
|
smolagents/.pre-commit-config.yaml
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
repos:
|
| 2 |
+
- repo: https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-pre-commit
|
| 3 |
+
rev: v0.2.1
|
| 4 |
+
hooks:
|
| 5 |
+
- id: ruff
|
| 6 |
+
args:
|
| 7 |
+
- --fix
|
| 8 |
+
- id: ruff-format
|
| 9 |
+
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks
|
| 10 |
+
rev: v4.5.0
|
| 11 |
+
hooks:
|
| 12 |
+
- id: check-merge-conflict
|
| 13 |
+
- id: check-yaml
|
smolagents/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,133 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
|
| 2 |
+
# Contributor Covenant Code of Conduct
|
| 3 |
+
|
| 4 |
+
## Our Pledge
|
| 5 |
+
|
| 6 |
+
We as members, contributors, and leaders pledge to make participation in our
|
| 7 |
+
community a harassment-free experience for everyone, regardless of age, body
|
| 8 |
+
size, visible or invisible disability, ethnicity, sex characteristics, gender
|
| 9 |
+
identity and expression, level of experience, education, socio-economic status,
|
| 10 |
+
nationality, personal appearance, race, caste, color, religion, or sexual
|
| 11 |
+
identity and orientation.
|
| 12 |
+
|
| 13 |
+
We pledge to act and interact in ways that contribute to an open, welcoming,
|
| 14 |
+
diverse, inclusive, and healthy community.
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
## Our Standards
|
| 17 |
+
|
| 18 |
+
Examples of behavior that contributes to a positive environment for our
|
| 19 |
+
community include:
|
| 20 |
+
|
| 21 |
+
* Demonstrating empathy and kindness toward other people
|
| 22 |
+
* Being respectful of differing opinions, viewpoints, and experiences
|
| 23 |
+
* Giving and gracefully accepting constructive feedback
|
| 24 |
+
* Accepting responsibility and apologizing to those affected by our mistakes,
|
| 25 |
+
and learning from the experience
|
| 26 |
+
* Focusing on what is best not just for us as individuals, but for the overall
|
| 27 |
+
community
|
| 28 |
+
|
| 29 |
+
Examples of unacceptable behavior include:
|
| 30 |
+
|
| 31 |
+
* The use of sexualized language or imagery, and sexual attention or advances of
|
| 32 |
+
any kind
|
| 33 |
+
* Trolling, insulting or derogatory comments, and personal or political attacks
|
| 34 |
+
* Public or private harassment
|
| 35 |
+
* Publishing others' private information, such as a physical or email address,
|
| 36 |
+
without their explicit permission
|
| 37 |
+
* Other conduct which could reasonably be considered inappropriate in a
|
| 38 |
+
professional setting
|
| 39 |
+
|
| 40 |
+
## Enforcement Responsibilities
|
| 41 |
+
|
| 42 |
+
Community leaders are responsible for clarifying and enforcing our standards of
|
| 43 |
+
acceptable behavior and will take appropriate and fair corrective action in
|
| 44 |
+
response to any behavior that they deem inappropriate, threatening, offensive,
|
| 45 |
+
or harmful.
|
| 46 |
+
|
| 47 |
+
Community leaders have the right and responsibility to remove, edit, or reject
|
| 48 |
+
comments, commits, code, wiki edits, issues, and other contributions that are
|
| 49 |
+
not aligned to this Code of Conduct, and will communicate reasons for moderation
|
| 50 |
+
decisions when appropriate.
|
| 51 |
+
|
| 52 |
+
## Scope
|
| 53 |
+
|
| 54 |
+
This Code of Conduct applies within all community spaces, and also applies when
|
| 55 |
+
an individual is officially representing the community in public spaces.
|
| 56 |
+
Examples of representing our community include using an official e-mail address,
|
| 57 |
+
posting via an official social media account, or acting as an appointed
|
| 58 |
+
representative at an online or offline event.
|
| 59 |
+
|
| 60 |
+
## Enforcement
|
| 61 |
+
|
| 62 |
+
Instances of abusive, harassing, or otherwise unacceptable behavior may be
|
| 63 |
+
reported to the community leaders responsible for enforcement at
|
| 64 | |
| 65 |
+
All complaints will be reviewed and investigated promptly and fairly.
|
| 66 |
+
|
| 67 |
+
All community leaders are obligated to respect the privacy and security of the
|
| 68 |
+
reporter of any incident.
|
| 69 |
+
|
| 70 |
+
## Enforcement Guidelines
|
| 71 |
+
|
| 72 |
+
Community leaders will follow these Community Impact Guidelines in determining
|
| 73 |
+
the consequences for any action they deem in violation of this Code of Conduct:
|
| 74 |
+
|
| 75 |
+
### 1. Correction
|
| 76 |
+
|
| 77 |
+
**Community Impact**: Use of inappropriate language or other behavior deemed
|
| 78 |
+
unprofessional or unwelcome in the community.
|
| 79 |
+
|
| 80 |
+
**Consequence**: A private, written warning from community leaders, providing
|
| 81 |
+
clarity around the nature of the violation and an explanation of why the
|
| 82 |
+
behavior was inappropriate. A public apology may be requested.
|
| 83 |
+
|
| 84 |
+
### 2. Warning
|
| 85 |
+
|
| 86 |
+
**Community Impact**: A violation through a single incident or series of
|
| 87 |
+
actions.
|
| 88 |
+
|
| 89 |
+
**Consequence**: A warning with consequences for continued behavior. No
|
| 90 |
+
interaction with the people involved, including unsolicited interaction with
|
| 91 |
+
those enforcing the Code of Conduct, for a specified period of time. This
|
| 92 |
+
includes avoiding interactions in community spaces as well as external channels
|
| 93 |
+
like social media. Violating these terms may lead to a temporary or permanent
|
| 94 |
+
ban.
|
| 95 |
+
|
| 96 |
+
### 3. Temporary Ban
|
| 97 |
+
|
| 98 |
+
**Community Impact**: A serious violation of community standards, including
|
| 99 |
+
sustained inappropriate behavior.
|
| 100 |
+
|
| 101 |
+
**Consequence**: A temporary ban from any sort of interaction or public
|
| 102 |
+
communication with the community for a specified period of time. No public or
|
| 103 |
+
private interaction with the people involved, including unsolicited interaction
|
| 104 |
+
with those enforcing the Code of Conduct, is allowed during this period.
|
| 105 |
+
Violating these terms may lead to a permanent ban.
|
| 106 |
+
|
| 107 |
+
### 4. Permanent Ban
|
| 108 |
+
|
| 109 |
+
**Community Impact**: Demonstrating a pattern of violation of community
|
| 110 |
+
standards, including sustained inappropriate behavior, harassment of an
|
| 111 |
+
individual, or aggression toward or disparagement of classes of individuals.
|
| 112 |
+
|
| 113 |
+
**Consequence**: A permanent ban from any sort of public interaction within the
|
| 114 |
+
community.
|
| 115 |
+
|
| 116 |
+
## Attribution
|
| 117 |
+
|
| 118 |
+
This Code of Conduct is adapted from the [Contributor Covenant][homepage],
|
| 119 |
+
version 2.1, available at
|
| 120 |
+
[https://www.contributor-covenant.org/version/2/1/code_of_conduct.html][v2.1].
|
| 121 |
+
|
| 122 |
+
Community Impact Guidelines were inspired by
|
| 123 |
+
[Mozilla's code of conduct enforcement ladder][Mozilla CoC].
|
| 124 |
+
|
| 125 |
+
For answers to common questions about this code of conduct, see the FAQ at
|
| 126 |
+
[https://www.contributor-covenant.org/faq][FAQ]. Translations are available at
|
| 127 |
+
[https://www.contributor-covenant.org/translations][translations].
|
| 128 |
+
|
| 129 |
+
[homepage]: https://www.contributor-covenant.org
|
| 130 |
+
[v2.1]: https://www.contributor-covenant.org/version/2/1/code_of_conduct.html
|
| 131 |
+
[Mozilla CoC]: https://github.com/mozilla/diversity
|
| 132 |
+
[FAQ]: https://www.contributor-covenant.org/faq
|
| 133 |
+
[translations]: https://www.contributor-covenant.org/translations
|
smolagents/CONTRIBUTING.md
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
<!---
|
| 2 |
+
Copyright 2025 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
| 3 |
+
|
| 4 |
+
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
| 5 |
+
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
| 6 |
+
You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
| 7 |
+
|
| 8 |
+
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
| 11 |
+
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
| 12 |
+
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
| 13 |
+
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
| 14 |
+
limitations under the License.
|
| 15 |
+
-->
|
| 16 |
+
|
| 17 |
+
# Contribute to smolagents
|
| 18 |
+
|
| 19 |
+
Everyone is welcome to contribute, and we value everybody's contribution. Code
|
| 20 |
+
contributions are not the only way to help the community. Answering questions, helping
|
| 21 |
+
others, and improving the documentation are also immensely valuable.
|
| 22 |
+
|
| 23 |
+
It also helps us if you spread the word! Reference the library in blog posts
|
| 24 |
+
about the awesome projects it made possible, shout out on Twitter every time it has
|
| 25 |
+
helped you, or simply ⭐️ the repository to say thank you.
|
| 26 |
+
|
| 27 |
+
However you choose to contribute, please be mindful and respect our
|
| 28 |
+
[code of conduct](https://github.com/huggingface/smolagents/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md).
|
| 29 |
+
|
| 30 |
+
**This guide was heavily inspired by the awesome [scikit-learn guide to contributing](https://github.com/scikit-learn/scikit-learn/blob/main/CONTRIBUTING.md).**
|
| 31 |
+
|
| 32 |
+
## Ways to contribute
|
| 33 |
+
|
| 34 |
+
There are several ways you can contribute to smolagents.
|
| 35 |
+
|
| 36 |
+
* Submit issues related to bugs or desired new features.
|
| 37 |
+
* Contribute to the examples or to the documentation.
|
| 38 |
+
* Fix outstanding issues with the existing code.
|
| 39 |
+
|
| 40 |
+
> All contributions are equally valuable to the community. 🥰
|
| 41 |
+
|
| 42 |
+
## Submitting a bug-related issue or feature request
|
| 43 |
+
|
| 44 |
+
At any moment, feel welcome to open an issue, citing your exact error traces and package versions if it's a bug.
|
| 45 |
+
It's often even better to open a PR with your proposed fixes/changes!
|
| 46 |
+
|
| 47 |
+
Do your best to follow these guidelines when submitting a bug-related issue or a feature
|
| 48 |
+
request. It will make it easier for us to come back to you quickly and with good
|
| 49 |
+
feedback.
|
| 50 |
+
|
| 51 |
+
### Did you find a bug?
|
| 52 |
+
|
| 53 |
+
The smolagents library is robust and reliable thanks to users who report the problems they encounter.
|
| 54 |
+
|
| 55 |
+
Before you report an issue, we would really appreciate it if you could **make sure the bug was not
|
| 56 |
+
already reported** (use the search bar on GitHub under Issues). Your issue should also be related to bugs in the
|
| 57 |
+
library itself, and not your code.
|
| 58 |
+
|
| 59 |
+
Once you've confirmed the bug hasn't already been reported, please include the following information in your issue so
|
| 60 |
+
we can quickly resolve it:
|
| 61 |
+
|
| 62 |
+
* Your **OS type and version**, as well as your environment versions (versions of rust, python, and dependencies).
|
| 63 |
+
* A short, self-contained, code snippet that allows us to reproduce the bug.
|
| 64 |
+
* The *full* traceback if an exception is raised.
|
| 65 |
+
* Attach any other additional information, like screenshots, you think may help.
|
| 66 |
+
|
| 67 |
+
### Do you want a new feature?
|
| 68 |
+
|
| 69 |
+
If there is a new feature you'd like to see in smolagents, please open an issue and describe:
|
| 70 |
+
|
| 71 |
+
1. What is the *motivation* behind this feature? Is it related to a problem or frustration with the library? Is it
|
| 72 |
+
a feature related to something you need for a project? Is it something you worked on and think it could benefit
|
| 73 |
+
the community?
|
| 74 |
+
|
| 75 |
+
Whatever it is, we'd love to hear about it!
|
| 76 |
+
|
| 77 |
+
2. Describe your requested feature in as much detail as possible. The more you can tell us about it, the better
|
| 78 |
+
we'll be able to help you.
|
| 79 |
+
3. Provide a *code snippet* that demonstrates the feature's usage.
|
| 80 |
+
4. If the feature is related to a paper, please include a link.
|
| 81 |
+
|
| 82 |
+
If your issue is well written we're already 80% of the way there by the time you create it.
|
| 83 |
+
|
| 84 |
+
## Do you want to add documentation?
|
| 85 |
+
|
| 86 |
+
We're always looking for improvements to the documentation that make it more clear and accurate. Please let us know
|
| 87 |
+
how the documentation can be improved such as typos and any content that is missing, unclear or inaccurate. We'll be
|
| 88 |
+
happy to make the changes or help you make a contribution if you're interested!
|
| 89 |
+
|
| 90 |
+
## Fixing outstanding issues
|
| 91 |
+
|
| 92 |
+
If you notice an issue with the existing code and have a fix in mind, feel free to [start contributing](https://docs.github.com/en/pull-requests/collaborating-with-pull-requests/proposing-changes-to-your-work-with-pull-requests/creating-a-pull-request) and open
|
| 93 |
+
a Pull Request!
|
| 94 |
+
|
| 95 |
+
### Making code changes
|
| 96 |
+
|
| 97 |
+
To install dev dependencies, run:
|
| 98 |
+
```
|
| 99 |
+
pip install -e ".[dev]"
|
| 100 |
+
```
|
| 101 |
+
|
| 102 |
+
When making changes to the codebase, please check that it follows the repo's code quality requirements by running:
|
| 103 |
+
To check code quality of the source code:
|
| 104 |
+
```
|
| 105 |
+
make quality
|
| 106 |
+
```
|
| 107 |
+
|
| 108 |
+
If the checks fail, you can run the formatter with:
|
| 109 |
+
```
|
| 110 |
+
make style
|
| 111 |
+
```
|
| 112 |
+
|
| 113 |
+
And commit the changes.
|
| 114 |
+
|
| 115 |
+
To run tests locally, run this command:
|
| 116 |
+
```bash
|
| 117 |
+
make test
|
| 118 |
+
```
|
| 119 |
+
</details>
|
| 120 |
+
|
| 121 |
+
## I want to become a maintainer of the project. How do I get there?
|
| 122 |
+
|
| 123 |
+
smolagents is a project led and managed by Hugging Face. We are more than
|
| 124 |
+
happy to have motivated individuals from other organizations join us as maintainers with the goal of helping smolagents
|
| 125 |
+
make a dent in the world of Agents.
|
| 126 |
+
|
| 127 |
+
If you are such an individual (or organization), please reach out to us and let's collaborate.
|
smolagents/LICENSE
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,201 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
Apache License
|
| 2 |
+
Version 2.0, January 2004
|
| 3 |
+
http://www.apache.org/licenses/
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR USE, REPRODUCTION, AND DISTRIBUTION
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
1. Definitions.
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
"License" shall mean the terms and conditions for use, reproduction,
|
| 10 |
+
and distribution as defined by Sections 1 through 9 of this document.
|
| 11 |
+
|
| 12 |
+
"Licensor" shall mean the copyright owner or entity authorized by
|
| 13 |
+
the copyright owner that is granting the License.
|
| 14 |
+
|
| 15 |
+
"Legal Entity" shall mean the union of the acting entity and all
|
| 16 |
+
other entities that control, are controlled by, or are under common
|
| 17 |
+
control with that entity. For the purposes of this definition,
|
| 18 |
+
"control" means (i) the power, direct or indirect, to cause the
|
| 19 |
+
direction or management of such entity, whether by contract or
|
| 20 |
+
otherwise, or (ii) ownership of fifty percent (50%) or more of the
|
| 21 |
+
outstanding shares, or (iii) beneficial ownership of such entity.
|
| 22 |
+
|
| 23 |
+
"You" (or "Your") shall mean an individual or Legal Entity
|
| 24 |
+
exercising permissions granted by this License.
|
| 25 |
+
|
| 26 |
+
"Source" form shall mean the preferred form for making modifications,
|
| 27 |
+
including but not limited to software source code, documentation
|
| 28 |
+
source, and configuration files.
|
| 29 |
+
|
| 30 |
+
"Object" form shall mean any form resulting from mechanical
|
| 31 |
+
transformation or translation of a Source form, including but
|
| 32 |
+
not limited to compiled object code, generated documentation,
|
| 33 |
+
and conversions to other media types.
|
| 34 |
+
|
| 35 |
+
"Work" shall mean the work of authorship, whether in Source or
|
| 36 |
+
Object form, made available under the License, as indicated by a
|
| 37 |
+
copyright notice that is included in or attached to the work
|
| 38 |
+
(an example is provided in the Appendix below).
|
| 39 |
+
|
| 40 |
+
"Derivative Works" shall mean any work, whether in Source or Object
|
| 41 |
+
form, that is based on (or derived from) the Work and for which the
|
| 42 |
+
editorial revisions, annotations, elaborations, or other modifications
|
| 43 |
+
represent, as a whole, an original work of authorship. For the purposes
|
| 44 |
+
of this License, Derivative Works shall not include works that remain
|
| 45 |
+
separable from, or merely link (or bind by name) to the interfaces of,
|
| 46 |
+
the Work and Derivative Works thereof.
|
| 47 |
+
|
| 48 |
+
"Contribution" shall mean any work of authorship, including
|
| 49 |
+
the original version of the Work and any modifications or additions
|
| 50 |
+
to that Work or Derivative Works thereof, that is intentionally
|
| 51 |
+
submitted to Licensor for inclusion in the Work by the copyright owner
|
| 52 |
+
or by an individual or Legal Entity authorized to submit on behalf of
|
| 53 |
+
the copyright owner. For the purposes of this definition, "submitted"
|
| 54 |
+
means any form of electronic, verbal, or written communication sent
|
| 55 |
+
to the Licensor or its representatives, including but not limited to
|
| 56 |
+
communication on electronic mailing lists, source code control systems,
|
| 57 |
+
and issue tracking systems that are managed by, or on behalf of, the
|
| 58 |
+
Licensor for the purpose of discussing and improving the Work, but
|
| 59 |
+
excluding communication that is conspicuously marked or otherwise
|
| 60 |
+
designated in writing by the copyright owner as "Not a Contribution."
|
| 61 |
+
|
| 62 |
+
"Contributor" shall mean Licensor and any individual or Legal Entity
|
| 63 |
+
on behalf of whom a Contribution has been received by Licensor and
|
| 64 |
+
subsequently incorporated within the Work.
|
| 65 |
+
|
| 66 |
+
2. Grant of Copyright License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
|
| 67 |
+
this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
|
| 68 |
+
worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
|
| 69 |
+
copyright license to reproduce, prepare Derivative Works of,
|
| 70 |
+
publicly display, publicly perform, sublicense, and distribute the
|
| 71 |
+
Work and such Derivative Works in Source or Object form.
|
| 72 |
+
|
| 73 |
+
3. Grant of Patent License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
|
| 74 |
+
this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
|
| 75 |
+
worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
|
| 76 |
+
(except as stated in this section) patent license to make, have made,
|
| 77 |
+
use, offer to sell, sell, import, and otherwise transfer the Work,
|
| 78 |
+
where such license applies only to those patent claims licensable
|
| 79 |
+
by such Contributor that are necessarily infringed by their
|
| 80 |
+
Contribution(s) alone or by combination of their Contribution(s)
|
| 81 |
+
with the Work to which such Contribution(s) was submitted. If You
|
| 82 |
+
institute patent litigation against any entity (including a
|
| 83 |
+
cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that the Work
|
| 84 |
+
or a Contribution incorporated within the Work constitutes direct
|
| 85 |
+
or contributory patent infringement, then any patent licenses
|
| 86 |
+
granted to You under this License for that Work shall terminate
|
| 87 |
+
as of the date such litigation is filed.
|
| 88 |
+
|
| 89 |
+
4. Redistribution. You may reproduce and distribute copies of the
|
| 90 |
+
Work or Derivative Works thereof in any medium, with or without
|
| 91 |
+
modifications, and in Source or Object form, provided that You
|
| 92 |
+
meet the following conditions:
|
| 93 |
+
|
| 94 |
+
(a) You must give any other recipients of the Work or
|
| 95 |
+
Derivative Works a copy of this License; and
|
| 96 |
+
|
| 97 |
+
(b) You must cause any modified files to carry prominent notices
|
| 98 |
+
stating that You changed the files; and
|
| 99 |
+
|
| 100 |
+
(c) You must retain, in the Source form of any Derivative Works
|
| 101 |
+
that You distribute, all copyright, patent, trademark, and
|
| 102 |
+
attribution notices from the Source form of the Work,
|
| 103 |
+
excluding those notices that do not pertain to any part of
|
| 104 |
+
the Derivative Works; and
|
| 105 |
+
|
| 106 |
+
(d) If the Work includes a "NOTICE" text file as part of its
|
| 107 |
+
distribution, then any Derivative Works that You distribute must
|
| 108 |
+
include a readable copy of the attribution notices contained
|
| 109 |
+
within such NOTICE file, excluding those notices that do not
|
| 110 |
+
pertain to any part of the Derivative Works, in at least one
|
| 111 |
+
of the following places: within a NOTICE text file distributed
|
| 112 |
+
as part of the Derivative Works; within the Source form or
|
| 113 |
+
documentation, if provided along with the Derivative Works; or,
|
| 114 |
+
within a display generated by the Derivative Works, if and
|
| 115 |
+
wherever such third-party notices normally appear. The contents
|
| 116 |
+
of the NOTICE file are for informational purposes only and
|
| 117 |
+
do not modify the License. You may add Your own attribution
|
| 118 |
+
notices within Derivative Works that You distribute, alongside
|
| 119 |
+
or as an addendum to the NOTICE text from the Work, provided
|
| 120 |
+
that such additional attribution notices cannot be construed
|
| 121 |
+
as modifying the License.
|
| 122 |
+
|
| 123 |
+
You may add Your own copyright statement to Your modifications and
|
| 124 |
+
may provide additional or different license terms and conditions
|
| 125 |
+
for use, reproduction, or distribution of Your modifications, or
|
| 126 |
+
for any such Derivative Works as a whole, provided Your use,
|
| 127 |
+
reproduction, and distribution of the Work otherwise complies with
|
| 128 |
+
the conditions stated in this License.
|
| 129 |
+
|
| 130 |
+
5. Submission of Contributions. Unless You explicitly state otherwise,
|
| 131 |
+
any Contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the Work
|
| 132 |
+
by You to the Licensor shall be under the terms and conditions of
|
| 133 |
+
this License, without any additional terms or conditions.
|
| 134 |
+
Notwithstanding the above, nothing herein shall supersede or modify
|
| 135 |
+
the terms of any separate license agreement you may have executed
|
| 136 |
+
with Licensor regarding such Contributions.
|
| 137 |
+
|
| 138 |
+
6. Trademarks. This License does not grant permission to use the trade
|
| 139 |
+
names, trademarks, service marks, or product names of the Licensor,
|
| 140 |
+
except as required for reasonable and customary use in describing the
|
| 141 |
+
origin of the Work and reproducing the content of the NOTICE file.
|
| 142 |
+
|
| 143 |
+
7. Disclaimer of Warranty. Unless required by applicable law or
|
| 144 |
+
agreed to in writing, Licensor provides the Work (and each
|
| 145 |
+
Contributor provides its Contributions) on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
| 146 |
+
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or
|
| 147 |
+
implied, including, without limitation, any warranties or conditions
|
| 148 |
+
of TITLE, NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, or FITNESS FOR A
|
| 149 |
+
PARTICULAR PURPOSE. You are solely responsible for determining the
|
| 150 |
+
appropriateness of using or redistributing the Work and assume any
|
| 151 |
+
risks associated with Your exercise of permissions under this License.
|
| 152 |
+
|
| 153 |
+
8. Limitation of Liability. In no event and under no legal theory,
|
| 154 |
+
whether in tort (including negligence), contract, or otherwise,
|
| 155 |
+
unless required by applicable law (such as deliberate and grossly
|
| 156 |
+
negligent acts) or agreed to in writing, shall any Contributor be
|
| 157 |
+
liable to You for damages, including any direct, indirect, special,
|
| 158 |
+
incidental, or consequential damages of any character arising as a
|
| 159 |
+
result of this License or out of the use or inability to use the
|
| 160 |
+
Work (including but not limited to damages for loss of goodwill,
|
| 161 |
+
work stoppage, computer failure or malfunction, or any and all
|
| 162 |
+
other commercial damages or losses), even if such Contributor
|
| 163 |
+
has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
|
| 164 |
+
|
| 165 |
+
9. Accepting Warranty or Additional Liability. While redistributing
|
| 166 |
+
the Work or Derivative Works thereof, You may choose to offer,
|
| 167 |
+
and charge a fee for, acceptance of support, warranty, indemnity,
|
| 168 |
+
or other liability obligations and/or rights consistent with this
|
| 169 |
+
License. However, in accepting such obligations, You may act only
|
| 170 |
+
on Your own behalf and on Your sole responsibility, not on behalf
|
| 171 |
+
of any other Contributor, and only if You agree to indemnify,
|
| 172 |
+
defend, and hold each Contributor harmless for any liability
|
| 173 |
+
incurred by, or claims asserted against, such Contributor by reason
|
| 174 |
+
of your accepting any such warranty or additional liability.
|
| 175 |
+
|
| 176 |
+
END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
|
| 177 |
+
|
| 178 |
+
APPENDIX: How to apply the Apache License to your work.
|
| 179 |
+
|
| 180 |
+
To apply the Apache License to your work, attach the following
|
| 181 |
+
boilerplate notice, with the fields enclosed by brackets "[]"
|
| 182 |
+
replaced with your own identifying information. (Don't include
|
| 183 |
+
the brackets!) The text should be enclosed in the appropriate
|
| 184 |
+
comment syntax for the file format. We also recommend that a
|
| 185 |
+
file or class name and description of purpose be included on the
|
| 186 |
+
same "printed page" as the copyright notice for easier
|
| 187 |
+
identification within third-party archives.
|
| 188 |
+
|
| 189 |
+
Copyright [yyyy] [name of copyright owner]
|
| 190 |
+
|
| 191 |
+
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
| 192 |
+
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
| 193 |
+
You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
| 194 |
+
|
| 195 |
+
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
| 196 |
+
|
| 197 |
+
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
| 198 |
+
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
| 199 |
+
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
| 200 |
+
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
| 201 |
+
limitations under the License.
|
smolagents/Makefile
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
.PHONY: quality style test docs
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
check_dirs := examples src tests utils
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
# Check code quality of the source code
|
| 6 |
+
quality:
|
| 7 |
+
ruff check $(check_dirs)
|
| 8 |
+
ruff format --check $(check_dirs)
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
# Format source code automatically
|
| 11 |
+
style:
|
| 12 |
+
ruff check $(check_dirs) --fix
|
| 13 |
+
ruff format $(check_dirs)
|
| 14 |
+
|
| 15 |
+
# Run smolagents tests
|
| 16 |
+
test:
|
| 17 |
+
pytest ./tests/
|
smolagents/README.md
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,262 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
<!---
|
| 2 |
+
Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
| 3 |
+
|
| 4 |
+
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
| 5 |
+
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
| 6 |
+
You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
| 7 |
+
|
| 8 |
+
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
| 11 |
+
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
| 12 |
+
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
| 13 |
+
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
| 14 |
+
limitations under the License.
|
| 15 |
+
-->
|
| 16 |
+
<p align="center">
|
| 17 |
+
<!-- Uncomment when CircleCI is set up
|
| 18 |
+
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/accelerate"><img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/master"></a>
|
| 19 |
+
-->
|
| 20 |
+
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/smolagents/blob/main/LICENSE"><img alt="License" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/smolagents.svg?color=blue"></a>
|
| 21 |
+
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/smolagents"><img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/smolagents/index.html.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online"></a>
|
| 22 |
+
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/smolagents/releases"><img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/smolagents.svg"></a>
|
| 23 |
+
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/smolagents/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md"><img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg"></a>
|
| 24 |
+
</p>
|
| 25 |
+
|
| 26 |
+
<h3 align="center">
|
| 27 |
+
<div style="display:flex;flex-direction:row;">
|
| 28 |
+
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/smolagents/smolagents.png" alt="Hugging Face mascot as James Bond" width=400px>
|
| 29 |
+
<p>Agents that think in code!</p>
|
| 30 |
+
</div>
|
| 31 |
+
</h3>
|
| 32 |
+
|
| 33 |
+
`smolagents` is a library that enables you to run powerful agents in a few lines of code. It offers:
|
| 34 |
+
|
| 35 |
+
✨ **Simplicity**: the logic for agents fits in ~1,000 lines of code (see [agents.py](https://github.com/huggingface/smolagents/blob/main/src/smolagents/agents.py)). We kept abstractions to their minimal shape above raw code!
|
| 36 |
+
|
| 37 |
+
🧑💻 **First-class support for Code Agents**. Our [`CodeAgent`](https://huggingface.co/docs/smolagents/reference/agents#smolagents.CodeAgent) writes its actions in code (as opposed to "agents being used to write code"). To make it secure, we support executing in sandboxed environments via [E2B](https://e2b.dev/) or via Docker.
|
| 38 |
+
|
| 39 |
+
🤗 **Hub integrations**: you can [share/pull tools or agents to/from the Hub](https://huggingface.co/docs/smolagents/reference/tools#smolagents.Tool.from_hub) for instant sharing of the most efficient agents!
|
| 40 |
+
|
| 41 |
+
🌐 **Model-agnostic**: smolagents supports any LLM. It can be a local `transformers` or `ollama` model, one of [many providers on the Hub](https://huggingface.co/blog/inference-providers), or any model from OpenAI, Anthropic and many others via our [LiteLLM](https://www.litellm.ai/) integration.
|
| 42 |
+
|
| 43 |
+
👁️ **Modality-agnostic**: Agents support text, vision, video, even audio inputs! Cf [this tutorial](https://huggingface.co/docs/smolagents/examples/web_browser) for vision.
|
| 44 |
+
|
| 45 |
+
🛠️ **Tool-agnostic**: you can use tools from [LangChain](https://huggingface.co/docs/smolagents/reference/tools#smolagents.Tool.from_langchain), [MCP](https://huggingface.co/docs/smolagents/reference/tools#smolagents.ToolCollection.from_mcp), you can even use a [Hub Space](https://huggingface.co/docs/smolagents/reference/tools#smolagents.Tool.from_space) as a tool.
|
| 46 |
+
|
| 47 |
+
Full documentation can be found [here](https://huggingface.co/docs/smolagents/index).
|
| 48 |
+
|
| 49 |
+
> [!NOTE]
|
| 50 |
+
> Check the our [launch blog post](https://huggingface.co/blog/smolagents) to learn more about `smolagents`!
|
| 51 |
+
|
| 52 |
+
## Quick demo
|
| 53 |
+
|
| 54 |
+
First install the package.
|
| 55 |
+
```bash
|
| 56 |
+
pip install smolagents
|
| 57 |
+
```
|
| 58 |
+
Then define your agent, give it the tools it needs and run it!
|
| 59 |
+
```py
|
| 60 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, DuckDuckGoSearchTool, InferenceClientModel
|
| 61 |
+
|
| 62 |
+
model = InferenceClientModel()
|
| 63 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[DuckDuckGoSearchTool()], model=model)
|
| 64 |
+
|
| 65 |
+
agent.run("How many seconds would it take for a leopard at full speed to run through Pont des Arts?")
|
| 66 |
+
```
|
| 67 |
+
|
| 68 |
+
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/cd0226e2-7479-4102-aea0-57c22ca47884
|
| 69 |
+
|
| 70 |
+
You can even share your agent to the Hub, as a Space repository:
|
| 71 |
+
```py
|
| 72 |
+
agent.push_to_hub("m-ric/my_agent")
|
| 73 |
+
|
| 74 |
+
# agent.from_hub("m-ric/my_agent") to load an agent from Hub
|
| 75 |
+
```
|
| 76 |
+
|
| 77 |
+
Our library is LLM-agnostic: you could switch the example above to any inference provider.
|
| 78 |
+
|
| 79 |
+
<details>
|
| 80 |
+
<summary> <b>InferenceClientModel, gateway for all <a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/inference-providers/index">inference providers</a> supported on HF</b></summary>
|
| 81 |
+
|
| 82 |
+
```py
|
| 83 |
+
from smolagents import InferenceClientModel
|
| 84 |
+
|
| 85 |
+
model = InferenceClientModel(
|
| 86 |
+
model_id="deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1",
|
| 87 |
+
provider="together",
|
| 88 |
+
)
|
| 89 |
+
```
|
| 90 |
+
</details>
|
| 91 |
+
<details>
|
| 92 |
+
<summary> <b>LiteLLM to access 100+ LLMs</b></summary>
|
| 93 |
+
|
| 94 |
+
```py
|
| 95 |
+
from smolagents import LiteLLMModel
|
| 96 |
+
|
| 97 |
+
model = LiteLLMModel(
|
| 98 |
+
model_id="anthropic/claude-3-5-sonnet-latest",
|
| 99 |
+
temperature=0.2,
|
| 100 |
+
api_key=os.environ["ANTHROPIC_API_KEY"]
|
| 101 |
+
)
|
| 102 |
+
```
|
| 103 |
+
</details>
|
| 104 |
+
<details>
|
| 105 |
+
<summary> <b>OpenAI-compatible servers</b></summary>
|
| 106 |
+
|
| 107 |
+
```py
|
| 108 |
+
import os
|
| 109 |
+
from smolagents import OpenAIServerModel
|
| 110 |
+
|
| 111 |
+
model = OpenAIServerModel(
|
| 112 |
+
model_id="deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1",
|
| 113 |
+
api_base="https://api.together.xyz/v1/", # Leave this blank to query OpenAI servers.
|
| 114 |
+
api_key=os.environ["TOGETHER_API_KEY"], # Switch to the API key for the server you're targeting.
|
| 115 |
+
)
|
| 116 |
+
```
|
| 117 |
+
</details>
|
| 118 |
+
<details>
|
| 119 |
+
<summary> <b>Local `transformers` model</b></summary>
|
| 120 |
+
|
| 121 |
+
```py
|
| 122 |
+
from smolagents import TransformersModel
|
| 123 |
+
|
| 124 |
+
model = TransformersModel(
|
| 125 |
+
model_id="Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct",
|
| 126 |
+
max_new_tokens=4096,
|
| 127 |
+
device_map="auto"
|
| 128 |
+
)
|
| 129 |
+
```
|
| 130 |
+
</details>
|
| 131 |
+
<details>
|
| 132 |
+
<summary> <b>Azure models</b></summary>
|
| 133 |
+
|
| 134 |
+
```py
|
| 135 |
+
import os
|
| 136 |
+
from smolagents import AzureOpenAIServerModel
|
| 137 |
+
|
| 138 |
+
model = AzureOpenAIServerModel(
|
| 139 |
+
model_id = os.environ.get("AZURE_OPENAI_MODEL"),
|
| 140 |
+
azure_endpoint=os.environ.get("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT"),
|
| 141 |
+
api_key=os.environ.get("AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY"),
|
| 142 |
+
api_version=os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_VERSION")
|
| 143 |
+
)
|
| 144 |
+
```
|
| 145 |
+
</details>
|
| 146 |
+
<details>
|
| 147 |
+
<summary> <b>Amazon Bedrock models</b></summary>
|
| 148 |
+
|
| 149 |
+
```py
|
| 150 |
+
import os
|
| 151 |
+
from smolagents import AmazonBedrockServerModel
|
| 152 |
+
|
| 153 |
+
model = AmazonBedrockServerModel(
|
| 154 |
+
model_id = os.environ.get("AMAZON_BEDROCK_MODEL_ID")
|
| 155 |
+
)
|
| 156 |
+
```
|
| 157 |
+
</details>
|
| 158 |
+
|
| 159 |
+
## CLI
|
| 160 |
+
|
| 161 |
+
You can run agents from CLI using two commands: `smolagent` and `webagent`.
|
| 162 |
+
|
| 163 |
+
`smolagent` is a generalist command to run a multi-step `CodeAgent` that can be equipped with various tools.
|
| 164 |
+
|
| 165 |
+
```bash
|
| 166 |
+
smolagent "Plan a trip to Tokyo, Kyoto and Osaka between Mar 28 and Apr 7." --model-type "InferenceClientModel" --model-id "Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct" --imports "pandas numpy" --tools "web_search"
|
| 167 |
+
```
|
| 168 |
+
|
| 169 |
+
Meanwhile `webagent` is a specific web-browsing agent using [helium](https://github.com/mherrmann/helium) (read more [here](https://github.com/huggingface/smolagents/blob/main/src/smolagents/vision_web_browser.py)).
|
| 170 |
+
|
| 171 |
+
For instance:
|
| 172 |
+
```bash
|
| 173 |
+
webagent "go to xyz.com/men, get to sale section, click the first clothing item you see. Get the product details, and the price, return them. note that I'm shopping from France" --model-type "LiteLLMModel" --model-id "gpt-4o"
|
| 174 |
+
```
|
| 175 |
+
|
| 176 |
+
## How do Code agents work?
|
| 177 |
+
|
| 178 |
+
Our [`CodeAgent`](https://huggingface.co/docs/smolagents/reference/agents#smolagents.CodeAgent) works mostly like classical ReAct agents - the exception being that the LLM engine writes its actions as Python code snippets.
|
| 179 |
+
|
| 180 |
+
```mermaid
|
| 181 |
+
flowchart TB
|
| 182 |
+
Task[User Task]
|
| 183 |
+
Memory[agent.memory]
|
| 184 |
+
Generate[Generate from agent.model]
|
| 185 |
+
Execute[Execute Code action - Tool calls are written as functions]
|
| 186 |
+
Answer[Return the argument given to 'final_answer']
|
| 187 |
+
|
| 188 |
+
Task -->|Add task to agent.memory| Memory
|
| 189 |
+
|
| 190 |
+
subgraph ReAct[ReAct loop]
|
| 191 |
+
Memory -->|Memory as chat messages| Generate
|
| 192 |
+
Generate -->|Parse output to extract code action| Execute
|
| 193 |
+
Execute -->|No call to 'final_answer' tool => Store execution logs in memory and keep running| Memory
|
| 194 |
+
end
|
| 195 |
+
|
| 196 |
+
Execute -->|Call to 'final_answer' tool| Answer
|
| 197 |
+
|
| 198 |
+
%% Styling
|
| 199 |
+
classDef default fill:#d4b702,stroke:#8b7701,color:#ffffff
|
| 200 |
+
classDef io fill:#4a5568,stroke:#2d3748,color:#ffffff
|
| 201 |
+
|
| 202 |
+
class Task,Answer io
|
| 203 |
+
```
|
| 204 |
+
|
| 205 |
+
Actions are now Python code snippets. Hence, tool calls will be performed as Python function calls. For instance, here is how the agent can perform web search over several websites in one single action:
|
| 206 |
+
```py
|
| 207 |
+
requests_to_search = ["gulf of mexico america", "greenland denmark", "tariffs"]
|
| 208 |
+
for request in requests_to_search:
|
| 209 |
+
print(f"Here are the search results for {request}:", web_search(request))
|
| 210 |
+
```
|
| 211 |
+
|
| 212 |
+
Writing actions as code snippets is demonstrated to work better than the current industry practice of letting the LLM output a dictionary of the tools it wants to call: [uses 30% fewer steps](https://huggingface.co/papers/2402.01030) (thus 30% fewer LLM calls) and [reaches higher performance on difficult benchmarks](https://huggingface.co/papers/2411.01747). Head to [our high-level intro to agents](https://huggingface.co/docs/smolagents/conceptual_guides/intro_agents) to learn more on that.
|
| 213 |
+
|
| 214 |
+
Especially, since code execution can be a security concern (arbitrary code execution!), we provide options at runtime:
|
| 215 |
+
- a secure python interpreter to run code more safely in your environment (more secure than raw code execution but still risky)
|
| 216 |
+
- a sandboxed environment using [E2B](https://e2b.dev/) or Docker (removes the risk to your own system).
|
| 217 |
+
|
| 218 |
+
On top of this [`CodeAgent`](https://huggingface.co/docs/smolagents/reference/agents#smolagents.CodeAgent) class, we still support the standard [`ToolCallingAgent`](https://huggingface.co/docs/smolagents/reference/agents#smolagents.ToolCallingAgent) that writes actions as JSON/text blobs. But we recommend always using `CodeAgent`.
|
| 219 |
+
|
| 220 |
+
## How smol is this library?
|
| 221 |
+
|
| 222 |
+
We strived to keep abstractions to a strict minimum: the main code in `agents.py` has <1,000 lines of code.
|
| 223 |
+
Still, we implement several types of agents: `CodeAgent` writes its actions as Python code snippets, and the more classic `ToolCallingAgent` leverages built-in tool calling methods. We also have multi-agent hierarchies, import from tool collections, remote code execution, vision models...
|
| 224 |
+
|
| 225 |
+
By the way, why use a framework at all? Well, because a big part of this stuff is non-trivial. For instance, the code agent has to keep a consistent format for code throughout its system prompt, its parser, the execution. So our framework handles this complexity for you. But of course we still encourage you to hack into the source code and use only the bits that you need, to the exclusion of everything else!
|
| 226 |
+
|
| 227 |
+
## How strong are open models for agentic workflows?
|
| 228 |
+
|
| 229 |
+
We've created [`CodeAgent`](https://huggingface.co/docs/smolagents/reference/agents#smolagents.CodeAgent) instances with some leading models, and compared them on [this benchmark](https://huggingface.co/datasets/m-ric/agents_medium_benchmark_2) that gathers questions from a few different benchmarks to propose a varied blend of challenges.
|
| 230 |
+
|
| 231 |
+
[Find the benchmarking code here](https://github.com/huggingface/smolagents/blob/main/examples/smolagents_benchmark/run.py) for more detail on the agentic setup used, and see a comparison of using LLMs code agents compared to vanilla (spoilers: code agents works better).
|
| 232 |
+
|
| 233 |
+
<p align="center">
|
| 234 |
+
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/smolagents/benchmark_code_agents.jpeg" alt="benchmark of different models on agentic workflows. Open model DeepSeek-R1 beats closed-source models." width=60% max-width=500px>
|
| 235 |
+
</p>
|
| 236 |
+
|
| 237 |
+
This comparison shows that open-source models can now take on the best closed models!
|
| 238 |
+
|
| 239 |
+
## Security
|
| 240 |
+
|
| 241 |
+
Security is a critical consideration when working with code-executing agents. Our library provides:
|
| 242 |
+
- Sandboxed execution options using [E2B](https://e2b.dev/) or Docker
|
| 243 |
+
- Best practices for running agent code securely
|
| 244 |
+
|
| 245 |
+
For security policies, vulnerability reporting, and more information on secure agent execution, please see our [Security Policy](SECURITY.md).
|
| 246 |
+
|
| 247 |
+
## Contribute
|
| 248 |
+
|
| 249 |
+
Everyone is welcome to contribute, get started with our [contribution guide](https://github.com/huggingface/smolagents/blob/main/CONTRIBUTING.md).
|
| 250 |
+
|
| 251 |
+
## Cite smolagents
|
| 252 |
+
|
| 253 |
+
If you use `smolagents` in your publication, please cite it by using the following BibTeX entry.
|
| 254 |
+
|
| 255 |
+
```bibtex
|
| 256 |
+
@Misc{smolagents,
|
| 257 |
+
title = {`smolagents`: a smol library to build great agentic systems.},
|
| 258 |
+
author = {Aymeric Roucher and Albert Villanova del Moral and Thomas Wolf and Leandro von Werra and Erik Kaunismäki},
|
| 259 |
+
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/huggingface/smolagents}},
|
| 260 |
+
year = {2025}
|
| 261 |
+
}
|
| 262 |
+
```
|
smolagents/SECURITY.md
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Security Policy
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
## Reporting a Vulnerability
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
To report a security vulnerability, please contact: [email protected]
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
## Learning More About Security
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
To learn more about running agents more securely, please see the [Secure Code Execution tutorial](docs/source/en/tutorials/secure_code_execution.mdx) which covers sandboxing with E2B and Docker.
|
smolagents/docs/README.md
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,271 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
<!---
|
| 2 |
+
Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
| 3 |
+
|
| 4 |
+
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
| 5 |
+
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
| 6 |
+
You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
| 7 |
+
|
| 8 |
+
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
| 11 |
+
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
| 12 |
+
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
| 13 |
+
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
| 14 |
+
limitations under the License.
|
| 15 |
+
-->
|
| 16 |
+
|
| 17 |
+
# Generating the documentation
|
| 18 |
+
|
| 19 |
+
To generate the documentation, you have to build it. Several packages are necessary to build the doc.
|
| 20 |
+
|
| 21 |
+
First, you need to install the project itself by running the following command at the root of the code repository:
|
| 22 |
+
|
| 23 |
+
```bash
|
| 24 |
+
pip install -e .
|
| 25 |
+
```
|
| 26 |
+
|
| 27 |
+
You also need to install 2 extra packages:
|
| 28 |
+
|
| 29 |
+
```bash
|
| 30 |
+
# `hf-doc-builder` to build the docs
|
| 31 |
+
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/doc-builder@main
|
| 32 |
+
# `watchdog` for live reloads
|
| 33 |
+
pip install watchdog
|
| 34 |
+
```
|
| 35 |
+
|
| 36 |
+
---
|
| 37 |
+
**NOTE**
|
| 38 |
+
|
| 39 |
+
You only need to generate the documentation to inspect it locally (if you're planning changes and want to
|
| 40 |
+
check how they look before committing for instance). You don't have to commit the built documentation.
|
| 41 |
+
|
| 42 |
+
---
|
| 43 |
+
|
| 44 |
+
## Building the documentation
|
| 45 |
+
|
| 46 |
+
Once you have setup the `doc-builder` and additional packages with the pip install command above,
|
| 47 |
+
you can generate the documentation by typing the following command:
|
| 48 |
+
|
| 49 |
+
```bash
|
| 50 |
+
doc-builder build smolagents docs/source/en/ --build_dir ~/tmp/test-build
|
| 51 |
+
```
|
| 52 |
+
|
| 53 |
+
You can adapt the `--build_dir` to set any temporary folder that you prefer. This command will create it and generate
|
| 54 |
+
the MDX files that will be rendered as the documentation on the main website. You can inspect them in your favorite
|
| 55 |
+
Markdown editor.
|
| 56 |
+
|
| 57 |
+
## Previewing the documentation
|
| 58 |
+
|
| 59 |
+
To preview the docs, run the following command:
|
| 60 |
+
|
| 61 |
+
```bash
|
| 62 |
+
doc-builder preview smolagents docs/source/en/
|
| 63 |
+
```
|
| 64 |
+
|
| 65 |
+
The docs will be viewable at [http://localhost:5173](http://localhost:5173). You can also preview the docs once you
|
| 66 |
+
have opened a PR. You will see a bot add a comment to a link where the documentation with your changes lives.
|
| 67 |
+
|
| 68 |
+
---
|
| 69 |
+
**NOTE**
|
| 70 |
+
|
| 71 |
+
The `preview` command only works with existing doc files. When you add a completely new file, you need to update
|
| 72 |
+
`_toctree.yml` & restart `preview` command (`ctrl-c` to stop it & call `doc-builder preview ...` again).
|
| 73 |
+
|
| 74 |
+
---
|
| 75 |
+
|
| 76 |
+
## Adding a new element to the navigation bar
|
| 77 |
+
|
| 78 |
+
Accepted files are Markdown (.md).
|
| 79 |
+
|
| 80 |
+
Create a file with its extension and put it in the source directory. You can then link it to the toc-tree by putting
|
| 81 |
+
the filename without the extension in the [`_toctree.yml`](https://github.com/huggingface/smolagents/blob/main/docs/source/_toctree.yml) file.
|
| 82 |
+
|
| 83 |
+
## Renaming section headers and moving sections
|
| 84 |
+
|
| 85 |
+
It helps to keep the old links working when renaming the section header and/or moving sections from one document to another. This is because the old links are likely to be used in Issues, Forums, and Social media and it'd make for a much more superior user experience if users reading those months later could still easily navigate to the originally intended information.
|
| 86 |
+
|
| 87 |
+
Therefore, we simply keep a little map of moved sections at the end of the document where the original section was. The key is to preserve the original anchor.
|
| 88 |
+
|
| 89 |
+
So if you renamed a section from: "Section A" to "Section B", then you can add at the end of the file:
|
| 90 |
+
|
| 91 |
+
```
|
| 92 |
+
Sections that were moved:
|
| 93 |
+
|
| 94 |
+
[ <a href="#section-b">Section A</a><a id="section-a"></a> ]
|
| 95 |
+
```
|
| 96 |
+
and of course, if you moved it to another file, then:
|
| 97 |
+
|
| 98 |
+
```
|
| 99 |
+
Sections that were moved:
|
| 100 |
+
|
| 101 |
+
[ <a href="../new-file#section-b">Section A</a><a id="section-a"></a> ]
|
| 102 |
+
```
|
| 103 |
+
|
| 104 |
+
Use the relative style to link to the new file so that the versioned docs continue to work.
|
| 105 |
+
|
| 106 |
+
For an example of a rich moved section set please see the very end of [the transformers Trainer doc](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/main_classes/trainer.md).
|
| 107 |
+
|
| 108 |
+
|
| 109 |
+
## Writing Documentation - Specification
|
| 110 |
+
|
| 111 |
+
The `huggingface/smolagents` documentation follows the
|
| 112 |
+
[Google documentation](https://sphinxcontrib-napoleon.readthedocs.io/en/latest/example_google.html) style for docstrings,
|
| 113 |
+
although we can write them directly in Markdown.
|
| 114 |
+
|
| 115 |
+
### Adding a new tutorial
|
| 116 |
+
|
| 117 |
+
Adding a new tutorial or section is done in two steps:
|
| 118 |
+
|
| 119 |
+
- Add a new Markdown (.md) file under `./source`.
|
| 120 |
+
- Link that file in `./source/_toctree.yml` on the correct toc-tree.
|
| 121 |
+
|
| 122 |
+
Make sure to put your new file under the proper section. If you have a doubt, feel free to ask in a Github Issue or PR.
|
| 123 |
+
|
| 124 |
+
### Writing source documentation
|
| 125 |
+
|
| 126 |
+
Values that should be put in `code` should either be surrounded by backticks: \`like so\`. Note that argument names
|
| 127 |
+
and objects like True, None, or any strings should usually be put in `code`.
|
| 128 |
+
|
| 129 |
+
When mentioning a class, function, or method, it is recommended to use our syntax for internal links so that our tool
|
| 130 |
+
adds a link to its documentation with this syntax: \[\`XXXClass\`\] or \[\`function\`\]. This requires the class or
|
| 131 |
+
function to be in the main package.
|
| 132 |
+
|
| 133 |
+
If you want to create a link to some internal class or function, you need to
|
| 134 |
+
provide its path. For instance: \[\`utils.ModelOutput\`\]. This will be converted into a link with
|
| 135 |
+
`utils.ModelOutput` in the description. To get rid of the path and only keep the name of the object you are
|
| 136 |
+
linking to in the description, add a ~: \[\`~utils.ModelOutput\`\] will generate a link with `ModelOutput` in the description.
|
| 137 |
+
|
| 138 |
+
The same works for methods so you can either use \[\`XXXClass.method\`\] or \[~\`XXXClass.method\`\].
|
| 139 |
+
|
| 140 |
+
#### Defining arguments in a method
|
| 141 |
+
|
| 142 |
+
Arguments should be defined with the `Args:` (or `Arguments:` or `Parameters:`) prefix, followed by a line return and
|
| 143 |
+
an indentation. The argument should be followed by its type, with its shape if it is a tensor, a colon, and its
|
| 144 |
+
description:
|
| 145 |
+
|
| 146 |
+
```
|
| 147 |
+
Args:
|
| 148 |
+
n_layers (`int`): The number of layers of the model.
|
| 149 |
+
```
|
| 150 |
+
|
| 151 |
+
If the description is too long to fit in one line, another indentation is necessary before writing the description
|
| 152 |
+
after the argument.
|
| 153 |
+
|
| 154 |
+
Here's an example showcasing everything so far:
|
| 155 |
+
|
| 156 |
+
```
|
| 157 |
+
Args:
|
| 158 |
+
input_ids (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length)`):
|
| 159 |
+
Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary.
|
| 160 |
+
|
| 161 |
+
Indices can be obtained using [`AlbertTokenizer`]. See [`~PreTrainedTokenizer.encode`] and
|
| 162 |
+
[`~PreTrainedTokenizer.__call__`] for details.
|
| 163 |
+
|
| 164 |
+
[What are input IDs?](../glossary#input-ids)
|
| 165 |
+
```
|
| 166 |
+
|
| 167 |
+
For optional arguments or arguments with defaults we follow the following syntax: imagine we have a function with the
|
| 168 |
+
following signature:
|
| 169 |
+
|
| 170 |
+
```
|
| 171 |
+
def my_function(x: str = None, a: float = 1):
|
| 172 |
+
```
|
| 173 |
+
|
| 174 |
+
then its documentation should look like this:
|
| 175 |
+
|
| 176 |
+
```
|
| 177 |
+
Args:
|
| 178 |
+
x (`str`, *optional*):
|
| 179 |
+
This argument controls ...
|
| 180 |
+
a (`float`, *optional*, defaults to 1):
|
| 181 |
+
This argument is used to ...
|
| 182 |
+
```
|
| 183 |
+
|
| 184 |
+
Note that we always omit the "defaults to \`None\`" when None is the default for any argument. Also note that even
|
| 185 |
+
if the first line describing your argument type and its default gets long, you can't break it on several lines. You can
|
| 186 |
+
however write as many lines as you want in the indented description (see the example above with `input_ids`).
|
| 187 |
+
|
| 188 |
+
#### Writing a multi-line code block
|
| 189 |
+
|
| 190 |
+
Multi-line code blocks can be useful for displaying examples. They are done between two lines of three backticks as usual in Markdown:
|
| 191 |
+
|
| 192 |
+
|
| 193 |
+
````
|
| 194 |
+
```
|
| 195 |
+
# first line of code
|
| 196 |
+
# second line
|
| 197 |
+
# etc
|
| 198 |
+
```
|
| 199 |
+
````
|
| 200 |
+
|
| 201 |
+
#### Writing a return block
|
| 202 |
+
|
| 203 |
+
The return block should be introduced with the `Returns:` prefix, followed by a line return and an indentation.
|
| 204 |
+
The first line should be the type of the return, followed by a line return. No need to indent further for the elements
|
| 205 |
+
building the return.
|
| 206 |
+
|
| 207 |
+
Here's an example of a single value return:
|
| 208 |
+
|
| 209 |
+
```
|
| 210 |
+
Returns:
|
| 211 |
+
`List[int]`: A list of integers in the range [0, 1] --- 1 for a special token, 0 for a sequence token.
|
| 212 |
+
```
|
| 213 |
+
|
| 214 |
+
Here's an example of a tuple return, comprising several objects:
|
| 215 |
+
|
| 216 |
+
```
|
| 217 |
+
Returns:
|
| 218 |
+
`tuple(torch.FloatTensor)` comprising various elements depending on the configuration ([`BertConfig`]) and inputs:
|
| 219 |
+
- ** loss** (*optional*, returned when `masked_lm_labels` is provided) `torch.FloatTensor` of shape `(1,)` --
|
| 220 |
+
Total loss is the sum of the masked language modeling loss and the next sequence prediction (classification) loss.
|
| 221 |
+
- **prediction_scores** (`torch.FloatTensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length, config.vocab_size)`) --
|
| 222 |
+
Prediction scores of the language modeling head (scores for each vocabulary token before SoftMax).
|
| 223 |
+
```
|
| 224 |
+
|
| 225 |
+
#### Adding an image
|
| 226 |
+
|
| 227 |
+
Due to the rapidly growing repository, it is important to make sure that no files that would significantly weigh down the repository are added. This includes images, videos, and other non-text files. We prefer to leverage a hf.co hosted `dataset` like
|
| 228 |
+
the ones hosted on [`hf-internal-testing`](https://huggingface.co/hf-internal-testing) in which to place these files and reference
|
| 229 |
+
them by URL. We recommend putting them in the following dataset: [huggingface/documentation-images](https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images).
|
| 230 |
+
If an external contribution, feel free to add the images to your PR and ask a Hugging Face member to migrate your images
|
| 231 |
+
to this dataset.
|
| 232 |
+
|
| 233 |
+
#### Writing documentation examples
|
| 234 |
+
|
| 235 |
+
The syntax for Example docstrings can look as follows:
|
| 236 |
+
|
| 237 |
+
```
|
| 238 |
+
Example:
|
| 239 |
+
|
| 240 |
+
```python
|
| 241 |
+
>>> from transformers import Wav2Vec2Processor, Wav2Vec2ForCTC
|
| 242 |
+
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
|
| 243 |
+
>>> import torch
|
| 244 |
+
|
| 245 |
+
>>> dataset = load_dataset("hf-internal-testing/librispeech_asr_demo", "clean", split="validation")
|
| 246 |
+
>>> dataset = dataset.sort("id")
|
| 247 |
+
>>> sampling_rate = dataset.features["audio"].sampling_rate
|
| 248 |
+
|
| 249 |
+
>>> processor = Wav2Vec2Processor.from_pretrained("facebook/wav2vec2-base-960h")
|
| 250 |
+
>>> model = Wav2Vec2ForCTC.from_pretrained("facebook/wav2vec2-base-960h")
|
| 251 |
+
|
| 252 |
+
>>> # audio file is decoded on the fly
|
| 253 |
+
>>> inputs = processor(dataset[0]["audio"]["array"], sampling_rate=sampling_rate, return_tensors="pt")
|
| 254 |
+
>>> with torch.no_grad():
|
| 255 |
+
... logits = model(**inputs).logits
|
| 256 |
+
>>> predicted_ids = torch.argmax(logits, dim=-1)
|
| 257 |
+
|
| 258 |
+
>>> # transcribe speech
|
| 259 |
+
>>> transcription = processor.batch_decode(predicted_ids)
|
| 260 |
+
>>> transcription[0]
|
| 261 |
+
'MISTER QUILTER IS THE APOSTLE OF THE MIDDLE CLASSES AND WE ARE GLAD TO WELCOME HIS GOSPEL'
|
| 262 |
+
```
|
| 263 |
+
```
|
| 264 |
+
|
| 265 |
+
The docstring should give a minimal, clear example of how the respective model
|
| 266 |
+
is to be used in inference and also include the expected (ideally sensible)
|
| 267 |
+
output.
|
| 268 |
+
Often, readers will try out the example before even going through the function
|
| 269 |
+
or class definitions. Therefore, it is of utmost importance that the example
|
| 270 |
+
works as expected.
|
| 271 |
+
|
smolagents/docs/source/en/_config.py
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# docstyle-ignore
|
| 2 |
+
INSTALL_CONTENT = """
|
| 3 |
+
# Installation
|
| 4 |
+
! pip install smolagents
|
| 5 |
+
# To install from source instead of the last release, comment the command above and uncomment the following one.
|
| 6 |
+
# ! pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/smolagents.git
|
| 7 |
+
"""
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
notebook_first_cells = [{"type": "code", "content": INSTALL_CONTENT}]
|
| 10 |
+
black_avoid_patterns = {
|
| 11 |
+
"{processor_class}": "FakeProcessorClass",
|
| 12 |
+
"{model_class}": "FakeModelClass",
|
| 13 |
+
"{object_class}": "FakeObjectClass",
|
| 14 |
+
}
|
smolagents/docs/source/en/_toctree.yml
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
- title: Get started
|
| 2 |
+
sections:
|
| 3 |
+
- local: index
|
| 4 |
+
title: 🤗 Agents
|
| 5 |
+
- local: guided_tour
|
| 6 |
+
title: Guided tour
|
| 7 |
+
- title: Tutorials
|
| 8 |
+
sections:
|
| 9 |
+
- local: tutorials/building_good_agents
|
| 10 |
+
title: ✨ Building good agents
|
| 11 |
+
- local: tutorials/inspect_runs
|
| 12 |
+
title: 📊 Inspect your agent runs using telemetry
|
| 13 |
+
- local: tutorials/tools
|
| 14 |
+
title: 🛠️ Tools - in-depth guide
|
| 15 |
+
- local: tutorials/secure_code_execution
|
| 16 |
+
title: 🛡️ Secure code execution
|
| 17 |
+
- local: tutorials/memory
|
| 18 |
+
title: 📚 Manage your agent's memory
|
| 19 |
+
- title: Conceptual guides
|
| 20 |
+
sections:
|
| 21 |
+
- local: conceptual_guides/intro_agents
|
| 22 |
+
title: 🤖 An introduction to agentic systems
|
| 23 |
+
- local: conceptual_guides/react
|
| 24 |
+
title: 🤔 How do Multi-step agents work?
|
| 25 |
+
- title: Examples
|
| 26 |
+
sections:
|
| 27 |
+
- local: examples/text_to_sql
|
| 28 |
+
title: Self-correcting Text-to-SQL
|
| 29 |
+
- local: examples/rag
|
| 30 |
+
title: Master your knowledge base with agentic RAG
|
| 31 |
+
- local: examples/multiagents
|
| 32 |
+
title: Orchestrate a multi-agent system
|
| 33 |
+
- local: examples/web_browser
|
| 34 |
+
title: Build a web browser agent using vision models
|
| 35 |
+
- title: Reference
|
| 36 |
+
sections:
|
| 37 |
+
- local: reference/agents
|
| 38 |
+
title: Agent-related objects
|
| 39 |
+
- local: reference/models
|
| 40 |
+
title: Model-related objects
|
| 41 |
+
- local: reference/tools
|
| 42 |
+
title: Tool-related objects
|
smolagents/docs/source/en/conceptual_guides/intro_agents.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,104 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Introduction to Agents
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
## 🤔 What are agents?
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
Any efficient system using AI will need to provide LLMs some kind of access to the real world: for instance the possibility to call a search tool to get external information, or to act on certain programs in order to solve a task. In other words, LLMs should have ***agency***. Agentic programs are the gateway to the outside world for LLMs.
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 8 |
+
> AI Agents are **programs where LLM outputs control the workflow**.
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
Any system leveraging LLMs will integrate the LLM outputs into code. The influence of the LLM's input on the code workflow is the level of agency of LLMs in the system.
|
| 11 |
+
|
| 12 |
+
Note that with this definition, "agent" is not a discrete, 0 or 1 definition: instead, "agency" evolves on a continuous spectrum, as you give more or less power to the LLM on your workflow.
|
| 13 |
+
|
| 14 |
+
See in the table below how agency can vary across systems:
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
| Agency Level | Description | Short name | Example Code |
|
| 17 |
+
| ------------ | ------------------------------------------------------ | ---------------- | -------------------------------------------------- |
|
| 18 |
+
| ☆☆☆ | LLM output has no impact on program flow | Simple processor | `process_llm_output(llm_response)` |
|
| 19 |
+
| ★☆☆ | LLM output controls an if/else switch | Router | `if llm_decision(): path_a() else: path_b()` |
|
| 20 |
+
| ★★☆ | LLM output controls function execution | Tool call | `run_function(llm_chosen_tool, llm_chosen_args)` |
|
| 21 |
+
| ★★☆ | LLM output controls iteration and program continuation | Multi-step Agent | `while llm_should_continue(): execute_next_step()` |
|
| 22 |
+
| ★★★ | One agentic workflow can start another agentic workflow | Multi-Agent | `if llm_trigger(): execute_agent()` |
|
| 23 |
+
| ★★★ | LLM acts in code, can define its own tools / start other agents | Code Agents | `def custom_tool(args): ...` |
|
| 24 |
+
|
| 25 |
+
The multi-step agent has this code structure:
|
| 26 |
+
|
| 27 |
+
```python
|
| 28 |
+
memory = [user_defined_task]
|
| 29 |
+
while llm_should_continue(memory): # this loop is the multi-step part
|
| 30 |
+
action = llm_get_next_action(memory) # this is the tool-calling part
|
| 31 |
+
observations = execute_action(action)
|
| 32 |
+
memory += [action, observations]
|
| 33 |
+
```
|
| 34 |
+
|
| 35 |
+
This agentic system runs in a loop, executing a new action at each step (the action can involve calling some pre-determined *tools* that are just functions), until its observations make it apparent that a satisfactory state has been reached to solve the given task. Here’s an example of how a multi-step agent can solve a simple math question:
|
| 36 |
+
|
| 37 |
+
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
| 38 |
+
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/Agent_ManimCE.gif"/>
|
| 39 |
+
</div>
|
| 40 |
+
|
| 41 |
+
|
| 42 |
+
## ✅ When to use agents / ⛔ when to avoid them
|
| 43 |
+
|
| 44 |
+
Agents are useful when you need an LLM to determine the workflow of an app. But they’re often overkill. The question is: do I really need flexibility in the workflow to efficiently solve the task at hand?
|
| 45 |
+
If the pre-determined workflow falls short too often, that means you need more flexibility.
|
| 46 |
+
Let's take an example: say you're making an app that handles customer requests on a surfing trip website.
|
| 47 |
+
|
| 48 |
+
You could know in advance that the requests will belong to either of 2 buckets (based on user choice), and you have a predefined workflow for each of these 2 cases.
|
| 49 |
+
|
| 50 |
+
1. Want some knowledge on the trips? ⇒ give them access to a search bar to search your knowledge base
|
| 51 |
+
2. Wants to talk to sales? ⇒ let them type in a contact form.
|
| 52 |
+
|
| 53 |
+
If that deterministic workflow fits all queries, by all means just code everything! This will give you a 100% reliable system with no risk of error introduced by letting unpredictable LLMs meddle in your workflow. For the sake of simplicity and robustness, it's advised to regularize towards not using any agentic behaviour.
|
| 54 |
+
|
| 55 |
+
But what if the workflow can't be determined that well in advance?
|
| 56 |
+
|
| 57 |
+
For instance, a user wants to ask: `"I can come on Monday, but I forgot my passport so risk being delayed to Wednesday, is it possible to take me and my stuff to surf on Tuesday morning, with a cancellation insurance?"` This question hinges on many factors, and probably none of the predetermined criteria above will suffice for this request.
|
| 58 |
+
|
| 59 |
+
If the pre-determined workflow falls short too often, that means you need more flexibility.
|
| 60 |
+
|
| 61 |
+
That is where an agentic setup helps.
|
| 62 |
+
|
| 63 |
+
In the above example, you could just make a multi-step agent that has access to a weather API for weather forecasts, Google Maps API to compute travel distance, an employee availability dashboard and a RAG system on your knowledge base.
|
| 64 |
+
|
| 65 |
+
Until recently, computer programs were restricted to pre-determined workflows, trying to handle complexity by piling up if/else switches. They focused on extremely narrow tasks, like "compute the sum of these numbers" or "find the shortest path in this graph". But actually, most real-life tasks, like our trip example above, do not fit in pre-determined workflows. Agentic systems open up the vast world of real-world tasks to programs!
|
| 66 |
+
|
| 67 |
+
## Why `smolagents`?
|
| 68 |
+
|
| 69 |
+
For some low-level agentic use cases, like chains or routers, you can write all the code yourself. You'll be much better that way, since it will let you control and understand your system better.
|
| 70 |
+
|
| 71 |
+
But once you start going for more complicated behaviours like letting an LLM call a function (that's "tool calling") or letting an LLM run a while loop ("multi-step agent"), some abstractions become necessary:
|
| 72 |
+
- For tool calling, you need to parse the agent's output, so this output needs a predefined format like "Thought: I should call tool 'get_weather'. Action: get_weather(Paris).", that you parse with a predefined function, and system prompt given to the LLM should notify it about this format.
|
| 73 |
+
- For a multi-step agent where the LLM output determines the loop, you need to give a different prompt to the LLM based on what happened in the last loop iteration: so you need some kind of memory.
|
| 74 |
+
|
| 75 |
+
See? With these two examples, we already found the need for a few items to help us:
|
| 76 |
+
|
| 77 |
+
- Of course, an LLM that acts as the engine powering the system
|
| 78 |
+
- A list of tools that the agent can access
|
| 79 |
+
- A parser that extracts tool calls from the LLM output
|
| 80 |
+
- A system prompt synced with the parser
|
| 81 |
+
- A memory
|
| 82 |
+
|
| 83 |
+
But wait, since we give room to LLMs in decisions, surely they will make mistakes: so we need error logging and retry mechanisms.
|
| 84 |
+
|
| 85 |
+
All these elements need tight coupling to make a well-functioning system. That's why we decided we needed to make basic building blocks to make all this stuff work together.
|
| 86 |
+
|
| 87 |
+
## Code agents
|
| 88 |
+
|
| 89 |
+
In a multi-step agent, at each step, the LLM can write an action, in the form of some calls to external tools. A common format (used by Anthropic, OpenAI, and many others) for writing these actions is generally different shades of "writing actions as a JSON of tools names and arguments to use, which you then parse to know which tool to execute and with which arguments".
|
| 90 |
+
|
| 91 |
+
[Multiple](https://huggingface.co/papers/2402.01030) [research](https://huggingface.co/papers/2411.01747) [papers](https://huggingface.co/papers/2401.00812) have shown that having the tool calling LLMs in code is much better.
|
| 92 |
+
|
| 93 |
+
The reason for this simply that *we crafted our code languages specifically to be the best possible way to express actions performed by a computer*. If JSON snippets were a better expression, JSON would be the top programming language and programming would be hell on earth.
|
| 94 |
+
|
| 95 |
+
The figure below, taken from [Executable Code Actions Elicit Better LLM Agents](https://huggingface.co/papers/2402.01030), illustrates some advantages of writing actions in code:
|
| 96 |
+
|
| 97 |
+
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/code_vs_json_actions.png">
|
| 98 |
+
|
| 99 |
+
Writing actions in code rather than JSON-like snippets provides better:
|
| 100 |
+
|
| 101 |
+
- **Composability:** could you nest JSON actions within each other, or define a set of JSON actions to re-use later, the same way you could just define a python function?
|
| 102 |
+
- **Object management:** how do you store the output of an action like `generate_image` in JSON?
|
| 103 |
+
- **Generality:** code is built to express simply anything you can have a computer do.
|
| 104 |
+
- **Representation in LLM training data:** plenty of quality code actions are already included in LLMs’ training data which means they’re already trained for this!
|
smolagents/docs/source/en/conceptual_guides/react.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# How do multi-step agents work?
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
The ReAct framework ([Yao et al., 2022](https://huggingface.co/papers/2210.03629)) is currently the main approach to building agents.
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
The name is based on the concatenation of two words, "Reason" and "Act." Indeed, agents following this architecture will solve their task in as many steps as needed, each step consisting of a Reasoning step, then an Action step where it formulates tool calls that will bring it closer to solving the task at hand.
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
All agents in `smolagents` are based on singular `MultiStepAgent` class, which is an abstraction of ReAct framework.
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
On a basic level, this class performs actions on a cycle of following steps, where existing variables and knowledge is incorporated into the agent logs like below:
|
| 10 |
+
|
| 11 |
+
Initialization: the system prompt is stored in a `SystemPromptStep`, and the user query is logged into a `TaskStep` .
|
| 12 |
+
|
| 13 |
+
While loop (ReAct loop):
|
| 14 |
+
|
| 15 |
+
- Use `agent.write_memory_to_messages()` to write the agent logs into a list of LLM-readable [chat messages](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/chat_templating).
|
| 16 |
+
- Send these messages to a `Model` object to get its completion. Parse the completion to get the action (a JSON blob for `ToolCallingAgent`, a code snippet for `CodeAgent`).
|
| 17 |
+
- Execute the action and logs result into memory (an `ActionStep`).
|
| 18 |
+
- At the end of each step, we run all callback functions defined in `agent.step_callbacks` .
|
| 19 |
+
|
| 20 |
+
Optionally, when planning is activated, a plan can be periodically revised and stored in a `PlanningStep` . This includes feeding facts about the task at hand to the memory.
|
| 21 |
+
|
| 22 |
+
For a `CodeAgent`, it looks like the figure below.
|
| 23 |
+
|
| 24 |
+
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
| 25 |
+
<img
|
| 26 |
+
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/smolagents/codeagent_docs.png"
|
| 27 |
+
/>
|
| 28 |
+
</div>
|
| 29 |
+
|
| 30 |
+
Here is a video overview of how that works:
|
| 31 |
+
|
| 32 |
+
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
| 33 |
+
<img
|
| 34 |
+
class="block dark:hidden"
|
| 35 |
+
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/Agent_ManimCE.gif"
|
| 36 |
+
/>
|
| 37 |
+
<img
|
| 38 |
+
class="hidden dark:block"
|
| 39 |
+
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/Agent_ManimCE.gif"
|
| 40 |
+
/>
|
| 41 |
+
</div>
|
| 42 |
+
|
| 43 |
+
We implement two versions of agents:
|
| 44 |
+
- [`CodeAgent`] is the preferred type of agent: it generates its tool calls as blobs of code.
|
| 45 |
+
- [`ToolCallingAgent`] generates tool calls as a JSON in its output, as is commonly done in agentic frameworks. We incorporate this option because it can be useful in some narrow cases where you can do fine with only one tool call per step: for instance, for web browsing, you need to wait after each action on the page to monitor how the page changes.
|
| 46 |
+
|
| 47 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 48 |
+
> Read [Open-source LLMs as LangChain Agents](https://huggingface.co/blog/open-source-llms-as-agents) blog post to learn more about multi-step agents.
|
smolagents/docs/source/en/examples/multiagents.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,174 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Orchestrate a multi-agent system 🤖🤝🤖
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
[[open-in-colab]]
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
In this notebook we will make a **multi-agent web browser: an agentic system with several agents collaborating to solve problems using the web!**
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
It will be a simple hierarchy:
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
```
|
| 10 |
+
+----------------+
|
| 11 |
+
| Manager agent |
|
| 12 |
+
+----------------+
|
| 13 |
+
|
|
| 14 |
+
_______________|______________
|
| 15 |
+
| |
|
| 16 |
+
Code Interpreter +------------------+
|
| 17 |
+
tool | Web Search agent |
|
| 18 |
+
+------------------+
|
| 19 |
+
| |
|
| 20 |
+
Web Search tool |
|
| 21 |
+
Visit webpage tool
|
| 22 |
+
```
|
| 23 |
+
Let's set up this system.
|
| 24 |
+
|
| 25 |
+
Run the line below to install the required dependencies:
|
| 26 |
+
|
| 27 |
+
```py
|
| 28 |
+
! pip install markdownify duckduckgo-search smolagents --upgrade -q
|
| 29 |
+
```
|
| 30 |
+
|
| 31 |
+
Let's login to HF in order to call Inference Providers:
|
| 32 |
+
|
| 33 |
+
```py
|
| 34 |
+
from huggingface_hub import login
|
| 35 |
+
|
| 36 |
+
login()
|
| 37 |
+
```
|
| 38 |
+
|
| 39 |
+
⚡️ Our agent will be powered by [Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct](https://huggingface.co/Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct) using `InferenceClientModel` class that uses HF's Inference API: the Inference API allows to quickly and easily run any OS model.
|
| 40 |
+
|
| 41 |
+
_Note:_ The Inference API hosts models based on various criteria, and deployed models may be updated or replaced without prior notice. Learn more about it [here](https://huggingface.co/docs/api-inference/supported-models).
|
| 42 |
+
|
| 43 |
+
```py
|
| 44 |
+
model_id = "Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct"
|
| 45 |
+
```
|
| 46 |
+
|
| 47 |
+
## 🔍 Create a web search tool
|
| 48 |
+
|
| 49 |
+
For web browsing, we can already use our pre-existing [`DuckDuckGoSearchTool`](https://github.com/huggingface/smolagents/blob/main/src/smolagents/default_tools.py#L151-L176) tool to provide a Google search equivalent.
|
| 50 |
+
|
| 51 |
+
But then we will also need to be able to peak into the page found by the `DuckDuckGoSearchTool`.
|
| 52 |
+
To do so, we could import the library's built-in `VisitWebpageTool`, but we will build it again to see how it's done.
|
| 53 |
+
|
| 54 |
+
So let's create our `VisitWebpageTool` tool from scratch using `markdownify`.
|
| 55 |
+
|
| 56 |
+
```py
|
| 57 |
+
import re
|
| 58 |
+
import requests
|
| 59 |
+
from markdownify import markdownify
|
| 60 |
+
from requests.exceptions import RequestException
|
| 61 |
+
from smolagents import tool
|
| 62 |
+
|
| 63 |
+
|
| 64 |
+
@tool
|
| 65 |
+
def visit_webpage(url: str) -> str:
|
| 66 |
+
"""Visits a webpage at the given URL and returns its content as a markdown string.
|
| 67 |
+
|
| 68 |
+
Args:
|
| 69 |
+
url: The URL of the webpage to visit.
|
| 70 |
+
|
| 71 |
+
Returns:
|
| 72 |
+
The content of the webpage converted to Markdown, or an error message if the request fails.
|
| 73 |
+
"""
|
| 74 |
+
try:
|
| 75 |
+
# Send a GET request to the URL
|
| 76 |
+
response = requests.get(url)
|
| 77 |
+
response.raise_for_status() # Raise an exception for bad status codes
|
| 78 |
+
|
| 79 |
+
# Convert the HTML content to Markdown
|
| 80 |
+
markdown_content = markdownify(response.text).strip()
|
| 81 |
+
|
| 82 |
+
# Remove multiple line breaks
|
| 83 |
+
markdown_content = re.sub(r"\n{3,}", "\n\n", markdown_content)
|
| 84 |
+
|
| 85 |
+
return markdown_content
|
| 86 |
+
|
| 87 |
+
except RequestException as e:
|
| 88 |
+
return f"Error fetching the webpage: {str(e)}"
|
| 89 |
+
except Exception as e:
|
| 90 |
+
return f"An unexpected error occurred: {str(e)}"
|
| 91 |
+
```
|
| 92 |
+
|
| 93 |
+
Ok, now let's initialize and test our tool!
|
| 94 |
+
|
| 95 |
+
```py
|
| 96 |
+
print(visit_webpage("https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hugging_Face")[:500])
|
| 97 |
+
```
|
| 98 |
+
|
| 99 |
+
## Build our multi-agent system 🤖🤝🤖
|
| 100 |
+
|
| 101 |
+
Now that we have all the tools `search` and `visit_webpage`, we can use them to create the web agent.
|
| 102 |
+
|
| 103 |
+
Which configuration to choose for this agent?
|
| 104 |
+
- Web browsing is a single-timeline task that does not require parallel tool calls, so JSON tool calling works well for that. We thus choose a `ToolCallingAgent`.
|
| 105 |
+
- Also, since sometimes web search requires exploring many pages before finding the correct answer, we prefer to increase the number of `max_steps` to 10.
|
| 106 |
+
|
| 107 |
+
```py
|
| 108 |
+
from smolagents import (
|
| 109 |
+
CodeAgent,
|
| 110 |
+
ToolCallingAgent,
|
| 111 |
+
InferenceClientModel,
|
| 112 |
+
DuckDuckGoSearchTool,
|
| 113 |
+
LiteLLMModel,
|
| 114 |
+
)
|
| 115 |
+
|
| 116 |
+
model = InferenceClientModel(model_id=model_id)
|
| 117 |
+
|
| 118 |
+
web_agent = ToolCallingAgent(
|
| 119 |
+
tools=[DuckDuckGoSearchTool(), visit_webpage],
|
| 120 |
+
model=model,
|
| 121 |
+
max_steps=10,
|
| 122 |
+
name="web_search_agent",
|
| 123 |
+
description="Runs web searches for you.",
|
| 124 |
+
)
|
| 125 |
+
```
|
| 126 |
+
|
| 127 |
+
Note that we gave this agent attributes `name` and `description`, mandatory attributes to make this agent callable by its manager agent.
|
| 128 |
+
|
| 129 |
+
Then we create a manager agent, and upon initialization we pass our managed agent to it in its `managed_agents` argument.
|
| 130 |
+
|
| 131 |
+
Since this agent is the one tasked with the planning and thinking, advanced reasoning will be beneficial, so a `CodeAgent` will be the best choice.
|
| 132 |
+
|
| 133 |
+
Also, we want to ask a question that involves the current year and does additional data calculations: so let us add `additional_authorized_imports=["time", "numpy", "pandas"]`, just in case the agent needs these packages.
|
| 134 |
+
|
| 135 |
+
```py
|
| 136 |
+
manager_agent = CodeAgent(
|
| 137 |
+
tools=[],
|
| 138 |
+
model=model,
|
| 139 |
+
managed_agents=[web_agent],
|
| 140 |
+
additional_authorized_imports=["time", "numpy", "pandas"],
|
| 141 |
+
)
|
| 142 |
+
```
|
| 143 |
+
|
| 144 |
+
That's all! Now let's run our system! We select a question that requires both some calculation and research:
|
| 145 |
+
|
| 146 |
+
```py
|
| 147 |
+
answer = manager_agent.run("If LLM training continues to scale up at the current rhythm until 2030, what would be the electric power in GW required to power the biggest training runs by 2030? What would that correspond to, compared to some countries? Please provide a source for any numbers used.")
|
| 148 |
+
```
|
| 149 |
+
|
| 150 |
+
We get this report as the answer:
|
| 151 |
+
```
|
| 152 |
+
Based on current growth projections and energy consumption estimates, if LLM trainings continue to scale up at the
|
| 153 |
+
current rhythm until 2030:
|
| 154 |
+
|
| 155 |
+
1. The electric power required to power the biggest training runs by 2030 would be approximately 303.74 GW, which
|
| 156 |
+
translates to about 2,660,762 GWh/year.
|
| 157 |
+
|
| 158 |
+
2. Comparing this to countries' electricity consumption:
|
| 159 |
+
- It would be equivalent to about 34% of China's total electricity consumption.
|
| 160 |
+
- It would exceed the total electricity consumption of India (184%), Russia (267%), and Japan (291%).
|
| 161 |
+
- It would be nearly 9 times the electricity consumption of countries like Italy or Mexico.
|
| 162 |
+
|
| 163 |
+
3. Source of numbers:
|
| 164 |
+
- The initial estimate of 5 GW for future LLM training comes from AWS CEO Matt Garman.
|
| 165 |
+
- The growth projection used a CAGR of 79.80% from market research by Springs.
|
| 166 |
+
- Country electricity consumption data is from the U.S. Energy Information Administration, primarily for the year
|
| 167 |
+
2021.
|
| 168 |
+
```
|
| 169 |
+
|
| 170 |
+
Seems like we'll need some sizeable powerplants if the [scaling hypothesis](https://gwern.net/scaling-hypothesis) continues to hold true.
|
| 171 |
+
|
| 172 |
+
Our agents managed to efficiently collaborate towards solving the task! ✅
|
| 173 |
+
|
| 174 |
+
💡 You can easily extend this orchestration to more agents: one does the code execution, one the web search, one handles file loadings...
|
smolagents/docs/source/en/examples/rag.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Agentic RAG
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
[[open-in-colab]]
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
Retrieval-Augmented-Generation (RAG) is “using an LLM to answer a user query, but basing the answer on information retrieved from a knowledge base”. It has many advantages over using a vanilla or fine-tuned LLM: to name a few, it allows to ground the answer on true facts and reduce confabulations, it allows to provide the LLM with domain-specific knowledge, and it allows fine-grained control of access to information from the knowledge base.
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
But vanilla RAG has limitations, most importantly these two:
|
| 8 |
+
- It performs only one retrieval step: if the results are bad, the generation in turn will be bad.
|
| 9 |
+
- Semantic similarity is computed with the user query as a reference, which might be suboptimal: for instance, the user query will often be a question and the document containing the true answer will be in affirmative voice, so its similarity score will be downgraded compared to other source documents in the interrogative form, leading to a risk of missing the relevant information.
|
| 10 |
+
|
| 11 |
+
We can alleviate these problems by making a RAG agent: very simply, an agent armed with a retriever tool!
|
| 12 |
+
|
| 13 |
+
This agent will: ✅ Formulate the query itself and ✅ Critique to re-retrieve if needed.
|
| 14 |
+
|
| 15 |
+
So it should naively recover some advanced RAG techniques!
|
| 16 |
+
- Instead of directly using the user query as the reference in semantic search, the agent formulates itself a reference sentence that can be closer to the targeted documents, as in [HyDE](https://huggingface.co/papers/2212.10496).
|
| 17 |
+
The agent can use the generated snippets and re-retrieve if needed, as in [Self-Query](https://docs.llamaindex.ai/en/stable/examples/evaluation/RetryQuery/).
|
| 18 |
+
|
| 19 |
+
Let's build this system. 🛠️
|
| 20 |
+
|
| 21 |
+
Run the line below to install required dependencies:
|
| 22 |
+
```bash
|
| 23 |
+
!pip install smolagents pandas langchain langchain-community sentence-transformers datasets python-dotenv rank_bm25 --upgrade -q
|
| 24 |
+
```
|
| 25 |
+
To call Inference Providers, you will need a valid token as your environment variable `HF_TOKEN`.
|
| 26 |
+
We use python-dotenv to load it.
|
| 27 |
+
```py
|
| 28 |
+
from dotenv import load_dotenv
|
| 29 |
+
load_dotenv()
|
| 30 |
+
```
|
| 31 |
+
|
| 32 |
+
We first load a knowledge base on which we want to perform RAG: this dataset is a compilation of the documentation pages for many Hugging Face libraries, stored as markdown. We will keep only the documentation for the `transformers` library.
|
| 33 |
+
|
| 34 |
+
Then prepare the knowledge base by processing the dataset and storing it into a vector database to be used by the retriever.
|
| 35 |
+
|
| 36 |
+
We use [LangChain](https://python.langchain.com/docs/introduction/) for its excellent vector database utilities.
|
| 37 |
+
|
| 38 |
+
```py
|
| 39 |
+
import datasets
|
| 40 |
+
from langchain.docstore.document import Document
|
| 41 |
+
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
|
| 42 |
+
from langchain_community.retrievers import BM25Retriever
|
| 43 |
+
|
| 44 |
+
knowledge_base = datasets.load_dataset("m-ric/huggingface_doc", split="train")
|
| 45 |
+
knowledge_base = knowledge_base.filter(lambda row: row["source"].startswith("huggingface/transformers"))
|
| 46 |
+
|
| 47 |
+
source_docs = [
|
| 48 |
+
Document(page_content=doc["text"], metadata={"source": doc["source"].split("/")[1]})
|
| 49 |
+
for doc in knowledge_base
|
| 50 |
+
]
|
| 51 |
+
|
| 52 |
+
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
|
| 53 |
+
chunk_size=500,
|
| 54 |
+
chunk_overlap=50,
|
| 55 |
+
add_start_index=True,
|
| 56 |
+
strip_whitespace=True,
|
| 57 |
+
separators=["\n\n", "\n", ".", " ", ""],
|
| 58 |
+
)
|
| 59 |
+
docs_processed = text_splitter.split_documents(source_docs)
|
| 60 |
+
```
|
| 61 |
+
|
| 62 |
+
Now the documents are ready.
|
| 63 |
+
|
| 64 |
+
So let’s build our agentic RAG system!
|
| 65 |
+
|
| 66 |
+
👉 We only need a RetrieverTool that our agent can leverage to retrieve information from the knowledge base.
|
| 67 |
+
|
| 68 |
+
Since we need to add a vectordb as an attribute of the tool, we cannot simply use the simple tool constructor with a `@tool` decorator: so we will follow the advanced setup highlighted in the [tools tutorial](../tutorials/tools).
|
| 69 |
+
|
| 70 |
+
```py
|
| 71 |
+
from smolagents import Tool
|
| 72 |
+
|
| 73 |
+
class RetrieverTool(Tool):
|
| 74 |
+
name = "retriever"
|
| 75 |
+
description = "Uses semantic search to retrieve the parts of transformers documentation that could be most relevant to answer your query."
|
| 76 |
+
inputs = {
|
| 77 |
+
"query": {
|
| 78 |
+
"type": "string",
|
| 79 |
+
"description": "The query to perform. This should be semantically close to your target documents. Use the affirmative form rather than a question.",
|
| 80 |
+
}
|
| 81 |
+
}
|
| 82 |
+
output_type = "string"
|
| 83 |
+
|
| 84 |
+
def __init__(self, docs, **kwargs):
|
| 85 |
+
super().__init__(**kwargs)
|
| 86 |
+
self.retriever = BM25Retriever.from_documents(
|
| 87 |
+
docs, k=10
|
| 88 |
+
)
|
| 89 |
+
|
| 90 |
+
def forward(self, query: str) -> str:
|
| 91 |
+
assert isinstance(query, str), "Your search query must be a string"
|
| 92 |
+
|
| 93 |
+
docs = self.retriever.invoke(
|
| 94 |
+
query,
|
| 95 |
+
)
|
| 96 |
+
return "\nRetrieved documents:\n" + "".join(
|
| 97 |
+
[
|
| 98 |
+
f"\n\n===== Document {str(i)} =====\n" + doc.page_content
|
| 99 |
+
for i, doc in enumerate(docs)
|
| 100 |
+
]
|
| 101 |
+
)
|
| 102 |
+
|
| 103 |
+
retriever_tool = RetrieverTool(docs_processed)
|
| 104 |
+
```
|
| 105 |
+
We have used BM25, a classic retrieval method, because it's lightning fast to setup.
|
| 106 |
+
To improve retrieval accuracy, you could use replace BM25 with semantic search using vector representations for documents: thus you can head to the [MTEB Leaderboard](https://huggingface.co/spaces/mteb/leaderboard) to select a good embedding model.
|
| 107 |
+
|
| 108 |
+
Now it’s straightforward to create an agent that leverages this `retriever_tool`!
|
| 109 |
+
|
| 110 |
+
The agent will need these arguments upon initialization:
|
| 111 |
+
- `tools`: a list of tools that the agent will be able to call.
|
| 112 |
+
- `model`: the LLM that powers the agent.
|
| 113 |
+
Our `model` must be a callable that takes as input a list of messages and returns text. It also needs to accept a stop_sequences argument that indicates when to stop its generation. For convenience, we directly use the HfEngine class provided in the package to get a LLM engine that calls Hugging Face's Inference API.
|
| 114 |
+
|
| 115 |
+
>[!NOTE] To use a specific model, pass it like this: `InferenceClientModel(model_id="meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct")`. The Inference API hosts models based on various criteria, and deployed models may be updated or replaced without prior notice. Learn more about it [here](https://huggingface.co/docs/api-inference/supported-models).
|
| 116 |
+
|
| 117 |
+
```py
|
| 118 |
+
from smolagents import InferenceClientModel, CodeAgent
|
| 119 |
+
|
| 120 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(
|
| 121 |
+
tools=[retriever_tool], model=InferenceClientModel(), max_steps=4, verbosity_level=2
|
| 122 |
+
)
|
| 123 |
+
```
|
| 124 |
+
Upon initializing the CodeAgent, it has been automatically given a default system prompt that tells the LLM engine to process step-by-step and generate tool calls as code snippets, but you could replace this prompt template with your own as needed.
|
| 125 |
+
|
| 126 |
+
Then when its `.run()` method is launched, the agent takes care of calling the LLM engine, and executing the tool calls, all in a loop that ends only when tool `final_answer` is called with the final answer as its argument.
|
| 127 |
+
|
| 128 |
+
```py
|
| 129 |
+
agent_output = agent.run("For a transformers model training, which is slower, the forward or the backward pass?")
|
| 130 |
+
|
| 131 |
+
print("Final output:")
|
| 132 |
+
print(agent_output)
|
| 133 |
+
```
|
| 134 |
+
|
| 135 |
+
|
| 136 |
+
|
smolagents/docs/source/en/examples/text_to_sql.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,197 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Text-to-SQL
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
[[open-in-colab]]
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
In this tutorial, we’ll see how to implement an agent that leverages SQL using `smolagents`.
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
> Let's start with the golden question: why not keep it simple and use a standard text-to-SQL pipeline?
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
A standard text-to-sql pipeline is brittle, since the generated SQL query can be incorrect. Even worse, the query could be incorrect, but not raise an error, instead giving some incorrect/useless outputs without raising an alarm.
|
| 10 |
+
|
| 11 |
+
👉 Instead, an agent system is able to critically inspect outputs and decide if the query needs to be changed or not, thus giving it a huge performance boost.
|
| 12 |
+
|
| 13 |
+
Let’s build this agent! 💪
|
| 14 |
+
|
| 15 |
+
Run the line below to install required dependencies:
|
| 16 |
+
```bash
|
| 17 |
+
!pip install smolagents python-dotenv sqlalchemy --upgrade -q
|
| 18 |
+
```
|
| 19 |
+
To call Inference Providers, you will need a valid token as your environment variable `HF_TOKEN`.
|
| 20 |
+
We use python-dotenv to load it.
|
| 21 |
+
```py
|
| 22 |
+
from dotenv import load_dotenv
|
| 23 |
+
load_dotenv()
|
| 24 |
+
```
|
| 25 |
+
|
| 26 |
+
Then, we setup the SQL environment:
|
| 27 |
+
```py
|
| 28 |
+
from sqlalchemy import (
|
| 29 |
+
create_engine,
|
| 30 |
+
MetaData,
|
| 31 |
+
Table,
|
| 32 |
+
Column,
|
| 33 |
+
String,
|
| 34 |
+
Integer,
|
| 35 |
+
Float,
|
| 36 |
+
insert,
|
| 37 |
+
inspect,
|
| 38 |
+
text,
|
| 39 |
+
)
|
| 40 |
+
|
| 41 |
+
engine = create_engine("sqlite:///:memory:")
|
| 42 |
+
metadata_obj = MetaData()
|
| 43 |
+
|
| 44 |
+
def insert_rows_into_table(rows, table, engine=engine):
|
| 45 |
+
for row in rows:
|
| 46 |
+
stmt = insert(table).values(**row)
|
| 47 |
+
with engine.begin() as connection:
|
| 48 |
+
connection.execute(stmt)
|
| 49 |
+
|
| 50 |
+
table_name = "receipts"
|
| 51 |
+
receipts = Table(
|
| 52 |
+
table_name,
|
| 53 |
+
metadata_obj,
|
| 54 |
+
Column("receipt_id", Integer, primary_key=True),
|
| 55 |
+
Column("customer_name", String(16), primary_key=True),
|
| 56 |
+
Column("price", Float),
|
| 57 |
+
Column("tip", Float),
|
| 58 |
+
)
|
| 59 |
+
metadata_obj.create_all(engine)
|
| 60 |
+
|
| 61 |
+
rows = [
|
| 62 |
+
{"receipt_id": 1, "customer_name": "Alan Payne", "price": 12.06, "tip": 1.20},
|
| 63 |
+
{"receipt_id": 2, "customer_name": "Alex Mason", "price": 23.86, "tip": 0.24},
|
| 64 |
+
{"receipt_id": 3, "customer_name": "Woodrow Wilson", "price": 53.43, "tip": 5.43},
|
| 65 |
+
{"receipt_id": 4, "customer_name": "Margaret James", "price": 21.11, "tip": 1.00},
|
| 66 |
+
]
|
| 67 |
+
insert_rows_into_table(rows, receipts)
|
| 68 |
+
```
|
| 69 |
+
|
| 70 |
+
### Build our agent
|
| 71 |
+
|
| 72 |
+
Now let’s make our SQL table retrievable by a tool.
|
| 73 |
+
|
| 74 |
+
The tool’s description attribute will be embedded in the LLM’s prompt by the agent system: it gives the LLM information about how to use the tool. This is where we want to describe the SQL table.
|
| 75 |
+
|
| 76 |
+
```py
|
| 77 |
+
inspector = inspect(engine)
|
| 78 |
+
columns_info = [(col["name"], col["type"]) for col in inspector.get_columns("receipts")]
|
| 79 |
+
|
| 80 |
+
table_description = "Columns:\n" + "\n".join([f" - {name}: {col_type}" for name, col_type in columns_info])
|
| 81 |
+
print(table_description)
|
| 82 |
+
```
|
| 83 |
+
|
| 84 |
+
```text
|
| 85 |
+
Columns:
|
| 86 |
+
- receipt_id: INTEGER
|
| 87 |
+
- customer_name: VARCHAR(16)
|
| 88 |
+
- price: FLOAT
|
| 89 |
+
- tip: FLOAT
|
| 90 |
+
```
|
| 91 |
+
|
| 92 |
+
Now let’s build our tool. It needs the following: (read [the tool doc](../tutorials/tools) for more detail)
|
| 93 |
+
- A docstring with an `Args:` part listing arguments.
|
| 94 |
+
- Type hints on both inputs and output.
|
| 95 |
+
|
| 96 |
+
```py
|
| 97 |
+
from smolagents import tool
|
| 98 |
+
|
| 99 |
+
@tool
|
| 100 |
+
def sql_engine(query: str) -> str:
|
| 101 |
+
"""
|
| 102 |
+
Allows you to perform SQL queries on the table. Returns a string representation of the result.
|
| 103 |
+
The table is named 'receipts'. Its description is as follows:
|
| 104 |
+
Columns:
|
| 105 |
+
- receipt_id: INTEGER
|
| 106 |
+
- customer_name: VARCHAR(16)
|
| 107 |
+
- price: FLOAT
|
| 108 |
+
- tip: FLOAT
|
| 109 |
+
|
| 110 |
+
Args:
|
| 111 |
+
query: The query to perform. This should be correct SQL.
|
| 112 |
+
"""
|
| 113 |
+
output = ""
|
| 114 |
+
with engine.connect() as con:
|
| 115 |
+
rows = con.execute(text(query))
|
| 116 |
+
for row in rows:
|
| 117 |
+
output += "\n" + str(row)
|
| 118 |
+
return output
|
| 119 |
+
```
|
| 120 |
+
|
| 121 |
+
Now let us create an agent that leverages this tool.
|
| 122 |
+
|
| 123 |
+
We use the `CodeAgent`, which is smolagents’ main agent class: an agent that writes actions in code and can iterate on previous output according to the ReAct framework.
|
| 124 |
+
|
| 125 |
+
The model is the LLM that powers the agent system. `InferenceClientModel` allows you to call LLMs using HF’s Inference API, either via Serverless or Dedicated endpoint, but you could also use any proprietary API.
|
| 126 |
+
|
| 127 |
+
```py
|
| 128 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel
|
| 129 |
+
|
| 130 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(
|
| 131 |
+
tools=[sql_engine],
|
| 132 |
+
model=InferenceClientModel(model_id="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct"),
|
| 133 |
+
)
|
| 134 |
+
agent.run("Can you give me the name of the client who got the most expensive receipt?")
|
| 135 |
+
```
|
| 136 |
+
|
| 137 |
+
### Level 2: Table joins
|
| 138 |
+
|
| 139 |
+
Now let’s make it more challenging! We want our agent to handle joins across multiple tables.
|
| 140 |
+
|
| 141 |
+
So let’s make a second table recording the names of waiters for each receipt_id!
|
| 142 |
+
|
| 143 |
+
```py
|
| 144 |
+
table_name = "waiters"
|
| 145 |
+
waiters = Table(
|
| 146 |
+
table_name,
|
| 147 |
+
metadata_obj,
|
| 148 |
+
Column("receipt_id", Integer, primary_key=True),
|
| 149 |
+
Column("waiter_name", String(16), primary_key=True),
|
| 150 |
+
)
|
| 151 |
+
metadata_obj.create_all(engine)
|
| 152 |
+
|
| 153 |
+
rows = [
|
| 154 |
+
{"receipt_id": 1, "waiter_name": "Corey Johnson"},
|
| 155 |
+
{"receipt_id": 2, "waiter_name": "Michael Watts"},
|
| 156 |
+
{"receipt_id": 3, "waiter_name": "Michael Watts"},
|
| 157 |
+
{"receipt_id": 4, "waiter_name": "Margaret James"},
|
| 158 |
+
]
|
| 159 |
+
insert_rows_into_table(rows, waiters)
|
| 160 |
+
```
|
| 161 |
+
Since we changed the table, we update the `SQLExecutorTool` with this table’s description to let the LLM properly leverage information from this table.
|
| 162 |
+
|
| 163 |
+
```py
|
| 164 |
+
updated_description = """Allows you to perform SQL queries on the table. Beware that this tool's output is a string representation of the execution output.
|
| 165 |
+
It can use the following tables:"""
|
| 166 |
+
|
| 167 |
+
inspector = inspect(engine)
|
| 168 |
+
for table in ["receipts", "waiters"]:
|
| 169 |
+
columns_info = [(col["name"], col["type"]) for col in inspector.get_columns(table)]
|
| 170 |
+
|
| 171 |
+
table_description = f"Table '{table}':\n"
|
| 172 |
+
|
| 173 |
+
table_description += "Columns:\n" + "\n".join([f" - {name}: {col_type}" for name, col_type in columns_info])
|
| 174 |
+
updated_description += "\n\n" + table_description
|
| 175 |
+
|
| 176 |
+
print(updated_description)
|
| 177 |
+
```
|
| 178 |
+
Since this request is a bit harder than the previous one, we’ll switch the LLM engine to use the more powerful [Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct](https://huggingface.co/Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct)!
|
| 179 |
+
|
| 180 |
+
```py
|
| 181 |
+
sql_engine.description = updated_description
|
| 182 |
+
|
| 183 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(
|
| 184 |
+
tools=[sql_engine],
|
| 185 |
+
model=InferenceClientModel(model_id="Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct"),
|
| 186 |
+
)
|
| 187 |
+
|
| 188 |
+
agent.run("Which waiter got more total money from tips?")
|
| 189 |
+
```
|
| 190 |
+
It directly works! The setup was surprisingly simple, wasn’t it?
|
| 191 |
+
|
| 192 |
+
This example is done! We've touched upon these concepts:
|
| 193 |
+
- Building new tools.
|
| 194 |
+
- Updating a tool's description.
|
| 195 |
+
- Switching to a stronger LLM helps agent reasoning.
|
| 196 |
+
|
| 197 |
+
✅ Now you can go build this text-to-SQL system you’ve always dreamt of! ✨
|
smolagents/docs/source/en/examples/web_browser.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,213 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Web Browser Automation with Agents 🤖🌐
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
[[open-in-colab]]
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
In this notebook, we'll create an **agent-powered web browser automation system**! This system can navigate websites, interact with elements, and extract information automatically.
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
The agent will be able to:
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
- [x] Navigate to web pages
|
| 10 |
+
- [x] Click on elements
|
| 11 |
+
- [x] Search within pages
|
| 12 |
+
- [x] Handle popups and modals
|
| 13 |
+
- [x] Extract information
|
| 14 |
+
|
| 15 |
+
Let's set up this system step by step!
|
| 16 |
+
|
| 17 |
+
First, run these lines to install the required dependencies:
|
| 18 |
+
|
| 19 |
+
```bash
|
| 20 |
+
pip install smolagents selenium helium pillow -q
|
| 21 |
+
```
|
| 22 |
+
|
| 23 |
+
Let's import our required libraries and set up environment variables:
|
| 24 |
+
|
| 25 |
+
```python
|
| 26 |
+
from io import BytesIO
|
| 27 |
+
from time import sleep
|
| 28 |
+
|
| 29 |
+
import helium
|
| 30 |
+
from dotenv import load_dotenv
|
| 31 |
+
from PIL import Image
|
| 32 |
+
from selenium import webdriver
|
| 33 |
+
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
|
| 34 |
+
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
|
| 35 |
+
|
| 36 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, tool
|
| 37 |
+
from smolagents.agents import ActionStep
|
| 38 |
+
|
| 39 |
+
# Load environment variables
|
| 40 |
+
load_dotenv()
|
| 41 |
+
```
|
| 42 |
+
|
| 43 |
+
Now let's create our core browser interaction tools that will allow our agent to navigate and interact with web pages:
|
| 44 |
+
|
| 45 |
+
```python
|
| 46 |
+
@tool
|
| 47 |
+
def search_item_ctrl_f(text: str, nth_result: int = 1) -> str:
|
| 48 |
+
"""
|
| 49 |
+
Searches for text on the current page via Ctrl + F and jumps to the nth occurrence.
|
| 50 |
+
Args:
|
| 51 |
+
text: The text to search for
|
| 52 |
+
nth_result: Which occurrence to jump to (default: 1)
|
| 53 |
+
"""
|
| 54 |
+
elements = driver.find_elements(By.XPATH, f"//*[contains(text(), '{text}')]")
|
| 55 |
+
if nth_result > len(elements):
|
| 56 |
+
raise Exception(f"Match n°{nth_result} not found (only {len(elements)} matches found)")
|
| 57 |
+
result = f"Found {len(elements)} matches for '{text}'."
|
| 58 |
+
elem = elements[nth_result - 1]
|
| 59 |
+
driver.execute_script("arguments[0].scrollIntoView(true);", elem)
|
| 60 |
+
result += f"Focused on element {nth_result} of {len(elements)}"
|
| 61 |
+
return result
|
| 62 |
+
|
| 63 |
+
@tool
|
| 64 |
+
def go_back() -> None:
|
| 65 |
+
"""Goes back to previous page."""
|
| 66 |
+
driver.back()
|
| 67 |
+
|
| 68 |
+
@tool
|
| 69 |
+
def close_popups() -> str:
|
| 70 |
+
"""
|
| 71 |
+
Closes any visible modal or pop-up on the page. Use this to dismiss pop-up windows!
|
| 72 |
+
This does not work on cookie consent banners.
|
| 73 |
+
"""
|
| 74 |
+
webdriver.ActionChains(driver).send_keys(Keys.ESCAPE).perform()
|
| 75 |
+
```
|
| 76 |
+
|
| 77 |
+
Let's set up our browser with Chrome and configure screenshot capabilities:
|
| 78 |
+
|
| 79 |
+
```python
|
| 80 |
+
# Configure Chrome options
|
| 81 |
+
chrome_options = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
|
| 82 |
+
chrome_options.add_argument("--force-device-scale-factor=1")
|
| 83 |
+
chrome_options.add_argument("--window-size=1000,1350")
|
| 84 |
+
chrome_options.add_argument("--disable-pdf-viewer")
|
| 85 |
+
chrome_options.add_argument("--window-position=0,0")
|
| 86 |
+
|
| 87 |
+
# Initialize the browser
|
| 88 |
+
driver = helium.start_chrome(headless=False, options=chrome_options)
|
| 89 |
+
|
| 90 |
+
# Set up screenshot callback
|
| 91 |
+
def save_screenshot(memory_step: ActionStep, agent: CodeAgent) -> None:
|
| 92 |
+
sleep(1.0) # Let JavaScript animations happen before taking the screenshot
|
| 93 |
+
driver = helium.get_driver()
|
| 94 |
+
current_step = memory_step.step_number
|
| 95 |
+
if driver is not None:
|
| 96 |
+
for previous_memory_step in agent.memory.steps: # Remove previous screenshots for lean processing
|
| 97 |
+
if isinstance(previous_memory_step, ActionStep) and previous_memory_step.step_number <= current_step - 2:
|
| 98 |
+
previous_memory_step.observations_images = None
|
| 99 |
+
png_bytes = driver.get_screenshot_as_png()
|
| 100 |
+
image = Image.open(BytesIO(png_bytes))
|
| 101 |
+
print(f"Captured a browser screenshot: {image.size} pixels")
|
| 102 |
+
memory_step.observations_images = [image.copy()] # Create a copy to ensure it persists
|
| 103 |
+
|
| 104 |
+
# Update observations with current URL
|
| 105 |
+
url_info = f"Current url: {driver.current_url}"
|
| 106 |
+
memory_step.observations = (
|
| 107 |
+
url_info if memory_step.observations is None else memory_step.observations + "\n" + url_info
|
| 108 |
+
)
|
| 109 |
+
```
|
| 110 |
+
|
| 111 |
+
Now let's create our web automation agent:
|
| 112 |
+
|
| 113 |
+
```python
|
| 114 |
+
from smolagents import InferenceClientModel
|
| 115 |
+
|
| 116 |
+
# Initialize the model
|
| 117 |
+
model_id = "meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct" # You can change this to your preferred model
|
| 118 |
+
model = InferenceClientModel(model_id=model_id)
|
| 119 |
+
|
| 120 |
+
# Create the agent
|
| 121 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(
|
| 122 |
+
tools=[go_back, close_popups, search_item_ctrl_f],
|
| 123 |
+
model=model,
|
| 124 |
+
additional_authorized_imports=["helium"],
|
| 125 |
+
step_callbacks=[save_screenshot],
|
| 126 |
+
max_steps=20,
|
| 127 |
+
verbosity_level=2,
|
| 128 |
+
)
|
| 129 |
+
|
| 130 |
+
# Import helium for the agent
|
| 131 |
+
agent.python_executor("from helium import *", agent.state)
|
| 132 |
+
```
|
| 133 |
+
|
| 134 |
+
The agent needs instructions on how to use Helium for web automation. Here are the instructions we'll provide:
|
| 135 |
+
|
| 136 |
+
```python
|
| 137 |
+
helium_instructions = """
|
| 138 |
+
You can use helium to access websites. Don't bother about the helium driver, it's already managed.
|
| 139 |
+
We've already ran "from helium import *"
|
| 140 |
+
Then you can go to pages!
|
| 141 |
+
Code:
|
| 142 |
+
```py
|
| 143 |
+
go_to('github.com/trending')
|
| 144 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 145 |
+
|
| 146 |
+
You can directly click clickable elements by inputting the text that appears on them.
|
| 147 |
+
Code:
|
| 148 |
+
```py
|
| 149 |
+
click("Top products")
|
| 150 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 151 |
+
|
| 152 |
+
If it's a link:
|
| 153 |
+
Code:
|
| 154 |
+
```py
|
| 155 |
+
click(Link("Top products"))
|
| 156 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 157 |
+
|
| 158 |
+
If you try to interact with an element and it's not found, you'll get a LookupError.
|
| 159 |
+
In general stop your action after each button click to see what happens on your screenshot.
|
| 160 |
+
Never try to login in a page.
|
| 161 |
+
|
| 162 |
+
To scroll up or down, use scroll_down or scroll_up with as an argument the number of pixels to scroll from.
|
| 163 |
+
Code:
|
| 164 |
+
```py
|
| 165 |
+
scroll_down(num_pixels=1200) # This will scroll one viewport down
|
| 166 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 167 |
+
|
| 168 |
+
When you have pop-ups with a cross icon to close, don't try to click the close icon by finding its element or targeting an 'X' element (this most often fails).
|
| 169 |
+
Just use your built-in tool `close_popups` to close them:
|
| 170 |
+
Code:
|
| 171 |
+
```py
|
| 172 |
+
close_popups()
|
| 173 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 174 |
+
|
| 175 |
+
You can use .exists() to check for the existence of an element. For example:
|
| 176 |
+
Code:
|
| 177 |
+
```py
|
| 178 |
+
if Text('Accept cookies?').exists():
|
| 179 |
+
click('I accept')
|
| 180 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 181 |
+
"""
|
| 182 |
+
```
|
| 183 |
+
|
| 184 |
+
Now we can run our agent with a task! Let's try finding information on Wikipedia:
|
| 185 |
+
|
| 186 |
+
```python
|
| 187 |
+
search_request = """
|
| 188 |
+
Please navigate to https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chicago and give me a sentence containing the word "1992" that mentions a construction accident.
|
| 189 |
+
"""
|
| 190 |
+
|
| 191 |
+
agent_output = agent.run(search_request + helium_instructions)
|
| 192 |
+
print("Final output:")
|
| 193 |
+
print(agent_output)
|
| 194 |
+
```
|
| 195 |
+
|
| 196 |
+
You can run different tasks by modifying the request. For example, here's for me to know if I should work harder:
|
| 197 |
+
|
| 198 |
+
```python
|
| 199 |
+
github_request = """
|
| 200 |
+
I'm trying to find how hard I have to work to get a repo in github.com/trending.
|
| 201 |
+
Can you navigate to the profile for the top author of the top trending repo, and give me their total number of commits over the last year?
|
| 202 |
+
"""
|
| 203 |
+
|
| 204 |
+
agent_output = agent.run(github_request + helium_instructions)
|
| 205 |
+
print("Final output:")
|
| 206 |
+
print(agent_output)
|
| 207 |
+
```
|
| 208 |
+
|
| 209 |
+
The system is particularly effective for tasks like:
|
| 210 |
+
- Data extraction from websites
|
| 211 |
+
- Web research automation
|
| 212 |
+
- UI testing and verification
|
| 213 |
+
- Content monitoring
|
smolagents/docs/source/en/guided_tour.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,498 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Agents - Guided tour
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
[[open-in-colab]]
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
In this guided visit, you will learn how to build an agent, how to run it, and how to customize it to make it work better for your use-case.
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
### Building your agent
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
To initialize a minimal agent, you need at least these two arguments:
|
| 10 |
+
|
| 11 |
+
- `model`, a text-generation model to power your agent - because the agent is different from a simple LLM, it is a system that uses a LLM as its engine. You can use any of these options:
|
| 12 |
+
- [`TransformersModel`] takes a pre-initialized `transformers` pipeline to run inference on your local machine using `transformers`.
|
| 13 |
+
- [`InferenceClientModel`] leverages a `huggingface_hub.InferenceClient` under the hood and supports all Inference Providers on the Hub: Cerebras, Cohere, Fal, Fireworks, HF-Inference, Hyperbolic, Nebius, Novita, Replicate, SambaNova, Together, and more.
|
| 14 |
+
- [`LiteLLMModel`] similarly lets you call 100+ different models and providers through [LiteLLM](https://docs.litellm.ai/)!
|
| 15 |
+
- [`AzureOpenAIServerModel`] allows you to use OpenAI models deployed in [Azure](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/products/ai-services/openai-service).
|
| 16 |
+
- [`AmazonBedrockServerModel`] allows you to use Amazon Bedrock in [AWS](https://aws.amazon.com/bedrock/?nc1=h_ls).
|
| 17 |
+
- [`MLXModel`] creates a [mlx-lm](https://pypi.org/project/mlx-lm/) pipeline to run inference on your local machine.
|
| 18 |
+
|
| 19 |
+
- `tools`, a list of `Tools` that the agent can use to solve the task. It can be an empty list. You can also add the default toolbox on top of your `tools` list by defining the optional argument `add_base_tools=True`.
|
| 20 |
+
|
| 21 |
+
Once you have these two arguments, `tools` and `model`, you can create an agent and run it. You can use any LLM you'd like, either through [Inference Providers](https://huggingface.co/blog/inference-providers), [transformers](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/), [ollama](https://ollama.com/), [LiteLLM](https://www.litellm.ai/), [Azure OpenAI](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/products/ai-services/openai-service), [Amazon Bedrock](https://aws.amazon.com/bedrock/?nc1=h_ls), or [mlx-lm](https://pypi.org/project/mlx-lm/).
|
| 22 |
+
|
| 23 |
+
<hfoptions id="Pick a LLM">
|
| 24 |
+
<hfoption id="Inference Providers">
|
| 25 |
+
|
| 26 |
+
Inference Providers need a `HF_TOKEN` to authenticate, but a free HF account already comes with included credits. Upgrade to PRO to raise your included credits.
|
| 27 |
+
|
| 28 |
+
To access gated models or rise your rate limits with a PRO account, you need to set the environment variable `HF_TOKEN` or pass `token` variable upon initialization of `InferenceClientModel`. You can get your token from your [settings page](https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens)
|
| 29 |
+
|
| 30 |
+
```python
|
| 31 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel
|
| 32 |
+
|
| 33 |
+
model_id = "meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct"
|
| 34 |
+
|
| 35 |
+
model = InferenceClientModel(model_id=model_id, token="<YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>") # You can choose to not pass any model_id to InferenceClientModel to use a default model
|
| 36 |
+
# you can also specify a particular provider e.g. provider="together" or provider="sambanova"
|
| 37 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
|
| 38 |
+
|
| 39 |
+
agent.run(
|
| 40 |
+
"Could you give me the 118th number in the Fibonacci sequence?",
|
| 41 |
+
)
|
| 42 |
+
```
|
| 43 |
+
</hfoption>
|
| 44 |
+
<hfoption id="Local Transformers Model">
|
| 45 |
+
|
| 46 |
+
```python
|
| 47 |
+
# !pip install smolagents[transformers]
|
| 48 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, TransformersModel
|
| 49 |
+
|
| 50 |
+
model_id = "meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct"
|
| 51 |
+
|
| 52 |
+
model = TransformersModel(model_id=model_id)
|
| 53 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
|
| 54 |
+
|
| 55 |
+
agent.run(
|
| 56 |
+
"Could you give me the 118th number in the Fibonacci sequence?",
|
| 57 |
+
)
|
| 58 |
+
```
|
| 59 |
+
</hfoption>
|
| 60 |
+
<hfoption id="OpenAI or Anthropic API">
|
| 61 |
+
|
| 62 |
+
To use `LiteLLMModel`, you need to set the environment variable `ANTHROPIC_API_KEY` or `OPENAI_API_KEY`, or pass `api_key` variable upon initialization.
|
| 63 |
+
|
| 64 |
+
```python
|
| 65 |
+
# !pip install smolagents[litellm]
|
| 66 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, LiteLLMModel
|
| 67 |
+
|
| 68 |
+
model = LiteLLMModel(model_id="anthropic/claude-3-5-sonnet-latest", api_key="YOUR_ANTHROPIC_API_KEY") # Could use 'gpt-4o'
|
| 69 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
|
| 70 |
+
|
| 71 |
+
agent.run(
|
| 72 |
+
"Could you give me the 118th number in the Fibonacci sequence?",
|
| 73 |
+
)
|
| 74 |
+
```
|
| 75 |
+
</hfoption>
|
| 76 |
+
<hfoption id="Ollama">
|
| 77 |
+
|
| 78 |
+
```python
|
| 79 |
+
# !pip install smolagents[litellm]
|
| 80 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, LiteLLMModel
|
| 81 |
+
|
| 82 |
+
model = LiteLLMModel(
|
| 83 |
+
model_id="ollama_chat/llama3.2", # This model is a bit weak for agentic behaviours though
|
| 84 |
+
api_base="http://localhost:11434", # replace with 127.0.0.1:11434 or remote open-ai compatible server if necessary
|
| 85 |
+
api_key="YOUR_API_KEY", # replace with API key if necessary
|
| 86 |
+
num_ctx=8192, # ollama default is 2048 which will fail horribly. 8192 works for easy tasks, more is better. Check https://huggingface.co/spaces/NyxKrage/LLM-Model-VRAM-Calculator to calculate how much VRAM this will need for the selected model.
|
| 87 |
+
)
|
| 88 |
+
|
| 89 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
|
| 90 |
+
|
| 91 |
+
agent.run(
|
| 92 |
+
"Could you give me the 118th number in the Fibonacci sequence?",
|
| 93 |
+
)
|
| 94 |
+
```
|
| 95 |
+
</hfoption>
|
| 96 |
+
<hfoption id="Azure OpenAI">
|
| 97 |
+
|
| 98 |
+
To connect to Azure OpenAI, you can either use `AzureOpenAIServerModel` directly, or use `LiteLLMModel` and configure it accordingly.
|
| 99 |
+
|
| 100 |
+
To initialize an instance of `AzureOpenAIServerModel`, you need to pass your model deployment name and then either pass the `azure_endpoint`, `api_key`, and `api_version` arguments, or set the environment variables `AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT`, `AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY`, and `OPENAI_API_VERSION`.
|
| 101 |
+
|
| 102 |
+
```python
|
| 103 |
+
# !pip install smolagents[openai]
|
| 104 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, AzureOpenAIServerModel
|
| 105 |
+
|
| 106 |
+
model = AzureOpenAIServerModel(model_id="gpt-4o-mini")
|
| 107 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
|
| 108 |
+
|
| 109 |
+
agent.run(
|
| 110 |
+
"Could you give me the 118th number in the Fibonacci sequence?",
|
| 111 |
+
)
|
| 112 |
+
```
|
| 113 |
+
|
| 114 |
+
Similarly, you can configure `LiteLLMModel` to connect to Azure OpenAI as follows:
|
| 115 |
+
|
| 116 |
+
- pass your model deployment name as `model_id`, and make sure to prefix it with `azure/`
|
| 117 |
+
- make sure to set the environment variable `AZURE_API_VERSION`
|
| 118 |
+
- either pass the `api_base` and `api_key` arguments, or set the environment variables `AZURE_API_KEY`, and `AZURE_API_BASE`
|
| 119 |
+
|
| 120 |
+
```python
|
| 121 |
+
import os
|
| 122 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, LiteLLMModel
|
| 123 |
+
|
| 124 |
+
AZURE_OPENAI_CHAT_DEPLOYMENT_NAME="gpt-35-turbo-16k-deployment" # example of deployment name
|
| 125 |
+
|
| 126 |
+
os.environ["AZURE_API_KEY"] = "" # api_key
|
| 127 |
+
os.environ["AZURE_API_BASE"] = "" # "https://example-endpoint.openai.azure.com"
|
| 128 |
+
os.environ["AZURE_API_VERSION"] = "" # "2024-10-01-preview"
|
| 129 |
+
|
| 130 |
+
model = LiteLLMModel(model_id="azure/" + AZURE_OPENAI_CHAT_DEPLOYMENT_NAME)
|
| 131 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
|
| 132 |
+
|
| 133 |
+
agent.run(
|
| 134 |
+
"Could you give me the 118th number in the Fibonacci sequence?",
|
| 135 |
+
)
|
| 136 |
+
```
|
| 137 |
+
|
| 138 |
+
</hfoption>
|
| 139 |
+
<hfoption id="Amazon Bedrock">
|
| 140 |
+
|
| 141 |
+
The `AmazonBedrockServerModel` class provides native integration with Amazon Bedrock, allowing for direct API calls and comprehensive configuration.
|
| 142 |
+
|
| 143 |
+
#### Basic Usage
|
| 144 |
+
|
| 145 |
+
```python
|
| 146 |
+
# !pip install smolagents[aws_sdk]
|
| 147 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, AmazonBedrockServerModel
|
| 148 |
+
|
| 149 |
+
model = AmazonBedrockServerModel(model_id="anthropic.claude-3-sonnet-20240229-v1:0")
|
| 150 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
|
| 151 |
+
|
| 152 |
+
agent.run(
|
| 153 |
+
"Could you give me the 118th number in the Fibonacci sequence?",
|
| 154 |
+
)
|
| 155 |
+
```
|
| 156 |
+
|
| 157 |
+
#### Advanced Configuration
|
| 158 |
+
|
| 159 |
+
```python
|
| 160 |
+
import boto3
|
| 161 |
+
from smolagents import AmazonBedrockServerModel
|
| 162 |
+
|
| 163 |
+
# Create a custom Bedrock client
|
| 164 |
+
bedrock_client = boto3.client(
|
| 165 |
+
'bedrock-runtime',
|
| 166 |
+
region_name='us-east-1',
|
| 167 |
+
aws_access_key_id='YOUR_ACCESS_KEY',
|
| 168 |
+
aws_secret_access_key='YOUR_SECRET_KEY'
|
| 169 |
+
)
|
| 170 |
+
|
| 171 |
+
additional_api_config = {
|
| 172 |
+
"inferenceConfig": {
|
| 173 |
+
"maxTokens": 3000
|
| 174 |
+
},
|
| 175 |
+
"guardrailConfig": {
|
| 176 |
+
"guardrailIdentifier": "identify1",
|
| 177 |
+
"guardrailVersion": 'v1'
|
| 178 |
+
},
|
| 179 |
+
}
|
| 180 |
+
|
| 181 |
+
# Initialize with comprehensive configuration
|
| 182 |
+
model = AmazonBedrockServerModel(
|
| 183 |
+
model_id="us.amazon.nova-pro-v1:0",
|
| 184 |
+
client=bedrock_client, # Use custom client
|
| 185 |
+
**additional_api_config
|
| 186 |
+
)
|
| 187 |
+
|
| 188 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
|
| 189 |
+
|
| 190 |
+
agent.run(
|
| 191 |
+
"Could you give me the 118th number in the Fibonacci sequence?",
|
| 192 |
+
)
|
| 193 |
+
```
|
| 194 |
+
|
| 195 |
+
#### Using LiteLLMModel
|
| 196 |
+
|
| 197 |
+
Alternatively, you can use `LiteLLMModel` with Bedrock models:
|
| 198 |
+
|
| 199 |
+
```python
|
| 200 |
+
from smolagents import LiteLLMModel, CodeAgent
|
| 201 |
+
|
| 202 |
+
model = LiteLLMModel(model_name="bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-sonnet-20240229-v1:0")
|
| 203 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model)
|
| 204 |
+
|
| 205 |
+
agent.run("Explain the concept of quantum computing")
|
| 206 |
+
```
|
| 207 |
+
|
| 208 |
+
</hfoption>
|
| 209 |
+
<hfoption id="mlx-lm">
|
| 210 |
+
|
| 211 |
+
```python
|
| 212 |
+
# !pip install smolagents[mlx-lm]
|
| 213 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, MLXModel
|
| 214 |
+
|
| 215 |
+
mlx_model = MLXModel("mlx-community/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct-4bit")
|
| 216 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(model=mlx_model, tools=[], add_base_tools=True)
|
| 217 |
+
|
| 218 |
+
agent.run("Could you give me the 118th number in the Fibonacci sequence?")
|
| 219 |
+
```
|
| 220 |
+
|
| 221 |
+
</hfoption>
|
| 222 |
+
</hfoptions>
|
| 223 |
+
|
| 224 |
+
#### CodeAgent and ToolCallingAgent
|
| 225 |
+
|
| 226 |
+
The [`CodeAgent`] is our default agent. It will write and execute python code snippets at each step.
|
| 227 |
+
|
| 228 |
+
By default, the execution is done in your local environment.
|
| 229 |
+
This should be safe because the only functions that can be called are the tools you provided (especially if it's only tools by Hugging Face) and a set of predefined safe functions like `print` or functions from the `math` module, so you're already limited in what can be executed.
|
| 230 |
+
|
| 231 |
+
The Python interpreter also doesn't allow imports by default outside of a safe list, so all the most obvious attacks shouldn't be an issue.
|
| 232 |
+
You can authorize additional imports by passing the authorized modules as a list of strings in argument `additional_authorized_imports` upon initialization of your [`CodeAgent`]:
|
| 233 |
+
|
| 234 |
+
```py
|
| 235 |
+
model = InferenceClientModel()
|
| 236 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, additional_authorized_imports=['requests', 'bs4'])
|
| 237 |
+
agent.run("Could you get me the title of the page at url 'https://huggingface.co/blog'?")
|
| 238 |
+
```
|
| 239 |
+
|
| 240 |
+
Additionally, as an extra security layer, access to submodule is forbidden by default, unless explicitly authorized within the import list.
|
| 241 |
+
For instance, to access the `numpy.random` submodule, you need to add `'numpy.random'` to the `additional_authorized_imports` list.
|
| 242 |
+
This could also be authorized by using `numpy.*`, which will allow `numpy` as well as any subpackage like `numpy.random` and its own subpackages.
|
| 243 |
+
|
| 244 |
+
> [!WARNING]
|
| 245 |
+
> The LLM can generate arbitrary code that will then be executed: do not add any unsafe imports!
|
| 246 |
+
|
| 247 |
+
The execution will stop at any code trying to perform an illegal operation or if there is a regular Python error with the code generated by the agent.
|
| 248 |
+
|
| 249 |
+
You can also use [E2B code executor](https://e2b.dev/docs#what-is-e2-b) or Docker instead of a local Python interpreter. For E2B, first [set the `E2B_API_KEY` environment variable](https://e2b.dev/dashboard?tab=keys) and then pass `executor_type="e2b"` upon agent initialization. For Docker, pass `executor_type="docker"` during initialization.
|
| 250 |
+
|
| 251 |
+
|
| 252 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 253 |
+
> Learn more about code execution [in this tutorial](tutorials/secure_code_execution).
|
| 254 |
+
|
| 255 |
+
We also support the widely-used way of writing actions as JSON-like blobs: this is [`ToolCallingAgent`], it works much in the same way like [`CodeAgent`], of course without `additional_authorized_imports` since it doesn't execute code:
|
| 256 |
+
|
| 257 |
+
```py
|
| 258 |
+
from smolagents import ToolCallingAgent
|
| 259 |
+
|
| 260 |
+
agent = ToolCallingAgent(tools=[], model=model)
|
| 261 |
+
agent.run("Could you get me the title of the page at url 'https://huggingface.co/blog'?")
|
| 262 |
+
```
|
| 263 |
+
|
| 264 |
+
### Inspecting an agent run
|
| 265 |
+
|
| 266 |
+
Here are a few useful attributes to inspect what happened after a run:
|
| 267 |
+
- `agent.logs` stores the fine-grained logs of the agent. At every step of the agent's run, everything gets stored in a dictionary that then is appended to `agent.logs`.
|
| 268 |
+
- Running `agent.write_memory_to_messages()` writes the agent's memory as list of chat messages for the Model to view. This method goes over each step of the log and only stores what it's interested in as a message: for instance, it will save the system prompt and task in separate messages, then for each step it will store the LLM output as a message, and the tool call output as another message. Use this if you want a higher-level view of what has happened - but not every log will be transcripted by this method.
|
| 269 |
+
|
| 270 |
+
## Tools
|
| 271 |
+
|
| 272 |
+
A tool is an atomic function to be used by an agent. To be used by an LLM, it also needs a few attributes that constitute its API and will be used to describe to the LLM how to call this tool:
|
| 273 |
+
- A name
|
| 274 |
+
- A description
|
| 275 |
+
- Input types and descriptions
|
| 276 |
+
- An output type
|
| 277 |
+
|
| 278 |
+
You can for instance check the [`PythonInterpreterTool`]: it has a name, a description, input descriptions, an output type, and a `forward` method to perform the action.
|
| 279 |
+
|
| 280 |
+
When the agent is initialized, the tool attributes are used to generate a tool description which is baked into the agent's system prompt. This lets the agent know which tools it can use and why.
|
| 281 |
+
|
| 282 |
+
### Default toolbox
|
| 283 |
+
|
| 284 |
+
`smolagents` comes with a default toolbox for empowering agents, that you can add to your agent upon initialization with argument `add_base_tools=True`:
|
| 285 |
+
|
| 286 |
+
- **DuckDuckGo web search***: performs a web search using DuckDuckGo browser.
|
| 287 |
+
- **Python code interpreter**: runs your LLM generated Python code in a secure environment. This tool will only be added to [`ToolCallingAgent`] if you initialize it with `add_base_tools=True`, since code-based agent can already natively execute Python code
|
| 288 |
+
- **Transcriber**: a speech-to-text pipeline built on Whisper-Turbo that transcribes an audio to text.
|
| 289 |
+
|
| 290 |
+
You can manually use a tool by calling it with its arguments.
|
| 291 |
+
|
| 292 |
+
```python
|
| 293 |
+
from smolagents import DuckDuckGoSearchTool
|
| 294 |
+
|
| 295 |
+
search_tool = DuckDuckGoSearchTool()
|
| 296 |
+
print(search_tool("Who's the current president of Russia?"))
|
| 297 |
+
```
|
| 298 |
+
|
| 299 |
+
### Create a new tool
|
| 300 |
+
|
| 301 |
+
You can create your own tool for use cases not covered by the default tools from Hugging Face.
|
| 302 |
+
For example, let's create a tool that returns the most downloaded model for a given task from the Hub.
|
| 303 |
+
|
| 304 |
+
You'll start with the code below.
|
| 305 |
+
|
| 306 |
+
```python
|
| 307 |
+
from huggingface_hub import list_models
|
| 308 |
+
|
| 309 |
+
task = "text-classification"
|
| 310 |
+
|
| 311 |
+
most_downloaded_model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
| 312 |
+
print(most_downloaded_model.id)
|
| 313 |
+
```
|
| 314 |
+
|
| 315 |
+
This code can quickly be converted into a tool, just by wrapping it in a function and adding the `tool` decorator:
|
| 316 |
+
This is not the only way to build the tool: you can directly define it as a subclass of [`Tool`], which gives you more flexibility, for instance the possibility to initialize heavy class attributes.
|
| 317 |
+
|
| 318 |
+
Let's see how it works for both options:
|
| 319 |
+
|
| 320 |
+
<hfoptions id="build-a-tool">
|
| 321 |
+
<hfoption id="Decorate a function with @tool">
|
| 322 |
+
|
| 323 |
+
```py
|
| 324 |
+
from smolagents import tool
|
| 325 |
+
|
| 326 |
+
@tool
|
| 327 |
+
def model_download_tool(task: str) -> str:
|
| 328 |
+
"""
|
| 329 |
+
This is a tool that returns the most downloaded model of a given task on the Hugging Face Hub.
|
| 330 |
+
It returns the name of the checkpoint.
|
| 331 |
+
|
| 332 |
+
Args:
|
| 333 |
+
task: The task for which to get the download count.
|
| 334 |
+
"""
|
| 335 |
+
most_downloaded_model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
| 336 |
+
return most_downloaded_model.id
|
| 337 |
+
```
|
| 338 |
+
|
| 339 |
+
The function needs:
|
| 340 |
+
- A clear name. The name should be descriptive enough of what this tool does to help the LLM brain powering the agent. Since this tool returns the model with the most downloads for a task, let's name it `model_download_tool`.
|
| 341 |
+
- Type hints on both inputs and output
|
| 342 |
+
- A description, that includes an 'Args:' part where each argument is described (without a type indication this time, it will be pulled from the type hint). Same as for the tool name, this description is an instruction manual for the LLM powering you agent, so do not neglect it.
|
| 343 |
+
|
| 344 |
+
All these elements will be automatically baked into the agent's system prompt upon initialization: so strive to make them as clear as possible!
|
| 345 |
+
|
| 346 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 347 |
+
> This definition format is the same as tool schemas used in `apply_chat_template`, the only difference is the added `tool` decorator: read more on our tool use API [here](https://huggingface.co/blog/unified-tool-use#passing-tools-to-a-chat-template).
|
| 348 |
+
</hfoption>
|
| 349 |
+
<hfoption id="Subclass Tool">
|
| 350 |
+
|
| 351 |
+
```py
|
| 352 |
+
from smolagents import Tool
|
| 353 |
+
|
| 354 |
+
class ModelDownloadTool(Tool):
|
| 355 |
+
name = "model_download_tool"
|
| 356 |
+
description = "This is a tool that returns the most downloaded model of a given task on the Hugging Face Hub. It returns the name of the checkpoint."
|
| 357 |
+
inputs = {"task": {"type": "string", "description": "The task for which to get the download count."}}
|
| 358 |
+
output_type = "string"
|
| 359 |
+
|
| 360 |
+
def forward(self, task: str) -> str:
|
| 361 |
+
most_downloaded_model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
| 362 |
+
return most_downloaded_model.id
|
| 363 |
+
```
|
| 364 |
+
|
| 365 |
+
The subclass needs the following attributes:
|
| 366 |
+
- A clear `name`. The name should be descriptive enough of what this tool does to help the LLM brain powering the agent. Since this tool returns the model with the most downloads for a task, let's name it `model_download_tool`.
|
| 367 |
+
- A `description`. Same as for the `name`, this description is an instruction manual for the LLM powering you agent, so do not neglect it.
|
| 368 |
+
- Input types and descriptions
|
| 369 |
+
- Output type
|
| 370 |
+
All these attributes will be automatically baked into the agent's system prompt upon initialization: so strive to make them as clear as possible!
|
| 371 |
+
</hfoption>
|
| 372 |
+
</hfoptions>
|
| 373 |
+
|
| 374 |
+
|
| 375 |
+
Then you can directly initialize your agent:
|
| 376 |
+
```py
|
| 377 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel
|
| 378 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[model_download_tool], model=InferenceClientModel())
|
| 379 |
+
agent.run(
|
| 380 |
+
"Can you give me the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub?"
|
| 381 |
+
)
|
| 382 |
+
```
|
| 383 |
+
|
| 384 |
+
You get the following logs:
|
| 385 |
+
```text
|
| 386 |
+
╭──────────────────────────────────────── New run ─────────────────────────────────────────╮
|
| 387 |
+
│ │
|
| 388 |
+
│ Can you give me the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' │
|
| 389 |
+
│ task on the Hugging Face Hub? │
|
| 390 |
+
│ │
|
| 391 |
+
╰─ InferenceClientModel - Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct ───────────────────────────────────────────╯
|
| 392 |
+
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ Step 0 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
|
| 393 |
+
╭─ Executing this code: ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
|
| 394 |
+
│ 1 model_name = model_download_tool(task="text-to-video") │
|
| 395 |
+
│ 2 print(model_name) │
|
| 396 |
+
╰──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
|
| 397 |
+
Execution logs:
|
| 398 |
+
ByteDance/AnimateDiff-Lightning
|
| 399 |
+
|
| 400 |
+
Out: None
|
| 401 |
+
[Step 0: Duration 0.27 seconds| Input tokens: 2,069 | Output tokens: 60]
|
| 402 |
+
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ Step 1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
|
| 403 |
+
╭─ Executing this code: ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
|
| 404 |
+
│ 1 final_answer("ByteDance/AnimateDiff-Lightning") │
|
| 405 |
+
╰──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
|
| 406 |
+
Out - Final answer: ByteDance/AnimateDiff-Lightning
|
| 407 |
+
[Step 1: Duration 0.10 seconds| Input tokens: 4,288 | Output tokens: 148]
|
| 408 |
+
Out[20]: 'ByteDance/AnimateDiff-Lightning'
|
| 409 |
+
```
|
| 410 |
+
|
| 411 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 412 |
+
> Read more on tools in the [dedicated tutorial](./tutorials/tools#what-is-a-tool-and-how-to-build-one).
|
| 413 |
+
|
| 414 |
+
## Multi-agents
|
| 415 |
+
|
| 416 |
+
Multi-agent systems have been introduced with Microsoft's framework [Autogen](https://huggingface.co/papers/2308.08155).
|
| 417 |
+
|
| 418 |
+
In this type of framework, you have several agents working together to solve your task instead of only one.
|
| 419 |
+
It empirically yields better performance on most benchmarks. The reason for this better performance is conceptually simple: for many tasks, rather than using a do-it-all system, you would prefer to specialize units on sub-tasks. Here, having agents with separate tool sets and memories allows to achieve efficient specialization. For instance, why fill the memory of the code generating agent with all the content of webpages visited by the web search agent? It's better to keep them separate.
|
| 420 |
+
|
| 421 |
+
You can easily build hierarchical multi-agent systems with `smolagents`.
|
| 422 |
+
|
| 423 |
+
To do so, just ensure your agent has `name` and`description` attributes, which will then be embedded in the manager agent's system prompt to let it know how to call this managed agent, as we also do for tools.
|
| 424 |
+
Then you can pass this managed agent in the parameter managed_agents upon initialization of the manager agent.
|
| 425 |
+
|
| 426 |
+
Here's an example of making an agent that managed a specific web search agent using our [`DuckDuckGoSearchTool`]:
|
| 427 |
+
|
| 428 |
+
```py
|
| 429 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel, DuckDuckGoSearchTool
|
| 430 |
+
|
| 431 |
+
model = InferenceClientModel()
|
| 432 |
+
|
| 433 |
+
web_agent = CodeAgent(
|
| 434 |
+
tools=[DuckDuckGoSearchTool()],
|
| 435 |
+
model=model,
|
| 436 |
+
name="web_search",
|
| 437 |
+
description="Runs web searches for you. Give it your query as an argument."
|
| 438 |
+
)
|
| 439 |
+
|
| 440 |
+
manager_agent = CodeAgent(
|
| 441 |
+
tools=[], model=model, managed_agents=[web_agent]
|
| 442 |
+
)
|
| 443 |
+
|
| 444 |
+
manager_agent.run("Who is the CEO of Hugging Face?")
|
| 445 |
+
```
|
| 446 |
+
|
| 447 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 448 |
+
> For an in-depth example of an efficient multi-agent implementation, see [how we pushed our multi-agent system to the top of the GAIA leaderboard](https://huggingface.co/blog/beating-gaia).
|
| 449 |
+
|
| 450 |
+
|
| 451 |
+
## Talk with your agent and visualize its thoughts in a cool Gradio interface
|
| 452 |
+
|
| 453 |
+
You can use `GradioUI` to interactively submit tasks to your agent and observe its thought and execution process, here is an example:
|
| 454 |
+
|
| 455 |
+
```py
|
| 456 |
+
from smolagents import (
|
| 457 |
+
load_tool,
|
| 458 |
+
CodeAgent,
|
| 459 |
+
InferenceClientModel,
|
| 460 |
+
GradioUI
|
| 461 |
+
)
|
| 462 |
+
|
| 463 |
+
# Import tool from Hub
|
| 464 |
+
image_generation_tool = load_tool("m-ric/text-to-image", trust_remote_code=True)
|
| 465 |
+
|
| 466 |
+
model = InferenceClientModel(model_id=model_id)
|
| 467 |
+
|
| 468 |
+
# Initialize the agent with the image generation tool
|
| 469 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[image_generation_tool], model=model)
|
| 470 |
+
|
| 471 |
+
GradioUI(agent).launch()
|
| 472 |
+
```
|
| 473 |
+
|
| 474 |
+
Under the hood, when the user types a new answer, the agent is launched with `agent.run(user_request, reset=False)`.
|
| 475 |
+
The `reset=False` flag means the agent's memory is not flushed before launching this new task, which lets the conversation go on.
|
| 476 |
+
|
| 477 |
+
You can also use this `reset=False` argument to keep the conversation going in any other agentic application.
|
| 478 |
+
|
| 479 |
+
In gradio UIs, if you want to allow users to interrupt a running agent, you could do this with a button that triggers method `agent.interrupt()`.
|
| 480 |
+
This will stop the agent at the end of its current step, then raise an error.
|
| 481 |
+
|
| 482 |
+
## Next steps
|
| 483 |
+
|
| 484 |
+
Finally, when you've configured your agent to your needs, you can share it to the Hub!
|
| 485 |
+
|
| 486 |
+
```py
|
| 487 |
+
agent.push_to_hub("m-ric/my_agent")
|
| 488 |
+
```
|
| 489 |
+
|
| 490 |
+
Similarly, to load an agent that has been pushed to hub, if you trust the code from its tools, use:
|
| 491 |
+
```py
|
| 492 |
+
agent.from_hub("m-ric/my_agent", trust_remote_code=True)
|
| 493 |
+
```
|
| 494 |
+
|
| 495 |
+
For more in-depth usage, you will then want to check out our tutorials:
|
| 496 |
+
- [the explanation of how our code agents work](./tutorials/secure_code_execution)
|
| 497 |
+
- [this guide on how to build good agents](./tutorials/building_good_agents).
|
| 498 |
+
- [the in-depth guide for tool usage](./tutorials/building_good_agents).
|
smolagents/docs/source/en/index.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# `smolagents`
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
| 4 |
+
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/smolagents/license_to_call.png" width=100%/>
|
| 5 |
+
</div>
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
This library is the simplest framework out there to build powerful agents! By the way, wtf are "agents"? We provide our definition [in this page](conceptual_guides/intro_agents), where you'll also find tips for when to use them or not (spoilers: you'll often be better off without agents).
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
This library offers:
|
| 10 |
+
|
| 11 |
+
✨ **Simplicity**: the logic for agents fits in ~thousand lines of code. We kept abstractions to their minimal shape above raw code!
|
| 12 |
+
|
| 13 |
+
🌐 **Support for any LLM**: it supports models hosted on the Hub loaded in their `transformers` version or through [Inference providers](https://huggingface.co/docs/inference-providers/index): Cerebras, Cohere, Fal, Fireworks, Hyperbolic, Nebius, Novita, Replicate, SambaNova, Together, etc. It also supports models from OpenAI, Anthropic... it's really easy to power an agent with any LLM.
|
| 14 |
+
|
| 15 |
+
🧑💻 **First-class support for Code Agents**, i.e. agents that write their actions in code (as opposed to "agents being used to write code"), [read more here](tutorials/secure_code_execution).
|
| 16 |
+
|
| 17 |
+
🤗 **Hub integrations**: you can share and load Gradio Spaces as tools to/from the Hub, and more is to come!
|
| 18 |
+
|
| 19 |
+
<div class="mt-10">
|
| 20 |
+
<div class="w-full flex flex-col space-y-4 md:space-y-0 md:grid md:grid-cols-2 md:gap-y-4 md:gap-x-5">
|
| 21 |
+
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="./guided_tour"
|
| 22 |
+
><div class="w-full text-center bg-gradient-to-br from-blue-400 to-blue-500 rounded-lg py-1.5 font-semibold mb-5 text-white text-lg leading-relaxed">Guided tour</div>
|
| 23 |
+
<p class="text-gray-700">Learn the basics and become familiar with using Agents. Start here if you are using Agents for the first time!</p>
|
| 24 |
+
</a>
|
| 25 |
+
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="./examples/text_to_sql"
|
| 26 |
+
><div class="w-full text-center bg-gradient-to-br from-indigo-400 to-indigo-500 rounded-lg py-1.5 font-semibold mb-5 text-white text-lg leading-relaxed">How-to guides</div>
|
| 27 |
+
<p class="text-gray-700">Practical guides to help you achieve a specific goal: create an agent to generate and test SQL queries!</p>
|
| 28 |
+
</a>
|
| 29 |
+
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="./conceptual_guides/intro_agents"
|
| 30 |
+
><div class="w-full text-center bg-gradient-to-br from-pink-400 to-pink-500 rounded-lg py-1.5 font-semibold mb-5 text-white text-lg leading-relaxed">Conceptual guides</div>
|
| 31 |
+
<p class="text-gray-700">High-level explanations for building a better understanding of important topics.</p>
|
| 32 |
+
</a>
|
| 33 |
+
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="./tutorials/building_good_agents"
|
| 34 |
+
><div class="w-full text-center bg-gradient-to-br from-purple-400 to-purple-500 rounded-lg py-1.5 font-semibold mb-5 text-white text-lg leading-relaxed">Tutorials</div>
|
| 35 |
+
<p class="text-gray-700">Horizontal tutorials that cover important aspects of building agents.</p>
|
| 36 |
+
</a>
|
| 37 |
+
</div>
|
| 38 |
+
</div>
|
smolagents/docs/source/en/reference/agents.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Agents
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
<Tip warning={true}>
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
Smolagents is an experimental API which is subject to change at any time. Results returned by the agents
|
| 6 |
+
can vary as the APIs or underlying models are prone to change.
|
| 7 |
+
|
| 8 |
+
</Tip>
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
To learn more about agents and tools make sure to read the [introductory guide](../index). This page
|
| 11 |
+
contains the API docs for the underlying classes.
|
| 12 |
+
|
| 13 |
+
## Agents
|
| 14 |
+
|
| 15 |
+
Our agents inherit from [`MultiStepAgent`], which means they can act in multiple steps, each step consisting of one thought, then one tool call and execution. Read more in [this conceptual guide](../conceptual_guides/react).
|
| 16 |
+
|
| 17 |
+
We provide two types of agents, based on the main [`Agent`] class.
|
| 18 |
+
- [`CodeAgent`] is the default agent, it writes its tool calls in Python code.
|
| 19 |
+
- [`ToolCallingAgent`] writes its tool calls in JSON.
|
| 20 |
+
|
| 21 |
+
Both require arguments `model` and list of tools `tools` at initialization.
|
| 22 |
+
|
| 23 |
+
### Classes of agents
|
| 24 |
+
|
| 25 |
+
[[autodoc]] MultiStepAgent
|
| 26 |
+
|
| 27 |
+
[[autodoc]] CodeAgent
|
| 28 |
+
|
| 29 |
+
[[autodoc]] ToolCallingAgent
|
| 30 |
+
|
| 31 |
+
### ManagedAgent
|
| 32 |
+
|
| 33 |
+
_This class is deprecated since 1.8.0: now you simply need to pass attributes `name` and `description` to a normal agent to make it callable by a manager agent._
|
| 34 |
+
|
| 35 |
+
### stream_to_gradio
|
| 36 |
+
|
| 37 |
+
[[autodoc]] stream_to_gradio
|
| 38 |
+
|
| 39 |
+
### GradioUI
|
| 40 |
+
|
| 41 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 42 |
+
> You must have `gradio` installed to use the UI. Please run `pip install smolagents[gradio]` if it's not the case.
|
| 43 |
+
|
| 44 |
+
[[autodoc]] GradioUI
|
| 45 |
+
|
| 46 |
+
## Prompts
|
| 47 |
+
|
| 48 |
+
[[autodoc]] smolagents.agents.PromptTemplates
|
| 49 |
+
|
| 50 |
+
[[autodoc]] smolagents.agents.PlanningPromptTemplate
|
| 51 |
+
|
| 52 |
+
[[autodoc]] smolagents.agents.ManagedAgentPromptTemplate
|
| 53 |
+
|
| 54 |
+
[[autodoc]] smolagents.agents.FinalAnswerPromptTemplate
|
smolagents/docs/source/en/reference/models.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,230 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Models
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
<Tip warning={true}>
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
Smolagents is an experimental API which is subject to change at any time. Results returned by the agents
|
| 6 |
+
can vary as the APIs or underlying models are prone to change.
|
| 7 |
+
|
| 8 |
+
</Tip>
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
To learn more about agents and tools make sure to read the [introductory guide](../index). This page
|
| 11 |
+
contains the API docs for the underlying classes.
|
| 12 |
+
|
| 13 |
+
## Models
|
| 14 |
+
|
| 15 |
+
### Your custom Model
|
| 16 |
+
|
| 17 |
+
You're free to create and use your own models to power your agent.
|
| 18 |
+
|
| 19 |
+
You could subclass the base `Model` class to create a model for your agent.
|
| 20 |
+
The main criteria is to subclass the `generate` method, with these two criteria:
|
| 21 |
+
1. It follows the [messages format](./chat_templating) (`List[Dict[str, str]]`) for its input `messages`, and it returns an object with a `.content` attribute.
|
| 22 |
+
2. It stops generating outputs at the sequences passed in the argument `stop_sequences`.
|
| 23 |
+
|
| 24 |
+
For defining your LLM, you can make a `CustomModel` class that inherits from the base `Model` class.
|
| 25 |
+
It should have a generate method that takes a list of [messages](./chat_templating) and returns an object with a .content attribute containing the text. The `generate` method also needs to accept a `stop_sequences` argument that indicates when to stop generating.
|
| 26 |
+
|
| 27 |
+
```python
|
| 28 |
+
from huggingface_hub import login, InferenceClient
|
| 29 |
+
|
| 30 |
+
login("<YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>")
|
| 31 |
+
|
| 32 |
+
model_id = "meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct"
|
| 33 |
+
|
| 34 |
+
client = InferenceClient(model=model_id)
|
| 35 |
+
|
| 36 |
+
class CustomModel(Model):
|
| 37 |
+
def generate(messages, stop_sequences=["Task"]):
|
| 38 |
+
response = client.chat_completion(messages, stop=stop_sequences, max_tokens=1024)
|
| 39 |
+
answer = response.choices[0].message
|
| 40 |
+
return answer
|
| 41 |
+
|
| 42 |
+
custom_model = CustomModel()
|
| 43 |
+
```
|
| 44 |
+
|
| 45 |
+
Additionally, `generate` can also take a `grammar` argument. In the case where you specify a `grammar` upon agent initialization, this argument will be passed to the calls to model, with the `grammar` that you defined upon initialization, to allow [constrained generation](https://huggingface.co/docs/text-generation-inference/conceptual/guidance) in order to force properly-formatted agent outputs.
|
| 46 |
+
|
| 47 |
+
### TransformersModel
|
| 48 |
+
|
| 49 |
+
For convenience, we have added a `TransformersModel` that implements the points above by building a local `transformers` pipeline for the model_id given at initialization.
|
| 50 |
+
|
| 51 |
+
```python
|
| 52 |
+
from smolagents import TransformersModel
|
| 53 |
+
|
| 54 |
+
model = TransformersModel(model_id="HuggingFaceTB/SmolLM-135M-Instruct")
|
| 55 |
+
|
| 56 |
+
print(model([{"role": "user", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": "Ok!"}]}], stop_sequences=["great"]))
|
| 57 |
+
```
|
| 58 |
+
```text
|
| 59 |
+
>>> What a
|
| 60 |
+
```
|
| 61 |
+
|
| 62 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 63 |
+
> You must have `transformers` and `torch` installed on your machine. Please run `pip install smolagents[transformers]` if it's not the case.
|
| 64 |
+
|
| 65 |
+
[[autodoc]] TransformersModel
|
| 66 |
+
|
| 67 |
+
### InferenceClientModel
|
| 68 |
+
|
| 69 |
+
The `HfApiModel` wraps huggingface_hub's [InferenceClient](https://huggingface.co/docs/huggingface_hub/main/en/guides/inference) for the execution of the LLM. It supports all [Inference Providers](https://huggingface.co/docs/inference-providers/index) available on the Hub: Cerebras, Cohere, Fal, Fireworks, HF-Inference, Hyperbolic, Nebius, Novita, Replicate, SambaNova, Together, and more.
|
| 70 |
+
|
| 71 |
+
```python
|
| 72 |
+
from smolagents import InferenceClientModel
|
| 73 |
+
|
| 74 |
+
messages = [
|
| 75 |
+
{"role": "user", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": "Hello, how are you?"}]}
|
| 76 |
+
]
|
| 77 |
+
|
| 78 |
+
model = InferenceClientModel(provider="novita")
|
| 79 |
+
print(model(messages))
|
| 80 |
+
```
|
| 81 |
+
```text
|
| 82 |
+
>>> Of course! If you change your mind, feel free to reach out. Take care!
|
| 83 |
+
```
|
| 84 |
+
[[autodoc]] InferenceClientModel
|
| 85 |
+
|
| 86 |
+
### LiteLLMModel
|
| 87 |
+
|
| 88 |
+
The `LiteLLMModel` leverages [LiteLLM](https://www.litellm.ai/) to support 100+ LLMs from various providers.
|
| 89 |
+
You can pass kwargs upon model initialization that will then be used whenever using the model, for instance below we pass `temperature`.
|
| 90 |
+
|
| 91 |
+
```python
|
| 92 |
+
from smolagents import LiteLLMModel
|
| 93 |
+
|
| 94 |
+
messages = [
|
| 95 |
+
{"role": "user", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": "Hello, how are you?"}]}
|
| 96 |
+
]
|
| 97 |
+
|
| 98 |
+
model = LiteLLMModel(model_id="anthropic/claude-3-5-sonnet-latest", temperature=0.2, max_tokens=10)
|
| 99 |
+
print(model(messages))
|
| 100 |
+
```
|
| 101 |
+
|
| 102 |
+
[[autodoc]] LiteLLMModel
|
| 103 |
+
|
| 104 |
+
### LiteLLMRouterModel
|
| 105 |
+
|
| 106 |
+
The `LiteLLMRouterModel` is a wrapper around the [LiteLLM Router](https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/routing) that leverages
|
| 107 |
+
advanced routing strategies: load-balancing across multiple deployments, prioritizing critical requests via queueing,
|
| 108 |
+
and implementing basic reliability measures such as cooldowns, fallbacks, and exponential backoff retries.
|
| 109 |
+
|
| 110 |
+
```python
|
| 111 |
+
from smolagents import LiteLLMRouterModel
|
| 112 |
+
|
| 113 |
+
messages = [
|
| 114 |
+
{"role": "user", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": "Hello, how are you?"}]}
|
| 115 |
+
]
|
| 116 |
+
|
| 117 |
+
model = LiteLLMRouterModel(
|
| 118 |
+
model_id="llama-3.3-70b",
|
| 119 |
+
model_list=[
|
| 120 |
+
{
|
| 121 |
+
"model_name": "llama-3.3-70b",
|
| 122 |
+
"litellm_params": {"model": "groq/llama-3.3-70b", "api_key": os.getenv("GROQ_API_KEY")},
|
| 123 |
+
},
|
| 124 |
+
{
|
| 125 |
+
"model_name": "llama-3.3-70b",
|
| 126 |
+
"litellm_params": {"model": "cerebras/llama-3.3-70b", "api_key": os.getenv("CEREBRAS_API_KEY")},
|
| 127 |
+
},
|
| 128 |
+
],
|
| 129 |
+
client_kwargs={
|
| 130 |
+
"routing_strategy": "simple-shuffle",
|
| 131 |
+
},
|
| 132 |
+
)
|
| 133 |
+
print(model(messages))
|
| 134 |
+
```
|
| 135 |
+
|
| 136 |
+
[[autodoc]] LiteLLMRouterModel
|
| 137 |
+
|
| 138 |
+
### OpenAIServerModel
|
| 139 |
+
|
| 140 |
+
This class lets you call any OpenAIServer compatible model.
|
| 141 |
+
Here's how you can set it (you can customise the `api_base` url to point to another server):
|
| 142 |
+
```py
|
| 143 |
+
import os
|
| 144 |
+
from smolagents import OpenAIServerModel
|
| 145 |
+
|
| 146 |
+
model = OpenAIServerModel(
|
| 147 |
+
model_id="gpt-4o",
|
| 148 |
+
api_base="https://api.openai.com/v1",
|
| 149 |
+
api_key=os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"],
|
| 150 |
+
)
|
| 151 |
+
```
|
| 152 |
+
|
| 153 |
+
[[autodoc]] OpenAIServerModel
|
| 154 |
+
|
| 155 |
+
### AzureOpenAIServerModel
|
| 156 |
+
|
| 157 |
+
`AzureOpenAIServerModel` allows you to connect to any Azure OpenAI deployment.
|
| 158 |
+
|
| 159 |
+
Below you can find an example of how to set it up, note that you can omit the `azure_endpoint`, `api_key`, and `api_version` arguments, provided you've set the corresponding environment variables -- `AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT`, `AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY`, and `OPENAI_API_VERSION`.
|
| 160 |
+
|
| 161 |
+
Pay attention to the lack of an `AZURE_` prefix for `OPENAI_API_VERSION`, this is due to the way the underlying [openai](https://github.com/openai/openai-python) package is designed.
|
| 162 |
+
|
| 163 |
+
```py
|
| 164 |
+
import os
|
| 165 |
+
|
| 166 |
+
from smolagents import AzureOpenAIServerModel
|
| 167 |
+
|
| 168 |
+
model = AzureOpenAIServerModel(
|
| 169 |
+
model_id = os.environ.get("AZURE_OPENAI_MODEL"),
|
| 170 |
+
azure_endpoint=os.environ.get("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT"),
|
| 171 |
+
api_key=os.environ.get("AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY"),
|
| 172 |
+
api_version=os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_VERSION")
|
| 173 |
+
)
|
| 174 |
+
```
|
| 175 |
+
|
| 176 |
+
[[autodoc]] AzureOpenAIServerModel
|
| 177 |
+
|
| 178 |
+
### AmazonBedrockServerModel
|
| 179 |
+
|
| 180 |
+
`AmazonBedrockServerModel` helps you connect to Amazon Bedrock and run your agent with any available models.
|
| 181 |
+
|
| 182 |
+
Below is an example setup. This class also offers additional options for customization.
|
| 183 |
+
|
| 184 |
+
```py
|
| 185 |
+
import os
|
| 186 |
+
|
| 187 |
+
from smolagents import AmazonBedrockServerModel
|
| 188 |
+
|
| 189 |
+
model = AmazonBedrockServerModel(
|
| 190 |
+
model_id = os.environ.get("AMAZON_BEDROCK_MODEL_ID"),
|
| 191 |
+
)
|
| 192 |
+
```
|
| 193 |
+
|
| 194 |
+
[[autodoc]] AmazonBedrockServerModel
|
| 195 |
+
|
| 196 |
+
### MLXModel
|
| 197 |
+
|
| 198 |
+
|
| 199 |
+
```python
|
| 200 |
+
from smolagents import MLXModel
|
| 201 |
+
|
| 202 |
+
model = MLXModel(model_id="HuggingFaceTB/SmolLM-135M-Instruct")
|
| 203 |
+
|
| 204 |
+
print(model([{"role": "user", "content": "Ok!"}], stop_sequences=["great"]))
|
| 205 |
+
```
|
| 206 |
+
```text
|
| 207 |
+
>>> What a
|
| 208 |
+
```
|
| 209 |
+
|
| 210 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 211 |
+
> You must have `mlx-lm` installed on your machine. Please run `pip install smolagents[mlx-lm]` if it's not the case.
|
| 212 |
+
|
| 213 |
+
[[autodoc]] MLXModel
|
| 214 |
+
|
| 215 |
+
### VLLMModel
|
| 216 |
+
|
| 217 |
+
Model to use [vLLM](https://docs.vllm.ai/) for fast LLM inference and serving.
|
| 218 |
+
|
| 219 |
+
```python
|
| 220 |
+
from smolagents import VLLMModel
|
| 221 |
+
|
| 222 |
+
model = VLLMModel(model_id="HuggingFaceTB/SmolLM-135M-Instruct")
|
| 223 |
+
|
| 224 |
+
print(model([{"role": "user", "content": "Ok!"}], stop_sequences=["great"]))
|
| 225 |
+
```
|
| 226 |
+
|
| 227 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 228 |
+
> You must have `vllm` installed on your machine. Please run `pip install smolagents[vllm]` if it's not the case.
|
| 229 |
+
|
| 230 |
+
[[autodoc]] VLLMModel
|
smolagents/docs/source/en/reference/tools.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Tools
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
<Tip warning={true}>
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
Smolagents is an experimental API which is subject to change at any time. Results returned by the agents
|
| 6 |
+
can vary as the APIs or underlying models are prone to change.
|
| 7 |
+
|
| 8 |
+
</Tip>
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
To learn more about agents and tools make sure to read the [introductory guide](../index). This page
|
| 11 |
+
contains the API docs for the underlying classes.
|
| 12 |
+
|
| 13 |
+
## Tools
|
| 14 |
+
|
| 15 |
+
### load_tool
|
| 16 |
+
|
| 17 |
+
[[autodoc]] load_tool
|
| 18 |
+
|
| 19 |
+
### tool
|
| 20 |
+
|
| 21 |
+
[[autodoc]] tool
|
| 22 |
+
|
| 23 |
+
### Tool
|
| 24 |
+
|
| 25 |
+
[[autodoc]] Tool
|
| 26 |
+
|
| 27 |
+
### launch_gradio_demo
|
| 28 |
+
|
| 29 |
+
[[autodoc]] launch_gradio_demo
|
| 30 |
+
|
| 31 |
+
## Default tools
|
| 32 |
+
|
| 33 |
+
### PythonInterpreterTool
|
| 34 |
+
|
| 35 |
+
[[autodoc]] PythonInterpreterTool
|
| 36 |
+
|
| 37 |
+
### FinalAnswerTool
|
| 38 |
+
|
| 39 |
+
[[autodoc]] FinalAnswerTool
|
| 40 |
+
|
| 41 |
+
### UserInputTool
|
| 42 |
+
|
| 43 |
+
[[autodoc]] UserInputTool
|
| 44 |
+
|
| 45 |
+
### DuckDuckGoSearchTool
|
| 46 |
+
|
| 47 |
+
[[autodoc]] DuckDuckGoSearchTool
|
| 48 |
+
|
| 49 |
+
### GoogleSearchTool
|
| 50 |
+
|
| 51 |
+
[[autodoc]] GoogleSearchTool
|
| 52 |
+
|
| 53 |
+
### VisitWebpageTool
|
| 54 |
+
|
| 55 |
+
[[autodoc]] VisitWebpageTool
|
| 56 |
+
|
| 57 |
+
### SpeechToTextTool
|
| 58 |
+
|
| 59 |
+
[[autodoc]] SpeechToTextTool
|
| 60 |
+
|
| 61 |
+
## ToolCollection
|
| 62 |
+
|
| 63 |
+
[[autodoc]] ToolCollection
|
| 64 |
+
|
| 65 |
+
## MCP Client
|
| 66 |
+
|
| 67 |
+
[[autodoc]] smolagents.mcp_client.MCPClient
|
| 68 |
+
|
| 69 |
+
## Agent Types
|
| 70 |
+
|
| 71 |
+
Agents can handle any type of object in-between tools; tools, being completely multimodal, can accept and return
|
| 72 |
+
text, image, audio, video, among other types. In order to increase compatibility between tools, as well as to
|
| 73 |
+
correctly render these returns in ipython (jupyter, colab, ipython notebooks, ...), we implement wrapper classes
|
| 74 |
+
around these types.
|
| 75 |
+
|
| 76 |
+
The wrapped objects should continue behaving as initially; a text object should still behave as a string, an image
|
| 77 |
+
object should still behave as a `PIL.Image`.
|
| 78 |
+
|
| 79 |
+
These types have three specific purposes:
|
| 80 |
+
|
| 81 |
+
- Calling `to_raw` on the type should return the underlying object
|
| 82 |
+
- Calling `to_string` on the type should return the object as a string: that can be the string in case of an `AgentText`
|
| 83 |
+
but will be the path of the serialized version of the object in other instances
|
| 84 |
+
- Displaying it in an ipython kernel should display the object correctly
|
| 85 |
+
|
| 86 |
+
### AgentText
|
| 87 |
+
|
| 88 |
+
[[autodoc]] smolagents.agent_types.AgentText
|
| 89 |
+
|
| 90 |
+
### AgentImage
|
| 91 |
+
|
| 92 |
+
[[autodoc]] smolagents.agent_types.AgentImage
|
| 93 |
+
|
| 94 |
+
### AgentAudio
|
| 95 |
+
|
| 96 |
+
[[autodoc]] smolagents.agent_types.AgentAudio
|
smolagents/docs/source/en/tutorials/building_good_agents.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,420 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Building good agents
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
[[open-in-colab]]
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
There's a world of difference between building an agent that works and one that doesn't.
|
| 6 |
+
How can we build agents that fall into the former category?
|
| 7 |
+
In this guide, we're going to talk about best practices for building agents.
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 10 |
+
> If you're new to building agents, make sure to first read the [intro to agents](../conceptual_guides/intro_agents) and the [guided tour of smolagents](../guided_tour).
|
| 11 |
+
|
| 12 |
+
### The best agentic systems are the simplest: simplify the workflow as much as you can
|
| 13 |
+
|
| 14 |
+
Giving an LLM some agency in your workflow introduces some risk of errors.
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
Well-programmed agentic systems have good error logging and retry mechanisms anyway, so the LLM engine has a chance to self-correct their mistake. But to reduce the risk of LLM error to the maximum, you should simplify your workflow!
|
| 17 |
+
|
| 18 |
+
Let's revisit the example from the [intro to agents](../conceptual_guides/intro_agents): a bot that answers user queries for a surf trip company.
|
| 19 |
+
Instead of letting the agent do 2 different calls for "travel distance API" and "weather API" each time they are asked about a new surf spot, you could just make one unified tool "return_spot_information", a function that calls both APIs at once and returns their concatenated outputs to the user.
|
| 20 |
+
|
| 21 |
+
This will reduce costs, latency, and error risk!
|
| 22 |
+
|
| 23 |
+
The main guideline is: Reduce the number of LLM calls as much as you can.
|
| 24 |
+
|
| 25 |
+
This leads to a few takeaways:
|
| 26 |
+
- Whenever possible, group 2 tools in one, like in our example of the two APIs.
|
| 27 |
+
- Whenever possible, logic should be based on deterministic functions rather than agentic decisions.
|
| 28 |
+
|
| 29 |
+
### Improve the information flow to the LLM engine
|
| 30 |
+
|
| 31 |
+
Remember that your LLM engine is like an *intelligent* robot, trapped into a room with the only communication with the outside world being notes passed under a door.
|
| 32 |
+
|
| 33 |
+
It won't know of anything that happened if you don't explicitly put that into its prompt.
|
| 34 |
+
|
| 35 |
+
So first start with making your task very clear!
|
| 36 |
+
Since an agent is powered by an LLM, minor variations in your task formulation might yield completely different results.
|
| 37 |
+
|
| 38 |
+
Then, improve the information flow towards your agent in tool use.
|
| 39 |
+
|
| 40 |
+
Particular guidelines to follow:
|
| 41 |
+
- Each tool should log (by simply using `print` statements inside the tool's `forward` method) everything that could be useful for the LLM engine.
|
| 42 |
+
- In particular, logging detail on tool execution errors would help a lot!
|
| 43 |
+
|
| 44 |
+
For instance, here's a tool that retrieves weather data based on location and date-time:
|
| 45 |
+
|
| 46 |
+
First, here's a poor version:
|
| 47 |
+
```python
|
| 48 |
+
import datetime
|
| 49 |
+
from smolagents import tool
|
| 50 |
+
|
| 51 |
+
def get_weather_report_at_coordinates(coordinates, date_time):
|
| 52 |
+
# Dummy function, returns a list of [temperature in °C, risk of rain on a scale 0-1, wave height in m]
|
| 53 |
+
return [28.0, 0.35, 0.85]
|
| 54 |
+
|
| 55 |
+
def convert_location_to_coordinates(location):
|
| 56 |
+
# Returns dummy coordinates
|
| 57 |
+
return [3.3, -42.0]
|
| 58 |
+
|
| 59 |
+
@tool
|
| 60 |
+
def get_weather_api(location: str, date_time: str) -> str:
|
| 61 |
+
"""
|
| 62 |
+
Returns the weather report.
|
| 63 |
+
|
| 64 |
+
Args:
|
| 65 |
+
location: the name of the place that you want the weather for.
|
| 66 |
+
date_time: the date and time for which you want the report.
|
| 67 |
+
"""
|
| 68 |
+
lon, lat = convert_location_to_coordinates(location)
|
| 69 |
+
date_time = datetime.strptime(date_time)
|
| 70 |
+
return str(get_weather_report_at_coordinates((lon, lat), date_time))
|
| 71 |
+
```
|
| 72 |
+
|
| 73 |
+
Why is it bad?
|
| 74 |
+
- there's no precision of the format that should be used for `date_time`
|
| 75 |
+
- there's no detail on how location should be specified.
|
| 76 |
+
- there's no logging mechanism trying to make explicit failure cases like location not being in a proper format, or date_time not being properly formatted.
|
| 77 |
+
- the output format is hard to understand
|
| 78 |
+
|
| 79 |
+
If the tool call fails, the error trace logged in memory can help the LLM reverse engineer the tool to fix the errors. But why leave it with so much heavy lifting to do?
|
| 80 |
+
|
| 81 |
+
A better way to build this tool would have been the following:
|
| 82 |
+
```python
|
| 83 |
+
@tool
|
| 84 |
+
def get_weather_api(location: str, date_time: str) -> str:
|
| 85 |
+
"""
|
| 86 |
+
Returns the weather report.
|
| 87 |
+
|
| 88 |
+
Args:
|
| 89 |
+
location: the name of the place that you want the weather for. Should be a place name, followed by possibly a city name, then a country, like "Anchor Point, Taghazout, Morocco".
|
| 90 |
+
date_time: the date and time for which you want the report, formatted as '%m/%d/%y %H:%M:%S'.
|
| 91 |
+
"""
|
| 92 |
+
lon, lat = convert_location_to_coordinates(location)
|
| 93 |
+
try:
|
| 94 |
+
date_time = datetime.strptime(date_time)
|
| 95 |
+
except Exception as e:
|
| 96 |
+
raise ValueError("Conversion of `date_time` to datetime format failed, make sure to provide a string in format '%m/%d/%y %H:%M:%S'. Full trace:" + str(e))
|
| 97 |
+
temperature_celsius, risk_of_rain, wave_height = get_weather_report_at_coordinates((lon, lat), date_time)
|
| 98 |
+
return f"Weather report for {location}, {date_time}: Temperature will be {temperature_celsius}°C, risk of rain is {risk_of_rain*100:.0f}%, wave height is {wave_height}m."
|
| 99 |
+
```
|
| 100 |
+
|
| 101 |
+
In general, to ease the load on your LLM, the good question to ask yourself is: "How easy would it be for me, if I was dumb and using this tool for the first time ever, to program with this tool and correct my own errors?".
|
| 102 |
+
|
| 103 |
+
### Give more arguments to the agent
|
| 104 |
+
|
| 105 |
+
To pass some additional objects to your agent beyond the simple string describing the task, you can use the `additional_args` argument to pass any type of object:
|
| 106 |
+
|
| 107 |
+
```py
|
| 108 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel
|
| 109 |
+
|
| 110 |
+
model_id = "meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct"
|
| 111 |
+
|
| 112 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=InferenceClientModel(model_id=model_id), add_base_tools=True)
|
| 113 |
+
|
| 114 |
+
agent.run(
|
| 115 |
+
"Why does Mike not know many people in New York?",
|
| 116 |
+
additional_args={"mp3_sound_file_url":'https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/recording.mp3'}
|
| 117 |
+
)
|
| 118 |
+
```
|
| 119 |
+
For instance, you can use this `additional_args` argument to pass images or strings that you want your agent to leverage.
|
| 120 |
+
|
| 121 |
+
|
| 122 |
+
|
| 123 |
+
## How to debug your agent
|
| 124 |
+
|
| 125 |
+
### 1. Use a stronger LLM
|
| 126 |
+
|
| 127 |
+
In an agentic workflows, some of the errors are actual errors, some other are the fault of your LLM engine not reasoning properly.
|
| 128 |
+
For instance, consider this trace for an `CodeAgent` that I asked to create a car picture:
|
| 129 |
+
```
|
| 130 |
+
==================================================================================================== New task ====================================================================================================
|
| 131 |
+
Make me a cool car picture
|
| 132 |
+
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── New step ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
|
| 133 |
+
Agent is executing the code below: ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
|
| 134 |
+
image_generator(prompt="A cool, futuristic sports car with LED headlights, aerodynamic design, and vibrant color, high-res, photorealistic")
|
| 135 |
+
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
|
| 136 |
+
|
| 137 |
+
Last output from code snippet: ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
|
| 138 |
+
/var/folders/6m/9b1tts6d5w960j80wbw9tx3m0000gn/T/tmpx09qfsdd/652f0007-3ee9-44e2-94ac-90dae6bb89a4.png
|
| 139 |
+
Step 1:
|
| 140 |
+
|
| 141 |
+
- Time taken: 16.35 seconds
|
| 142 |
+
- Input tokens: 1,383
|
| 143 |
+
- Output tokens: 77
|
| 144 |
+
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── New step ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
|
| 145 |
+
Agent is executing the code below: ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
|
| 146 |
+
final_answer("/var/folders/6m/9b1tts6d5w960j80wbw9tx3m0000gn/T/tmpx09qfsdd/652f0007-3ee9-44e2-94ac-90dae6bb89a4.png")
|
| 147 |
+
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
|
| 148 |
+
Print outputs:
|
| 149 |
+
|
| 150 |
+
Last output from code snippet: ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
|
| 151 |
+
/var/folders/6m/9b1tts6d5w960j80wbw9tx3m0000gn/T/tmpx09qfsdd/652f0007-3ee9-44e2-94ac-90dae6bb89a4.png
|
| 152 |
+
Final answer:
|
| 153 |
+
/var/folders/6m/9b1tts6d5w960j80wbw9tx3m0000gn/T/tmpx09qfsdd/652f0007-3ee9-44e2-94ac-90dae6bb89a4.png
|
| 154 |
+
```
|
| 155 |
+
The user sees, instead of an image being returned, a path being returned to them.
|
| 156 |
+
It could look like a bug from the system, but actually the agentic system didn't cause the error: it's just that the LLM brain did the mistake of not saving the image output into a variable.
|
| 157 |
+
Thus it cannot access the image again except by leveraging the path that was logged while saving the image, so it returns the path instead of an image.
|
| 158 |
+
|
| 159 |
+
The first step to debugging your agent is thus "Use a more powerful LLM". Alternatives like `Qwen2/5-72B-Instruct` wouldn't have made that mistake.
|
| 160 |
+
|
| 161 |
+
### 2. Provide more guidance / more information
|
| 162 |
+
|
| 163 |
+
You can also use less powerful models, provided you guide them more effectively.
|
| 164 |
+
|
| 165 |
+
Put yourself in the shoes of your model: if you were the model solving the task, would you struggle with the information available to you (from the system prompt + task formulation + tool description) ?
|
| 166 |
+
|
| 167 |
+
Would you need some added clarifications?
|
| 168 |
+
|
| 169 |
+
To provide extra information, we do not recommend to change the system prompt right away: the default system prompt has many adjustments that you do not want to mess up except if you understand the prompt very well.
|
| 170 |
+
Better ways to guide your LLM engine are:
|
| 171 |
+
- If it's about the task to solve: add all these details to the task. The task could be 100s of pages long.
|
| 172 |
+
- If it's about how to use tools: the description attribute of your tools.
|
| 173 |
+
|
| 174 |
+
|
| 175 |
+
### 3. Change the system prompt (generally not advised)
|
| 176 |
+
|
| 177 |
+
If above clarifications are not sufficient, you can change the system prompt.
|
| 178 |
+
|
| 179 |
+
Let's see how it works. For example, let us check the default system prompt for the [`CodeAgent`] (below version is shortened by skipping zero-shot examples).
|
| 180 |
+
|
| 181 |
+
```python
|
| 182 |
+
print(agent.prompt_templates["system_prompt"])
|
| 183 |
+
```
|
| 184 |
+
Here is what you get:
|
| 185 |
+
```text
|
| 186 |
+
You are an expert assistant who can solve any task using code blobs. You will be given a task to solve as best you can.
|
| 187 |
+
To do so, you have been given access to a list of tools: these tools are basically Python functions which you can call with code.
|
| 188 |
+
To solve the task, you must plan forward to proceed in a series of steps, in a cycle of 'Thought:', 'Code:', and 'Observation:' sequences.
|
| 189 |
+
|
| 190 |
+
At each step, in the 'Thought:' sequence, you should first explain your reasoning towards solving the task and the tools that you want to use.
|
| 191 |
+
Then in the 'Code:' sequence, you should write the code in simple Python. The code sequence must end with '<end_code>' sequence.
|
| 192 |
+
During each intermediate step, you can use 'print()' to save whatever important information you will then need.
|
| 193 |
+
These print outputs will then appear in the 'Observation:' field, which will be available as input for the next step.
|
| 194 |
+
In the end you have to return a final answer using the `final_answer` tool.
|
| 195 |
+
|
| 196 |
+
Here are a few examples using notional tools:
|
| 197 |
+
---
|
| 198 |
+
Task: "Generate an image of the oldest person in this document."
|
| 199 |
+
|
| 200 |
+
Thought: I will proceed step by step and use the following tools: `document_qa` to find the oldest person in the document, then `image_generator` to generate an image according to the answer.
|
| 201 |
+
Code:
|
| 202 |
+
```py
|
| 203 |
+
answer = document_qa(document=document, question="Who is the oldest person mentioned?")
|
| 204 |
+
print(answer)
|
| 205 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 206 |
+
Observation: "The oldest person in the document is John Doe, a 55 year old lumberjack living in Newfoundland."
|
| 207 |
+
|
| 208 |
+
Thought: I will now generate an image showcasing the oldest person.
|
| 209 |
+
Code:
|
| 210 |
+
```py
|
| 211 |
+
image = image_generator("A portrait of John Doe, a 55-year-old man living in Canada.")
|
| 212 |
+
final_answer(image)
|
| 213 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 214 |
+
|
| 215 |
+
---
|
| 216 |
+
Task: "What is the result of the following operation: 5 + 3 + 1294.678?"
|
| 217 |
+
|
| 218 |
+
Thought: I will use python code to compute the result of the operation and then return the final answer using the `final_answer` tool
|
| 219 |
+
Code:
|
| 220 |
+
```py
|
| 221 |
+
result = 5 + 3 + 1294.678
|
| 222 |
+
final_answer(result)
|
| 223 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 224 |
+
|
| 225 |
+
---
|
| 226 |
+
Task:
|
| 227 |
+
"Answer the question in the variable `question` about the image stored in the variable `image`. The question is in French.
|
| 228 |
+
You have been provided with these additional arguments, that you can access using the keys as variables in your python code:
|
| 229 |
+
{'question': 'Quel est l'animal sur l'image?', 'image': 'path/to/image.jpg'}"
|
| 230 |
+
|
| 231 |
+
Thought: I will use the following tools: `translator` to translate the question into English and then `image_qa` to answer the question on the input image.
|
| 232 |
+
Code:
|
| 233 |
+
```py
|
| 234 |
+
translated_question = translator(question=question, src_lang="French", tgt_lang="English")
|
| 235 |
+
print(f"The translated question is {translated_question}.")
|
| 236 |
+
answer = image_qa(image=image, question=translated_question)
|
| 237 |
+
final_answer(f"The answer is {answer}")
|
| 238 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 239 |
+
|
| 240 |
+
---
|
| 241 |
+
Task:
|
| 242 |
+
In a 1979 interview, Stanislaus Ulam discusses with Martin Sherwin about other great physicists of his time, including Oppenheimer.
|
| 243 |
+
What does he say was the consequence of Einstein learning too much math on his creativity, in one word?
|
| 244 |
+
|
| 245 |
+
Thought: I need to find and read the 1979 interview of Stanislaus Ulam with Martin Sherwin.
|
| 246 |
+
Code:
|
| 247 |
+
```py
|
| 248 |
+
pages = search(query="1979 interview Stanislaus Ulam Martin Sherwin physicists Einstein")
|
| 249 |
+
print(pages)
|
| 250 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 251 |
+
Observation:
|
| 252 |
+
No result found for query "1979 interview Stanislaus Ulam Martin Sherwin physicists Einstein".
|
| 253 |
+
|
| 254 |
+
Thought: The query was maybe too restrictive and did not find any results. Let's try again with a broader query.
|
| 255 |
+
Code:
|
| 256 |
+
```py
|
| 257 |
+
pages = search(query="1979 interview Stanislaus Ulam")
|
| 258 |
+
print(pages)
|
| 259 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 260 |
+
Observation:
|
| 261 |
+
Found 6 pages:
|
| 262 |
+
[Stanislaus Ulam 1979 interview](https://ahf.nuclearmuseum.org/voices/oral-histories/stanislaus-ulams-interview-1979/)
|
| 263 |
+
|
| 264 |
+
[Ulam discusses Manhattan Project](https://ahf.nuclearmuseum.org/manhattan-project/ulam-manhattan-project/)
|
| 265 |
+
|
| 266 |
+
(truncated)
|
| 267 |
+
|
| 268 |
+
Thought: I will read the first 2 pages to know more.
|
| 269 |
+
Code:
|
| 270 |
+
```py
|
| 271 |
+
for url in ["https://ahf.nuclearmuseum.org/voices/oral-histories/stanislaus-ulams-interview-1979/", "https://ahf.nuclearmuseum.org/manhattan-project/ulam-manhattan-project/"]:
|
| 272 |
+
whole_page = visit_webpage(url)
|
| 273 |
+
print(whole_page)
|
| 274 |
+
print("\n" + "="*80 + "\n") # Print separator between pages
|
| 275 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 276 |
+
Observation:
|
| 277 |
+
Manhattan Project Locations:
|
| 278 |
+
Los Alamos, NM
|
| 279 |
+
Stanislaus Ulam was a Polish-American mathematician. He worked on the Manhattan Project at Los Alamos and later helped design the hydrogen bomb. In this interview, he discusses his work at
|
| 280 |
+
(truncated)
|
| 281 |
+
|
| 282 |
+
Thought: I now have the final answer: from the webpages visited, Stanislaus Ulam says of Einstein: "He learned too much mathematics and sort of diminished, it seems to me personally, it seems to me his purely physics creativity." Let's answer in one word.
|
| 283 |
+
Code:
|
| 284 |
+
```py
|
| 285 |
+
final_answer("diminished")
|
| 286 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 287 |
+
|
| 288 |
+
---
|
| 289 |
+
Task: "Which city has the highest population: Guangzhou or Shanghai?"
|
| 290 |
+
|
| 291 |
+
Thought: I need to get the populations for both cities and compare them: I will use the tool `search` to get the population of both cities.
|
| 292 |
+
Code:
|
| 293 |
+
```py
|
| 294 |
+
for city in ["Guangzhou", "Shanghai"]:
|
| 295 |
+
print(f"Population {city}:", search(f"{city} population")
|
| 296 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 297 |
+
Observation:
|
| 298 |
+
Population Guangzhou: ['Guangzhou has a population of 15 million inhabitants as of 2021.']
|
| 299 |
+
Population Shanghai: '26 million (2019)'
|
| 300 |
+
|
| 301 |
+
Thought: Now I know that Shanghai has the highest population.
|
| 302 |
+
Code:
|
| 303 |
+
```py
|
| 304 |
+
final_answer("Shanghai")
|
| 305 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 306 |
+
|
| 307 |
+
---
|
| 308 |
+
Task: "What is the current age of the pope, raised to the power 0.36?"
|
| 309 |
+
|
| 310 |
+
Thought: I will use the tool `wiki` to get the age of the pope, and confirm that with a web search.
|
| 311 |
+
Code:
|
| 312 |
+
```py
|
| 313 |
+
pope_age_wiki = wiki(query="current pope age")
|
| 314 |
+
print("Pope age as per wikipedia:", pope_age_wiki)
|
| 315 |
+
pope_age_search = web_search(query="current pope age")
|
| 316 |
+
print("Pope age as per google search:", pope_age_search)
|
| 317 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 318 |
+
Observation:
|
| 319 |
+
Pope age: "The pope Francis is currently 88 years old."
|
| 320 |
+
|
| 321 |
+
Thought: I know that the pope is 88 years old. Let's compute the result using python code.
|
| 322 |
+
Code:
|
| 323 |
+
```py
|
| 324 |
+
pope_current_age = 88 ** 0.36
|
| 325 |
+
final_answer(pope_current_age)
|
| 326 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 327 |
+
|
| 328 |
+
Above example were using notional tools that might not exist for you. On top of performing computations in the Python code snippets that you create, you only have access to these tools:
|
| 329 |
+
{%- for tool in tools.values() %}
|
| 330 |
+
- {{ tool.name }}: {{ tool.description }}
|
| 331 |
+
Takes inputs: {{tool.inputs}}
|
| 332 |
+
Returns an output of type: {{tool.output_type}}
|
| 333 |
+
{%- endfor %}
|
| 334 |
+
|
| 335 |
+
{%- if managed_agents and managed_agents.values() | list %}
|
| 336 |
+
You can also give tasks to team members.
|
| 337 |
+
Calling a team member works the same as for calling a tool: simply, the only argument you can give in the call is 'task', a long string explaining your task.
|
| 338 |
+
Given that this team member is a real human, you should be very verbose in your task.
|
| 339 |
+
Here is a list of the team members that you can call:
|
| 340 |
+
{%- for agent in managed_agents.values() %}
|
| 341 |
+
- {{ agent.name }}: {{ agent.description }}
|
| 342 |
+
{%- endfor %}
|
| 343 |
+
{%- else %}
|
| 344 |
+
{%- endif %}
|
| 345 |
+
|
| 346 |
+
Here are the rules you should always follow to solve your task:
|
| 347 |
+
1. Always provide a 'Thought:' sequence, and a 'Code:\n```py' sequence ending with '```<end_code>' sequence, else you will fail.
|
| 348 |
+
2. Use only variables that you have defined!
|
| 349 |
+
3. Always use the right arguments for the tools. DO NOT pass the arguments as a dict as in 'answer = wiki({'query': "What is the place where James Bond lives?"})', but use the arguments directly as in 'answer = wiki(query="What is the place where James Bond lives?")'.
|
| 350 |
+
4. Take care to not chain too many sequential tool calls in the same code block, especially when the output format is unpredictable. For instance, a call to search has an unpredictable return format, so do not have another tool call that depends on its output in the same block: rather output results with print() to use them in the next block.
|
| 351 |
+
5. Call a tool only when needed, and never re-do a tool call that you previously did with the exact same parameters.
|
| 352 |
+
6. Don't name any new variable with the same name as a tool: for instance don't name a variable 'final_answer'.
|
| 353 |
+
7. Never create any notional variables in our code, as having these in your logs will derail you from the true variables.
|
| 354 |
+
8. You can use imports in your code, but only from the following list of modules: {{authorized_imports}}
|
| 355 |
+
9. The state persists between code executions: so if in one step you've created variables or imported modules, these will all persist.
|
| 356 |
+
10. Don't give up! You're in charge of solving the task, not providing directions to solve it.
|
| 357 |
+
|
| 358 |
+
Now Begin! If you solve the task correctly, you will receive a reward of $1,000,000.
|
| 359 |
+
```
|
| 360 |
+
|
| 361 |
+
As you can see, there are placeholders like `"{{ tool.description }}"`: these will be used upon agent initialization to insert certain automatically generated descriptions of tools or managed agents.
|
| 362 |
+
|
| 363 |
+
So while you can overwrite this system prompt template by passing your custom prompt as an argument to the `system_prompt` parameter, your new system prompt can contain the following placeholders:
|
| 364 |
+
- To insert tool descriptions:
|
| 365 |
+
```
|
| 366 |
+
{%- for tool in tools.values() %}
|
| 367 |
+
- {{ tool.name }}: {{ tool.description }}
|
| 368 |
+
Takes inputs: {{tool.inputs}}
|
| 369 |
+
Returns an output of type: {{tool.output_type}}
|
| 370 |
+
{%- endfor %}
|
| 371 |
+
```
|
| 372 |
+
- To insert the descriptions for managed agents if there are any:
|
| 373 |
+
```
|
| 374 |
+
{%- if managed_agents and managed_agents.values() | list %}
|
| 375 |
+
You can also give tasks to team members.
|
| 376 |
+
Calling a team member works the same as for calling a tool: simply, the only argument you can give in the call is 'task', a long string explaining your task.
|
| 377 |
+
Given that this team member is a real human, you should be very verbose in your task.
|
| 378 |
+
Here is a list of the team members that you can call:
|
| 379 |
+
{%- for agent in managed_agents.values() %}
|
| 380 |
+
- {{ agent.name }}: {{ agent.description }}
|
| 381 |
+
{%- endfor %}
|
| 382 |
+
{%- endif %}
|
| 383 |
+
```
|
| 384 |
+
- For `CodeAgent` only, to insert the list of authorized imports: `"{{authorized_imports}}"`
|
| 385 |
+
|
| 386 |
+
Then you can change the system prompt as follows:
|
| 387 |
+
|
| 388 |
+
```py
|
| 389 |
+
agent.prompt_templates["system_prompt"] = agent.prompt_templates["system_prompt"] + "\nHere you go!"
|
| 390 |
+
```
|
| 391 |
+
|
| 392 |
+
This also works with the [`ToolCallingAgent`].
|
| 393 |
+
|
| 394 |
+
|
| 395 |
+
### 4. Extra planning
|
| 396 |
+
|
| 397 |
+
We provide a model for a supplementary planning step, that an agent can run regularly in-between normal action steps. In this step, there is no tool call, the LLM is simply asked to update a list of facts it knows and to reflect on what steps it should take next based on those facts.
|
| 398 |
+
|
| 399 |
+
```py
|
| 400 |
+
from smolagents import load_tool, CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel, DuckDuckGoSearchTool
|
| 401 |
+
from dotenv import load_dotenv
|
| 402 |
+
|
| 403 |
+
load_dotenv()
|
| 404 |
+
|
| 405 |
+
# Import tool from Hub
|
| 406 |
+
image_generation_tool = load_tool("m-ric/text-to-image", trust_remote_code=True)
|
| 407 |
+
|
| 408 |
+
search_tool = DuckDuckGoSearchTool()
|
| 409 |
+
|
| 410 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(
|
| 411 |
+
tools=[search_tool, image_generation_tool],
|
| 412 |
+
model=InferenceClientModel(model_id="Qwen/Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct"),
|
| 413 |
+
planning_interval=3 # This is where you activate planning!
|
| 414 |
+
)
|
| 415 |
+
|
| 416 |
+
# Run it!
|
| 417 |
+
result = agent.run(
|
| 418 |
+
"How long would a cheetah at full speed take to run the length of Pont Alexandre III?",
|
| 419 |
+
)
|
| 420 |
+
```
|
smolagents/docs/source/en/tutorials/inspect_runs.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,178 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Inspecting runs with OpenTelemetry
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
[[open-in-colab]]
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 6 |
+
> If you're new to building agents, make sure to first read the [intro to agents](../conceptual_guides/intro_agents) and the [guided tour of smolagents](../guided_tour).
|
| 7 |
+
|
| 8 |
+
## Why log your agent runs?
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
Agent runs are complicated to debug.
|
| 11 |
+
|
| 12 |
+
Validating that a run went properly is hard, since agent workflows are [unpredictable by design](../conceptual_guides/intro_agents) (if they were predictable, you'd just be using good old code).
|
| 13 |
+
|
| 14 |
+
And inspecting a run is hard as well: multi-step agents tend to quickly fill a console with logs, and most of the errors are just "LLM dumb" kind of errors, from which the LLM auto-corrects in the next step by writing better code or tool calls.
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
So using instrumentation to record agent runs is necessary in production for later inspection and monitoring!
|
| 17 |
+
|
| 18 |
+
We've adopted the [OpenTelemetry](https://opentelemetry.io/) standard for instrumenting agent runs.
|
| 19 |
+
|
| 20 |
+
This means that you can just run some instrumentation code, then run your agents normally, and everything gets logged into your platform. Below are some examples of how to do this with different OpenTelemetry backends.
|
| 21 |
+
|
| 22 |
+
Here's how it then looks like on the platform:
|
| 23 |
+
|
| 24 |
+
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
| 25 |
+
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/smolagents/inspect_run_phoenix.gif"/>
|
| 26 |
+
</div>
|
| 27 |
+
|
| 28 |
+
|
| 29 |
+
## Setting up telemetry with Arize AI Phoenix
|
| 30 |
+
First install the required packages. Here we install [Phoenix by Arize AI](https://github.com/Arize-ai/phoenix) because that's a good solution to collect and inspect the logs, but there are other OpenTelemetry-compatible platforms that you could use for this collection & inspection part.
|
| 31 |
+
|
| 32 |
+
```shell
|
| 33 |
+
pip install 'smolagents[telemetry]'
|
| 34 |
+
```
|
| 35 |
+
|
| 36 |
+
Then run the collector in the background.
|
| 37 |
+
|
| 38 |
+
```shell
|
| 39 |
+
python -m phoenix.server.main serve
|
| 40 |
+
```
|
| 41 |
+
|
| 42 |
+
Finally, set up `SmolagentsInstrumentor` to trace your agents and send the traces to Phoenix default endpoint.
|
| 43 |
+
|
| 44 |
+
```python
|
| 45 |
+
from phoenix.otel import register
|
| 46 |
+
from openinference.instrumentation.smolagents import SmolagentsInstrumentor
|
| 47 |
+
|
| 48 |
+
register()
|
| 49 |
+
SmolagentsInstrumentor().instrument()
|
| 50 |
+
```
|
| 51 |
+
Then you can run your agents!
|
| 52 |
+
|
| 53 |
+
```py
|
| 54 |
+
from smolagents import (
|
| 55 |
+
CodeAgent,
|
| 56 |
+
ToolCallingAgent,
|
| 57 |
+
DuckDuckGoSearchTool,
|
| 58 |
+
VisitWebpageTool,
|
| 59 |
+
InferenceClientModel,
|
| 60 |
+
)
|
| 61 |
+
|
| 62 |
+
model = InferenceClientModel()
|
| 63 |
+
|
| 64 |
+
search_agent = ToolCallingAgent(
|
| 65 |
+
tools=[DuckDuckGoSearchTool(), VisitWebpageTool()],
|
| 66 |
+
model=model,
|
| 67 |
+
name="search_agent",
|
| 68 |
+
description="This is an agent that can do web search.",
|
| 69 |
+
)
|
| 70 |
+
|
| 71 |
+
manager_agent = CodeAgent(
|
| 72 |
+
tools=[],
|
| 73 |
+
model=model,
|
| 74 |
+
managed_agents=[search_agent],
|
| 75 |
+
)
|
| 76 |
+
manager_agent.run(
|
| 77 |
+
"If the US keeps its 2024 growth rate, how many years will it take for the GDP to double?"
|
| 78 |
+
)
|
| 79 |
+
```
|
| 80 |
+
Voilà!
|
| 81 |
+
You can then navigate to `http://0.0.0.0:6006/projects/` to inspect your run!
|
| 82 |
+
|
| 83 |
+
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/smolagents/inspect_run_phoenix.png">
|
| 84 |
+
|
| 85 |
+
You can see that the CodeAgent called its managed ToolCallingAgent (by the way, the managed agent could have been a CodeAgent as well) to ask it to run the web search for the U.S. 2024 growth rate. Then the managed agent returned its report and the manager agent acted upon it to calculate the economy doubling time! Sweet, isn't it?
|
| 86 |
+
|
| 87 |
+
## Setting up telemetry with Langfuse
|
| 88 |
+
|
| 89 |
+
This part shows how to monitor and debug your Hugging Face **smolagents** with **Langfuse** using the `SmolagentsInstrumentor`.
|
| 90 |
+
|
| 91 |
+
> **What is Langfuse?** [Langfuse](https://langfuse.com) is an open-source platform for LLM engineering. It provides tracing and monitoring capabilities for AI agents, helping developers debug, analyze, and optimize their products. Langfuse integrates with various tools and frameworks via native integrations, OpenTelemetry, and SDKs.
|
| 92 |
+
|
| 93 |
+
### Step 1: Install Dependencies
|
| 94 |
+
|
| 95 |
+
```python
|
| 96 |
+
%pip install smolagents
|
| 97 |
+
%pip install opentelemetry-sdk opentelemetry-exporter-otlp openinference-instrumentation-smolagents
|
| 98 |
+
```
|
| 99 |
+
|
| 100 |
+
### Step 2: Set Up Environment Variables
|
| 101 |
+
|
| 102 |
+
Set your Langfuse API keys and configure the OpenTelemetry endpoint to send traces to Langfuse. Get your Langfuse API keys by signing up for [Langfuse Cloud](https://cloud.langfuse.com) or [self-hosting Langfuse](https://langfuse.com/self-hosting).
|
| 103 |
+
|
| 104 |
+
Also, add your [Hugging Face token](https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens) (`HF_TOKEN`) as an environment variable.
|
| 105 |
+
|
| 106 |
+
```python
|
| 107 |
+
import os
|
| 108 |
+
import base64
|
| 109 |
+
|
| 110 |
+
LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY="pk-lf-..."
|
| 111 |
+
LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY="sk-lf-..."
|
| 112 |
+
LANGFUSE_AUTH=base64.b64encode(f"{LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY}:{LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY}".encode()).decode()
|
| 113 |
+
|
| 114 |
+
os.environ["OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT"] = "https://cloud.langfuse.com/api/public/otel" # EU data region
|
| 115 |
+
# os.environ["OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT"] = "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com/api/public/otel" # US data region
|
| 116 |
+
os.environ["OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS"] = f"Authorization=Basic {LANGFUSE_AUTH}"
|
| 117 |
+
|
| 118 |
+
# your Hugging Face token
|
| 119 |
+
os.environ["HF_TOKEN"] = "hf_..."
|
| 120 |
+
```
|
| 121 |
+
|
| 122 |
+
### Step 3: Initialize the `SmolagentsInstrumentor`
|
| 123 |
+
|
| 124 |
+
Initialize the `SmolagentsInstrumentor` before your application code. Configure `tracer_provider` and add a span processor to export traces to Langfuse. `OTLPSpanExporter()` uses the endpoint and headers from the environment variables.
|
| 125 |
+
|
| 126 |
+
|
| 127 |
+
```python
|
| 128 |
+
from opentelemetry.sdk.trace import TracerProvider
|
| 129 |
+
|
| 130 |
+
from openinference.instrumentation.smolagents import SmolagentsInstrumentor
|
| 131 |
+
from opentelemetry.exporter.otlp.proto.http.trace_exporter import OTLPSpanExporter
|
| 132 |
+
from opentelemetry.sdk.trace.export import SimpleSpanProcessor
|
| 133 |
+
|
| 134 |
+
trace_provider = TracerProvider()
|
| 135 |
+
trace_provider.add_span_processor(SimpleSpanProcessor(OTLPSpanExporter()))
|
| 136 |
+
|
| 137 |
+
SmolagentsInstrumentor().instrument(tracer_provider=trace_provider)
|
| 138 |
+
```
|
| 139 |
+
|
| 140 |
+
### Step 4: Run your smolagent
|
| 141 |
+
|
| 142 |
+
```python
|
| 143 |
+
from smolagents import (
|
| 144 |
+
CodeAgent,
|
| 145 |
+
ToolCallingAgent,
|
| 146 |
+
DuckDuckGoSearchTool,
|
| 147 |
+
VisitWebpageTool,
|
| 148 |
+
InferenceClientModel,
|
| 149 |
+
)
|
| 150 |
+
|
| 151 |
+
model = InferenceClientModel(
|
| 152 |
+
model_id="deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B"
|
| 153 |
+
)
|
| 154 |
+
|
| 155 |
+
search_agent = ToolCallingAgent(
|
| 156 |
+
tools=[DuckDuckGoSearchTool(), VisitWebpageTool()],
|
| 157 |
+
model=model,
|
| 158 |
+
name="search_agent",
|
| 159 |
+
description="This is an agent that can do web search.",
|
| 160 |
+
)
|
| 161 |
+
|
| 162 |
+
manager_agent = CodeAgent(
|
| 163 |
+
tools=[],
|
| 164 |
+
model=model,
|
| 165 |
+
managed_agents=[search_agent],
|
| 166 |
+
)
|
| 167 |
+
manager_agent.run(
|
| 168 |
+
"How can Langfuse be used to monitor and improve the reasoning and decision-making of smolagents when they execute multi-step tasks, like dynamically adjusting a recipe based on user feedback or available ingredients?"
|
| 169 |
+
)
|
| 170 |
+
```
|
| 171 |
+
|
| 172 |
+
### Step 5: View Traces in Langfuse
|
| 173 |
+
|
| 174 |
+
After running the agent, you can view the traces generated by your smolagents application in [Langfuse](https://cloud.langfuse.com). You should see detailed steps of the LLM interactions, which can help you debug and optimize your AI agent.
|
| 175 |
+
|
| 176 |
+
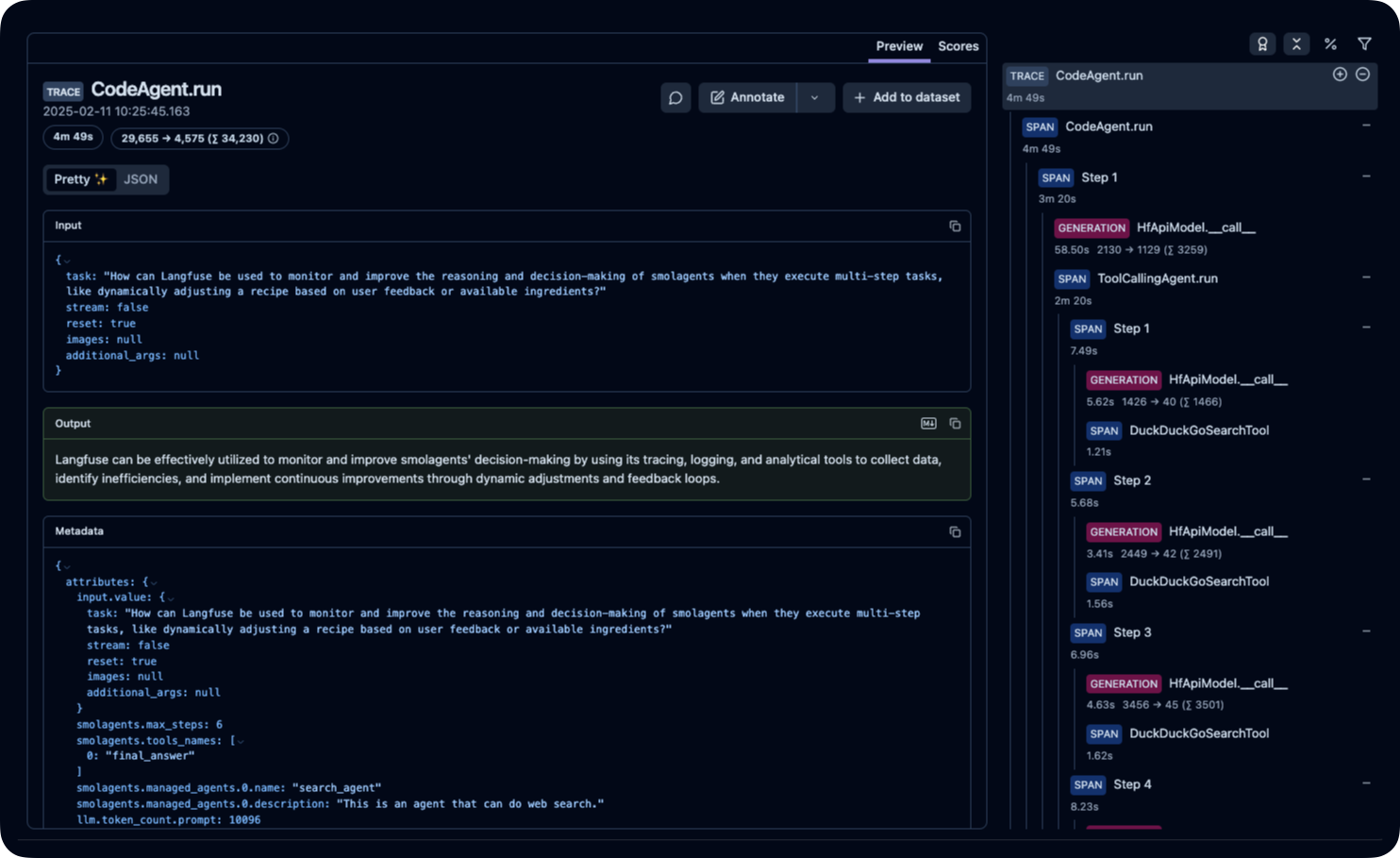
|
| 177 |
+
|
| 178 |
+
_[Public example trace in Langfuse](https://cloud.langfuse.com/project/cloramnkj0002jz088vzn1ja4/traces/ce5160f9bfd5a6cd63b07d2bfcec6f54?timestamp=2025-02-11T09%3A25%3A45.163Z&display=details)_
|
smolagents/docs/source/en/tutorials/memory.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,134 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# 📚 Manage your agent's memory
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
[[open-in-colab]]
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
In the end, an agent can be defined by simple components: it has tools, prompts.
|
| 6 |
+
And most importantly, it has a memory of past steps, drawing a history of planning, execution, and errors.
|
| 7 |
+
|
| 8 |
+
### Replay your agent's memory
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
We propose several features to inspect a past agent run.
|
| 11 |
+
|
| 12 |
+
You can instrument the agent's run to display it in a great UI that lets you zoom in/out on specific steps, as highlighted in the [instrumentation guide](./inspect_runs).
|
| 13 |
+
|
| 14 |
+
You can also use `agent.replay()`, as follows:
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
After the agent has run:
|
| 17 |
+
```py
|
| 18 |
+
from smolagents import InferenceClientModel, CodeAgent
|
| 19 |
+
|
| 20 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=InferenceClientModel(), verbosity_level=0)
|
| 21 |
+
|
| 22 |
+
result = agent.run("What's the 20th Fibonacci number?")
|
| 23 |
+
```
|
| 24 |
+
|
| 25 |
+
If you want to replay this last run, just use:
|
| 26 |
+
```py
|
| 27 |
+
agent.replay()
|
| 28 |
+
```
|
| 29 |
+
|
| 30 |
+
### Dynamically change the agent's memory
|
| 31 |
+
|
| 32 |
+
Many advanced use cases require dynamic modification of the agent's memory.
|
| 33 |
+
|
| 34 |
+
You can access the agent's memory using:
|
| 35 |
+
|
| 36 |
+
```py
|
| 37 |
+
from smolagents import ActionStep
|
| 38 |
+
|
| 39 |
+
system_prompt_step = agent.memory.system_prompt
|
| 40 |
+
print("The system prompt given to the agent was:")
|
| 41 |
+
print(system_prompt_step.system_prompt)
|
| 42 |
+
|
| 43 |
+
task_step = agent.memory.steps[0]
|
| 44 |
+
print("\n\nThe first task step was:")
|
| 45 |
+
print(task_step.task)
|
| 46 |
+
|
| 47 |
+
for step in agent.memory.steps:
|
| 48 |
+
if isinstance(step, ActionStep):
|
| 49 |
+
if step.error is not None:
|
| 50 |
+
print(f"\nStep {step.step_number} got this error:\n{step.error}\n")
|
| 51 |
+
else:
|
| 52 |
+
print(f"\nStep {step.step_number} got these observations:\n{step.observations}\n")
|
| 53 |
+
```
|
| 54 |
+
|
| 55 |
+
Use `agent.memory.get_full_steps()` to get full steps as dictionaries.
|
| 56 |
+
|
| 57 |
+
You can also use step callbacks to dynamically change the agent's memory.
|
| 58 |
+
|
| 59 |
+
Step callbacks can access the `agent` itself in their arguments, so they can access any memory step as highlighted above, and change it if needed. For instance, let's say you are observing screenshots of each step performed by a web browser agent. You want to log the newest screenshot, and remove the images from ancient steps to save on token costs.
|
| 60 |
+
|
| 61 |
+
You could run something like the following.
|
| 62 |
+
_Note: this code is incomplete, some imports and object definitions have been removed for the sake of concision, visit [the original script](https://github.com/huggingface/smolagents/blob/main/src/smolagents/vision_web_browser.py) to get the full working code._
|
| 63 |
+
|
| 64 |
+
```py
|
| 65 |
+
import helium
|
| 66 |
+
from PIL import Image
|
| 67 |
+
from io import BytesIO
|
| 68 |
+
from time import sleep
|
| 69 |
+
|
| 70 |
+
def update_screenshot(memory_step: ActionStep, agent: CodeAgent) -> None:
|
| 71 |
+
sleep(1.0) # Let JavaScript animations happen before taking the screenshot
|
| 72 |
+
driver = helium.get_driver()
|
| 73 |
+
latest_step = memory_step.step_number
|
| 74 |
+
for previous_memory_step in agent.memory.steps: # Remove previous screenshots from logs for lean processing
|
| 75 |
+
if isinstance(previous_memory_step, ActionStep) and previous_memory_step.step_number <= latest_step - 2:
|
| 76 |
+
previous_memory_step.observations_images = None
|
| 77 |
+
png_bytes = driver.get_screenshot_as_png()
|
| 78 |
+
image = Image.open(BytesIO(png_bytes))
|
| 79 |
+
memory_step.observations_images = [image.copy()]
|
| 80 |
+
```
|
| 81 |
+
|
| 82 |
+
Then you should pass this function in the `step_callbacks` argument upon initialization of your agent:
|
| 83 |
+
|
| 84 |
+
```py
|
| 85 |
+
CodeAgent(
|
| 86 |
+
tools=[DuckDuckGoSearchTool(), go_back, close_popups, search_item_ctrl_f],
|
| 87 |
+
model=model,
|
| 88 |
+
additional_authorized_imports=["helium"],
|
| 89 |
+
step_callbacks=[update_screenshot],
|
| 90 |
+
max_steps=20,
|
| 91 |
+
verbosity_level=2,
|
| 92 |
+
)
|
| 93 |
+
```
|
| 94 |
+
|
| 95 |
+
Head to our [vision web browser code](https://github.com/huggingface/smolagents/blob/main/src/smolagents/vision_web_browser.py) to see the full working example.
|
| 96 |
+
|
| 97 |
+
### Run agents one step at a time
|
| 98 |
+
|
| 99 |
+
This can be useful in case you have tool calls that take days: you can just run your agents step by step.
|
| 100 |
+
This will also let you update the memory on each step.
|
| 101 |
+
|
| 102 |
+
```py
|
| 103 |
+
from smolagents import InferenceClientModel, CodeAgent, ActionStep, TaskStep
|
| 104 |
+
|
| 105 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=InferenceClientModel(), verbosity_level=1)
|
| 106 |
+
agent.python_executor.send_tools({**agent.tools})
|
| 107 |
+
print(agent.memory.system_prompt)
|
| 108 |
+
|
| 109 |
+
task = "What is the 20th Fibonacci number?"
|
| 110 |
+
|
| 111 |
+
# You could modify the memory as needed here by inputting the memory of another agent.
|
| 112 |
+
# agent.memory.steps = previous_agent.memory.steps
|
| 113 |
+
|
| 114 |
+
# Let's start a new task!
|
| 115 |
+
agent.memory.steps.append(TaskStep(task=task, task_images=[]))
|
| 116 |
+
|
| 117 |
+
final_answer = None
|
| 118 |
+
step_number = 1
|
| 119 |
+
while final_answer is None and step_number <= 10:
|
| 120 |
+
memory_step = ActionStep(
|
| 121 |
+
step_number=step_number,
|
| 122 |
+
observations_images=[],
|
| 123 |
+
)
|
| 124 |
+
# Run one step.
|
| 125 |
+
final_answer = agent.step(memory_step)
|
| 126 |
+
agent.memory.steps.append(memory_step)
|
| 127 |
+
step_number += 1
|
| 128 |
+
|
| 129 |
+
# Change the memory as you please!
|
| 130 |
+
# For instance to update the latest step:
|
| 131 |
+
# agent.memory.steps[-1] = ...
|
| 132 |
+
|
| 133 |
+
print("The final answer is:", final_answer)
|
| 134 |
+
```
|
smolagents/docs/source/en/tutorials/secure_code_execution.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,414 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Secure code execution
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
[[open-in-colab]]
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 6 |
+
> If you're new to building agents, make sure to first read the [intro to agents](../conceptual_guides/intro_agents) and the [guided tour of smolagents](../guided_tour).
|
| 7 |
+
|
| 8 |
+
### Code agents
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
[Multiple](https://huggingface.co/papers/2402.01030) [research](https://huggingface.co/papers/2411.01747) [papers](https://huggingface.co/papers/2401.00812) have shown that having the LLM write its actions (the tool calls) in code is much better than the current standard format for tool calling, which is across the industry different shades of "writing actions as a JSON of tools names and arguments to use".
|
| 11 |
+
|
| 12 |
+
Why is code better? Well, because we crafted our code languages specifically to be great at expressing actions performed by a computer. If JSON snippets were a better way, this package would have been written in JSON snippets and the devil would be laughing at us.
|
| 13 |
+
|
| 14 |
+
Code is just a better way to express actions on a computer. It has better:
|
| 15 |
+
- **Composability:** could you nest JSON actions within each other, or define a set of JSON actions to re-use later, the same way you could just define a python function?
|
| 16 |
+
- **Object management:** how do you store the output of an action like `generate_image` in JSON?
|
| 17 |
+
- **Generality:** code is built to express simply anything you can have a computer do.
|
| 18 |
+
- **Representation in LLM training corpus:** why not leverage this benediction of the sky that plenty of quality actions have already been included in LLM training corpus?
|
| 19 |
+
|
| 20 |
+
This is illustrated on the figure below, taken from [Executable Code Actions Elicit Better LLM Agents](https://huggingface.co/papers/2402.01030).
|
| 21 |
+
|
| 22 |
+
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/code_vs_json_actions.png">
|
| 23 |
+
|
| 24 |
+
This is why we put emphasis on proposing code agents, in this case python agents, which meant putting higher effort on building secure python interpreters.
|
| 25 |
+
|
| 26 |
+
### Local code execution??
|
| 27 |
+
|
| 28 |
+
By default, the `CodeAgent` runs LLM-generated code in your environment.
|
| 29 |
+
|
| 30 |
+
This is inherently risky, LLM-generated code could be harmful to your environment.
|
| 31 |
+
|
| 32 |
+
Malicious code execution can occur in several ways:
|
| 33 |
+
- **Plain LLM error:** LLMs are still far from perfect and may unintentionally generate harmful commands while attempting to be helpful. While this risk is low, instances have been observed where an LLM attempted to execute potentially dangerous code.
|
| 34 |
+
- **Supply chain attack:** Running an untrusted or compromised LLM could expose a system to harmful code generation. While this risk is extremely low when using well-known models on secure inference infrastructure, it remains a theoretical possibility.
|
| 35 |
+
- **Prompt injection:** an agent browsing the web could arrive on a malicious website that contains harmful instructions, thus injecting an attack into the agent's memory
|
| 36 |
+
- **Exploitation of publicly accessible agents:** Agents exposed to the public can be misused by malicious actors to execute harmful code. Attackers may craft adversarial inputs to exploit the agent's execution capabilities, leading to unintended consequences.
|
| 37 |
+
Once malicious code is executed, whether accidentally or intentionally, it can damage the file system, exploit local or cloud-based resources, abuse API services, and even compromise network security.
|
| 38 |
+
|
| 39 |
+
One could argue that on the [spectrum of agency](../conceptual_guides/intro_agents), code agents give much higher agency to the LLM on your system than other less agentic setups: this goes hand-in-hand with higher risk.
|
| 40 |
+
|
| 41 |
+
So you need to be very mindful of security.
|
| 42 |
+
|
| 43 |
+
To improve safety, we propose a range of measures that propose elevated levels of security, at a higher setup cost.
|
| 44 |
+
|
| 45 |
+
We advise you to keep in mind that no solution will be 100% safe.
|
| 46 |
+
|
| 47 |
+
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/smolagents/code_execution_safety_diagram.png">
|
| 48 |
+
|
| 49 |
+
### Our local Python executor
|
| 50 |
+
|
| 51 |
+
To add a first layer of security, code execution in `smolagents` is not performed by the vanilla Python interpreter.
|
| 52 |
+
We have re-built a more secure `LocalPythonExecutor` from the ground up.
|
| 53 |
+
|
| 54 |
+
To be precise, this interpreter works by loading the Abstract Syntax Tree (AST) from your Code and executes it operation by operation, making sure to always follow certain rules:
|
| 55 |
+
- By default, imports are disallowed unless they have been explicitly added to an authorization list by the user.
|
| 56 |
+
- Furthermore, access to submodules is disabled by default, and each must be explicitly authorized in the import list as well, or you can pass for instance `numpy.*` to allow both `numpy` and all its subpackags, like `numpy.random` or `numpy.a.b`.
|
| 57 |
+
- Note that some seemingly innocuous packages like `random` can give access to potentially harmful submodules, as in `random._os`.
|
| 58 |
+
- The total count of elementary operations processed is capped to prevent infinite loops and resource bloating.
|
| 59 |
+
- Any operation that has not been explicitly defined in our custom interpreter will raise an error.
|
| 60 |
+
|
| 61 |
+
You could try these safeguards as follows:
|
| 62 |
+
|
| 63 |
+
```py
|
| 64 |
+
from smolagents.local_python_executor import LocalPythonExecutor
|
| 65 |
+
|
| 66 |
+
# Set up custom executor, authorize package "numpy"
|
| 67 |
+
custom_executor = LocalPythonExecutor(["numpy"])
|
| 68 |
+
|
| 69 |
+
# Utilisty for pretty printing errors
|
| 70 |
+
def run_capture_exception(command: str):
|
| 71 |
+
try:
|
| 72 |
+
custom_executor(harmful_command)
|
| 73 |
+
except Exception as e:
|
| 74 |
+
print("ERROR:\n", e)
|
| 75 |
+
|
| 76 |
+
# Undefined command just do not work
|
| 77 |
+
harmful_command="!echo Bad command"
|
| 78 |
+
run_capture_exception(harmful_command)
|
| 79 |
+
# >>> ERROR: invalid syntax (<unknown>, line 1)
|
| 80 |
+
|
| 81 |
+
|
| 82 |
+
# Imports like os will not be performed unless explicitly added to `additional_authorized_imports`
|
| 83 |
+
harmful_command="import os; exit_code = os.system("echo Bad command")"
|
| 84 |
+
run_capture_exception(harmful_command)
|
| 85 |
+
# >>> ERROR: Code execution failed at line 'import os' due to: InterpreterError: Import of os is not allowed. Authorized imports are: ['statistics', 'numpy', 'itertools', 'time', 'queue', 'collections', 'math', 'random', 're', 'datetime', 'stat', 'unicodedata']
|
| 86 |
+
|
| 87 |
+
# Even in authorized imports, potentially harmful packages will not be imported
|
| 88 |
+
harmful_command="import random; random._os.system('echo Bad command')"
|
| 89 |
+
run_capture_exception(harmful_command)
|
| 90 |
+
# >>> ERROR: Code execution failed at line 'random._os.system('echo Bad command')' due to: InterpreterError: Forbidden access to module: os
|
| 91 |
+
|
| 92 |
+
# Infinite loop are interrupted after N operations
|
| 93 |
+
harmful_command="""
|
| 94 |
+
while True:
|
| 95 |
+
pass
|
| 96 |
+
"""
|
| 97 |
+
run_capture_exception(harmful_command)
|
| 98 |
+
# >>> ERROR: Code execution failed at line 'while True: pass' due to: InterpreterError: Maximum number of 1000000 iterations in While loop exceeded
|
| 99 |
+
```
|
| 100 |
+
|
| 101 |
+
These safeguards make out interpreter is safer.
|
| 102 |
+
We have used it on a diversity of use cases, without ever observing any damage to the environment.
|
| 103 |
+
|
| 104 |
+
> [!WARNING]
|
| 105 |
+
> It's important to understand that no local python sandbox can ever be completely secure. While our interpreter provides significant safety improvements over the standard Python interpreter, it is still possible for a determined attacker or a fine-tuned malicious LLM to find vulnerabilities and potentially harm your environment.
|
| 106 |
+
>
|
| 107 |
+
> For example, if you've allowed packages like `Pillow` to process images, the LLM could generate code that creates thousands of large image files to fill your hard drive. Other advanced escape techniques might exploit deeper vulnerabilities in authorized packages.
|
| 108 |
+
>
|
| 109 |
+
> Running LLM-generated code in your local environment always carries some inherent risk. The only way to run LLM-generated code with truly robust security isolation is to use remote execution options like E2B or Docker, as detailed below.
|
| 110 |
+
|
| 111 |
+
The risk of a malicious attack is low when using well-known LLMs from trusted inference providers, but it is not zero.
|
| 112 |
+
For high-security applications or when using less trusted models, you should consider using a remote execution sandbox.
|
| 113 |
+
|
| 114 |
+
## Sandbox approaches for secure code execution
|
| 115 |
+
|
| 116 |
+
When working with AI agents that execute code, security is paramount. There are two main approaches to sandboxing code execution in smolagents, each with different security properties and capabilities:
|
| 117 |
+
|
| 118 |
+
|
| 119 |
+

|
| 120 |
+
|
| 121 |
+
1. **Running individual code snippets in a sandbox**: This approach (left side of diagram) only executes the agent-generated Python code snippets in a sandbox while keeping the rest of the agentic system in your local environment. It's simpler to set up using `executor_type="e2b"` or `executor_type="docker"`, but it doesn't support multi-agents and still requires passing state data between your environment and the sandbox.
|
| 122 |
+
|
| 123 |
+
2. **Running the entire agentic system in a sandbox**: This approach (right side of diagram) runs the entire agentic system, including the agent, model, and tools, within a sandbox environment. This provides better isolation but requires more manual setup and may require passing sensitive credentials (like API keys) to the sandbox environment.
|
| 124 |
+
|
| 125 |
+
This guide describes how to set up and use both types of sandbox approaches for your agent applications.
|
| 126 |
+
|
| 127 |
+
### E2B setup
|
| 128 |
+
|
| 129 |
+
#### Installation
|
| 130 |
+
|
| 131 |
+
1. Create an E2B account at [e2b.dev](https://e2b.dev)
|
| 132 |
+
2. Install the required packages:
|
| 133 |
+
```bash
|
| 134 |
+
pip install 'smolagents[e2b]'
|
| 135 |
+
```
|
| 136 |
+
|
| 137 |
+
#### Running your agent in E2B: quick start
|
| 138 |
+
|
| 139 |
+
We provide a simple way to use an E2B Sandbox: simply add `executor_type="e2b"` to the agent initialization, as follows:
|
| 140 |
+
|
| 141 |
+
```py
|
| 142 |
+
from smolagents import InferenceClientModel, CodeAgent
|
| 143 |
+
|
| 144 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(model=InferenceClientModel(), tools=[], executor_type="e2b")
|
| 145 |
+
|
| 146 |
+
agent.run("Can you give me the 100th Fibonacci number?")
|
| 147 |
+
```
|
| 148 |
+
|
| 149 |
+
This solution send the agent state to the server at the start of each `agent.run()`.
|
| 150 |
+
Then the models are called from the local environment, but the generated code will be sent to the sandbox for execution, and only the output will be returned.
|
| 151 |
+
|
| 152 |
+
This is illustrated in the figure below.
|
| 153 |
+
|
| 154 |
+
<p align="center">
|
| 155 |
+
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/smolagents/sandboxed_execution.png" alt="sandboxed code execution" width=60% max-width=500px>
|
| 156 |
+
</p>
|
| 157 |
+
|
| 158 |
+
|
| 159 |
+
However, since any call to a [managed agent](../examples/multiagents) would require model calls, since we do not transfer secrets to the remote sandbox, the model call would lack credentials.
|
| 160 |
+
Hence this solution does not work (yet) with more complicated multi-agent setups.
|
| 161 |
+
|
| 162 |
+
#### Running your agent in E2B: multi-agents
|
| 163 |
+
|
| 164 |
+
To use multi-agents in an E2B sandbox, you need to run your agents completely from within E2B.
|
| 165 |
+
|
| 166 |
+
Here is how to do it:
|
| 167 |
+
|
| 168 |
+
```python
|
| 169 |
+
from e2b_code_interpreter import Sandbox
|
| 170 |
+
import os
|
| 171 |
+
|
| 172 |
+
# Create the sandbox
|
| 173 |
+
sandbox = Sandbox()
|
| 174 |
+
|
| 175 |
+
# Install required packages
|
| 176 |
+
sandbox.commands.run("pip install smolagents")
|
| 177 |
+
|
| 178 |
+
def run_code_raise_errors(sandbox, code: str, verbose: bool = False) -> str:
|
| 179 |
+
execution = sandbox.run_code(
|
| 180 |
+
code,
|
| 181 |
+
envs={'HF_TOKEN': os.getenv('HF_TOKEN')}
|
| 182 |
+
)
|
| 183 |
+
if execution.error:
|
| 184 |
+
execution_logs = "\n".join([str(log) for log in execution.logs.stdout])
|
| 185 |
+
logs = execution_logs
|
| 186 |
+
logs += execution.error.traceback
|
| 187 |
+
raise ValueError(logs)
|
| 188 |
+
return "\n".join([str(log) for log in execution.logs.stdout])
|
| 189 |
+
|
| 190 |
+
# Define your agent application
|
| 191 |
+
agent_code = """
|
| 192 |
+
import os
|
| 193 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel
|
| 194 |
+
|
| 195 |
+
# Initialize the agents
|
| 196 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(
|
| 197 |
+
model=InferenceClientModel(token=os.getenv("HF_TOKEN"), provider="together"),
|
| 198 |
+
tools=[],
|
| 199 |
+
name="coder_agent",
|
| 200 |
+
description="This agent takes care of your difficult algorithmic problems using code."
|
| 201 |
+
)
|
| 202 |
+
|
| 203 |
+
manager_agent = CodeAgent(
|
| 204 |
+
model=InferenceClientModel(token=os.getenv("HF_TOKEN"), provider="together"),
|
| 205 |
+
tools=[],
|
| 206 |
+
managed_agents=[agent],
|
| 207 |
+
)
|
| 208 |
+
|
| 209 |
+
# Run the agent
|
| 210 |
+
response = manager_agent.run("What's the 20th Fibonacci number?")
|
| 211 |
+
print(response)
|
| 212 |
+
"""
|
| 213 |
+
|
| 214 |
+
# Run the agent code in the sandbox
|
| 215 |
+
execution_logs = run_code_raise_errors(sandbox, agent_code)
|
| 216 |
+
print(execution_logs)
|
| 217 |
+
```
|
| 218 |
+
|
| 219 |
+
### Docker setup
|
| 220 |
+
|
| 221 |
+
#### Installation
|
| 222 |
+
|
| 223 |
+
1. [Install Docker on your system](https://docs.docker.com/get-started/get-docker/)
|
| 224 |
+
2. Install the required packages:
|
| 225 |
+
```bash
|
| 226 |
+
pip install 'smolagents[docker]'
|
| 227 |
+
```
|
| 228 |
+
|
| 229 |
+
#### Running your agent in E2B: quick start
|
| 230 |
+
|
| 231 |
+
Similar to the E2B Sandbox above, to quickly get started with Docker, simply add `executor_type="docker"` to the agent initialization, like:
|
| 232 |
+
```py
|
| 233 |
+
from smolagents import InferenceClientModel, CodeAgent
|
| 234 |
+
|
| 235 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(model=InferenceClientModel(), tools=[], executor_type="docker")
|
| 236 |
+
|
| 237 |
+
agent.run("Can you give me the 100th Fibonacci number?")
|
| 238 |
+
```
|
| 239 |
+
|
| 240 |
+
#### Advanced docker usage
|
| 241 |
+
|
| 242 |
+
If you want to run multi-agent systems in Docker, you'll need to setup a custom interpreter in a sandbox.
|
| 243 |
+
|
| 244 |
+
Here is how to setup the a Dockerfile:
|
| 245 |
+
|
| 246 |
+
```dockerfile
|
| 247 |
+
FROM python:3.10-bullseye
|
| 248 |
+
|
| 249 |
+
# Install build dependencies
|
| 250 |
+
RUN apt-get update && \
|
| 251 |
+
apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends \
|
| 252 |
+
build-essential \
|
| 253 |
+
python3-dev && \
|
| 254 |
+
pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip && \
|
| 255 |
+
pip install --no-cache-dir smolagents && \
|
| 256 |
+
apt-get clean && \
|
| 257 |
+
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
| 258 |
+
|
| 259 |
+
# Set working directory
|
| 260 |
+
WORKDIR /app
|
| 261 |
+
|
| 262 |
+
# Run with limited privileges
|
| 263 |
+
USER nobody
|
| 264 |
+
|
| 265 |
+
# Default command
|
| 266 |
+
CMD ["python", "-c", "print('Container ready')"]
|
| 267 |
+
```
|
| 268 |
+
|
| 269 |
+
Create a sandbox manager to run code:
|
| 270 |
+
|
| 271 |
+
```python
|
| 272 |
+
import docker
|
| 273 |
+
import os
|
| 274 |
+
from typing import Optional
|
| 275 |
+
|
| 276 |
+
class DockerSandbox:
|
| 277 |
+
def __init__(self):
|
| 278 |
+
self.client = docker.from_env()
|
| 279 |
+
self.container = None
|
| 280 |
+
|
| 281 |
+
def create_container(self):
|
| 282 |
+
try:
|
| 283 |
+
image, build_logs = self.client.images.build(
|
| 284 |
+
path=".",
|
| 285 |
+
tag="agent-sandbox",
|
| 286 |
+
rm=True,
|
| 287 |
+
forcerm=True,
|
| 288 |
+
buildargs={},
|
| 289 |
+
# decode=True
|
| 290 |
+
)
|
| 291 |
+
except docker.errors.BuildError as e:
|
| 292 |
+
print("Build error logs:")
|
| 293 |
+
for log in e.build_log:
|
| 294 |
+
if 'stream' in log:
|
| 295 |
+
print(log['stream'].strip())
|
| 296 |
+
raise
|
| 297 |
+
|
| 298 |
+
# Create container with security constraints and proper logging
|
| 299 |
+
self.container = self.client.containers.run(
|
| 300 |
+
"agent-sandbox",
|
| 301 |
+
command="tail -f /dev/null", # Keep container running
|
| 302 |
+
detach=True,
|
| 303 |
+
tty=True,
|
| 304 |
+
mem_limit="512m",
|
| 305 |
+
cpu_quota=50000,
|
| 306 |
+
pids_limit=100,
|
| 307 |
+
security_opt=["no-new-privileges"],
|
| 308 |
+
cap_drop=["ALL"],
|
| 309 |
+
environment={
|
| 310 |
+
"HF_TOKEN": os.getenv("HF_TOKEN")
|
| 311 |
+
},
|
| 312 |
+
)
|
| 313 |
+
|
| 314 |
+
def run_code(self, code: str) -> Optional[str]:
|
| 315 |
+
if not self.container:
|
| 316 |
+
self.create_container()
|
| 317 |
+
|
| 318 |
+
# Execute code in container
|
| 319 |
+
exec_result = self.container.exec_run(
|
| 320 |
+
cmd=["python", "-c", code],
|
| 321 |
+
user="nobody"
|
| 322 |
+
)
|
| 323 |
+
|
| 324 |
+
# Collect all output
|
| 325 |
+
return exec_result.output.decode() if exec_result.output else None
|
| 326 |
+
|
| 327 |
+
|
| 328 |
+
def cleanup(self):
|
| 329 |
+
if self.container:
|
| 330 |
+
try:
|
| 331 |
+
self.container.stop()
|
| 332 |
+
except docker.errors.NotFound:
|
| 333 |
+
# Container already removed, this is expected
|
| 334 |
+
pass
|
| 335 |
+
except Exception as e:
|
| 336 |
+
print(f"Error during cleanup: {e}")
|
| 337 |
+
finally:
|
| 338 |
+
self.container = None # Clear the reference
|
| 339 |
+
|
| 340 |
+
# Example usage:
|
| 341 |
+
sandbox = DockerSandbox()
|
| 342 |
+
|
| 343 |
+
try:
|
| 344 |
+
# Define your agent code
|
| 345 |
+
agent_code = """
|
| 346 |
+
import os
|
| 347 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel
|
| 348 |
+
|
| 349 |
+
# Initialize the agent
|
| 350 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(
|
| 351 |
+
model=InferenceClientModel(token=os.getenv("HF_TOKEN"), provider="together"),
|
| 352 |
+
tools=[]
|
| 353 |
+
)
|
| 354 |
+
|
| 355 |
+
# Run the agent
|
| 356 |
+
response = agent.run("What's the 20th Fibonacci number?")
|
| 357 |
+
print(response)
|
| 358 |
+
"""
|
| 359 |
+
|
| 360 |
+
# Run the code in the sandbox
|
| 361 |
+
output = sandbox.run_code(agent_code)
|
| 362 |
+
print(output)
|
| 363 |
+
|
| 364 |
+
finally:
|
| 365 |
+
sandbox.cleanup()
|
| 366 |
+
```
|
| 367 |
+
|
| 368 |
+
### Best practices for sandboxes
|
| 369 |
+
|
| 370 |
+
These key practices apply to both E2B and Docker sandboxes:
|
| 371 |
+
|
| 372 |
+
- Resource management
|
| 373 |
+
- Set memory and CPU limits
|
| 374 |
+
- Implement execution timeouts
|
| 375 |
+
- Monitor resource usage
|
| 376 |
+
- Security
|
| 377 |
+
- Run with minimal privileges
|
| 378 |
+
- Disable unnecessary network access
|
| 379 |
+
- Use environment variables for secrets
|
| 380 |
+
- Environment
|
| 381 |
+
- Keep dependencies minimal
|
| 382 |
+
- Use fixed package versions
|
| 383 |
+
- If you use base images, update them regularly
|
| 384 |
+
|
| 385 |
+
- Cleanup
|
| 386 |
+
- Always ensure proper cleanup of resources, especially for Docker containers, to avoid having dangling containers eating up resources.
|
| 387 |
+
|
| 388 |
+
✨ By following these practices and implementing proper cleanup procedures, you can ensure your agent runs safely and efficiently in a sandboxed environment.
|
| 389 |
+
|
| 390 |
+
## Comparing security approaches
|
| 391 |
+
|
| 392 |
+
As illustrated in the diagram earlier, both sandboxing approaches have different security implications:
|
| 393 |
+
|
| 394 |
+
### Approach 1: Running just the code snippets in a sandbox
|
| 395 |
+
- **Pros**:
|
| 396 |
+
- Easier to set up with a simple parameter (`executor_type="e2b"` or `executor_type="docker"`)
|
| 397 |
+
- No need to transfer API keys to the sandbox
|
| 398 |
+
- Better protection for your local environment
|
| 399 |
+
- **Cons**:
|
| 400 |
+
- Doesn't support multi-agents (managed agents)
|
| 401 |
+
- Still requires transferring state between your environment and the sandbox
|
| 402 |
+
- Limited to specific code execution
|
| 403 |
+
|
| 404 |
+
### Approach 2: Running the entire agentic system in a sandbox
|
| 405 |
+
- **Pros**:
|
| 406 |
+
- Supports multi-agents
|
| 407 |
+
- Complete isolation of the entire agent system
|
| 408 |
+
- More flexible for complex agent architectures
|
| 409 |
+
- **Cons**:
|
| 410 |
+
- Requires more manual setup
|
| 411 |
+
- May require transferring sensitive API keys to the sandbox
|
| 412 |
+
- Potentially higher latency due to more complex operations
|
| 413 |
+
|
| 414 |
+
Choose the approach that best balances your security needs with your application's requirements. For most applications with simpler agent architectures, Approach 1 provides a good balance of security and ease of use. For more complex multi-agent systems where you need full isolation, Approach 2, while more involved to set up, offers better security guarantees.
|
smolagents/docs/source/en/tutorials/tools.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,332 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Tools
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
[[open-in-colab]]
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
Here, we're going to see advanced tool usage.
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 8 |
+
> If you're new to building agents, make sure to first read the [intro to agents](../conceptual_guides/intro_agents) and the [guided tour of smolagents](../guided_tour).
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
- [Tools](#tools)
|
| 11 |
+
- [What is a tool, and how to build one?](#what-is-a-tool-and-how-to-build-one)
|
| 12 |
+
- [Share your tool to the Hub](#share-your-tool-to-the-hub)
|
| 13 |
+
- [Import a Space as a tool](#import-a-space-as-a-tool)
|
| 14 |
+
- [Use LangChain tools](#use-langchain-tools)
|
| 15 |
+
- [Manage your agent's toolbox](#manage-your-agents-toolbox)
|
| 16 |
+
- [Use a collection of tools](#use-a-collection-of-tools)
|
| 17 |
+
|
| 18 |
+
### What is a tool, and how to build one?
|
| 19 |
+
|
| 20 |
+
A tool is mostly a function that an LLM can use in an agentic system.
|
| 21 |
+
|
| 22 |
+
But to use it, the LLM will need to be given an API: name, tool description, input types and descriptions, output type.
|
| 23 |
+
|
| 24 |
+
So it cannot be only a function. It should be a class.
|
| 25 |
+
|
| 26 |
+
So at core, the tool is a class that wraps a function with metadata that helps the LLM understand how to use it.
|
| 27 |
+
|
| 28 |
+
Here's how it looks:
|
| 29 |
+
|
| 30 |
+
```python
|
| 31 |
+
from smolagents import Tool
|
| 32 |
+
|
| 33 |
+
class HFModelDownloadsTool(Tool):
|
| 34 |
+
name = "model_download_counter"
|
| 35 |
+
description = """
|
| 36 |
+
This is a tool that returns the most downloaded model of a given task on the Hugging Face Hub.
|
| 37 |
+
It returns the name of the checkpoint."""
|
| 38 |
+
inputs = {
|
| 39 |
+
"task": {
|
| 40 |
+
"type": "string",
|
| 41 |
+
"description": "the task category (such as text-classification, depth-estimation, etc)",
|
| 42 |
+
}
|
| 43 |
+
}
|
| 44 |
+
output_type = "string"
|
| 45 |
+
|
| 46 |
+
def forward(self, task: str):
|
| 47 |
+
from huggingface_hub import list_models
|
| 48 |
+
|
| 49 |
+
model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
| 50 |
+
return model.id
|
| 51 |
+
|
| 52 |
+
model_downloads_tool = HFModelDownloadsTool()
|
| 53 |
+
```
|
| 54 |
+
|
| 55 |
+
The custom tool subclasses [`Tool`] to inherit useful methods. The child class also defines:
|
| 56 |
+
- An attribute `name`, which corresponds to the name of the tool itself. The name usually describes what the tool does. Since the code returns the model with the most downloads for a task, let's name it `model_download_counter`.
|
| 57 |
+
- An attribute `description` is used to populate the agent's system prompt.
|
| 58 |
+
- An `inputs` attribute, which is a dictionary with keys `"type"` and `"description"`. It contains information that helps the Python interpreter make educated choices about the input.
|
| 59 |
+
- An `output_type` attribute, which specifies the output type. The types for both `inputs` and `output_type` should be [Pydantic formats](https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/concepts/json_schema/#generating-json-schema), they can be either of these: [`~AUTHORIZED_TYPES`].
|
| 60 |
+
- A `forward` method which contains the inference code to be executed.
|
| 61 |
+
|
| 62 |
+
And that's all it needs to be used in an agent!
|
| 63 |
+
|
| 64 |
+
There's another way to build a tool. In the [guided_tour](../guided_tour), we implemented a tool using the `@tool` decorator. The [`tool`] decorator is the recommended way to define simple tools, but sometimes you need more than this: using several methods in a class for more clarity, or using additional class attributes.
|
| 65 |
+
|
| 66 |
+
In this case, you can build your tool by subclassing [`Tool`] as described above.
|
| 67 |
+
|
| 68 |
+
### Share your tool to the Hub
|
| 69 |
+
|
| 70 |
+
You can share your custom tool to the Hub as a Space repository by calling [`~Tool.push_to_hub`] on the tool. Make sure you've created a repository for it on the Hub and are using a token with read access.
|
| 71 |
+
|
| 72 |
+
```python
|
| 73 |
+
model_downloads_tool.push_to_hub("{your_username}/hf-model-downloads", token="<YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>")
|
| 74 |
+
```
|
| 75 |
+
|
| 76 |
+
For the push to Hub to work, your tool will need to respect some rules:
|
| 77 |
+
- All methods are self-contained, e.g. use variables that come either from their args.
|
| 78 |
+
- As per the above point, **all imports should be defined directly within the tool's functions**, else you will get an error when trying to call [`~Tool.save`] or [`~Tool.push_to_hub`] with your custom tool.
|
| 79 |
+
- If you subclass the `__init__` method, you can give it no other argument than `self`. This is because arguments set during a specific tool instance's initialization are hard to track, which prevents from sharing them properly to the hub. And anyway, the idea of making a specific class is that you can already set class attributes for anything you need to hard-code (just set `your_variable=(...)` directly under the `class YourTool(Tool):` line). And of course you can still create a class attribute anywhere in your code by assigning stuff to `self.your_variable`.
|
| 80 |
+
|
| 81 |
+
|
| 82 |
+
Once your tool is pushed to Hub, you can visualize it. [Here](https://huggingface.co/spaces/m-ric/hf-model-downloads) is the `model_downloads_tool` that I've pushed. It has a nice gradio interface.
|
| 83 |
+
|
| 84 |
+
When diving into the tool files, you can find that all the tool's logic is under [tool.py](https://huggingface.co/spaces/m-ric/hf-model-downloads/blob/main/tool.py). That is where you can inspect a tool shared by someone else.
|
| 85 |
+
|
| 86 |
+
Then you can load the tool with [`load_tool`] or create it with [`~Tool.from_hub`] and pass it to the `tools` parameter in your agent.
|
| 87 |
+
Since running tools means running custom code, you need to make sure you trust the repository, thus we require to pass `trust_remote_code=True` to load a tool from the Hub.
|
| 88 |
+
|
| 89 |
+
```python
|
| 90 |
+
from smolagents import load_tool, CodeAgent
|
| 91 |
+
|
| 92 |
+
model_download_tool = load_tool(
|
| 93 |
+
"{your_username}/hf-model-downloads",
|
| 94 |
+
trust_remote_code=True
|
| 95 |
+
)
|
| 96 |
+
```
|
| 97 |
+
|
| 98 |
+
### Import a Space as a tool
|
| 99 |
+
|
| 100 |
+
You can directly import a Gradio Space from the Hub as a tool using the [`Tool.from_space`] method!
|
| 101 |
+
|
| 102 |
+
You only need to provide the id of the Space on the Hub, its name, and a description that will help you agent understand what the tool does. Under the hood, this will use [`gradio-client`](https://pypi.org/project/gradio-client/) library to call the Space.
|
| 103 |
+
|
| 104 |
+
For instance, let's import the [FLUX.1-dev](https://huggingface.co/black-forest-labs/FLUX.1-dev) Space from the Hub and use it to generate an image.
|
| 105 |
+
|
| 106 |
+
```python
|
| 107 |
+
image_generation_tool = Tool.from_space(
|
| 108 |
+
"black-forest-labs/FLUX.1-schnell",
|
| 109 |
+
name="image_generator",
|
| 110 |
+
description="Generate an image from a prompt"
|
| 111 |
+
)
|
| 112 |
+
|
| 113 |
+
image_generation_tool("A sunny beach")
|
| 114 |
+
```
|
| 115 |
+
And voilà, here's your image! 🏖️
|
| 116 |
+
|
| 117 |
+
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/sunny_beach.webp">
|
| 118 |
+
|
| 119 |
+
Then you can use this tool just like any other tool. For example, let's improve the prompt `a rabbit wearing a space suit` and generate an image of it. This example also shows how you can pass additional arguments to the agent.
|
| 120 |
+
|
| 121 |
+
```python
|
| 122 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel
|
| 123 |
+
|
| 124 |
+
model = InferenceClientModel(model_id="Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct")
|
| 125 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[image_generation_tool], model=model)
|
| 126 |
+
|
| 127 |
+
agent.run(
|
| 128 |
+
"Improve this prompt, then generate an image of it.", additional_args={'user_prompt': 'A rabbit wearing a space suit'}
|
| 129 |
+
)
|
| 130 |
+
```
|
| 131 |
+
|
| 132 |
+
```text
|
| 133 |
+
=== Agent thoughts:
|
| 134 |
+
improved_prompt could be "A bright blue space suit wearing rabbit, on the surface of the moon, under a bright orange sunset, with the Earth visible in the background"
|
| 135 |
+
|
| 136 |
+
Now that I have improved the prompt, I can use the image generator tool to generate an image based on this prompt.
|
| 137 |
+
>>> Agent is executing the code below:
|
| 138 |
+
image = image_generator(prompt="A bright blue space suit wearing rabbit, on the surface of the moon, under a bright orange sunset, with the Earth visible in the background")
|
| 139 |
+
final_answer(image)
|
| 140 |
+
```
|
| 141 |
+
|
| 142 |
+
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rabbit_spacesuit_flux.webp">
|
| 143 |
+
|
| 144 |
+
How cool is this? 🤩
|
| 145 |
+
|
| 146 |
+
### Use LangChain tools
|
| 147 |
+
|
| 148 |
+
We love Langchain and think it has a very compelling suite of tools.
|
| 149 |
+
To import a tool from LangChain, use the `from_langchain()` method.
|
| 150 |
+
|
| 151 |
+
Here is how you can use it to recreate the intro's search result using a LangChain web search tool.
|
| 152 |
+
This tool will need `pip install langchain google-search-results -q` to work properly.
|
| 153 |
+
```python
|
| 154 |
+
from langchain.agents import load_tools
|
| 155 |
+
|
| 156 |
+
search_tool = Tool.from_langchain(load_tools(["serpapi"])[0])
|
| 157 |
+
|
| 158 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[search_tool], model=model)
|
| 159 |
+
|
| 160 |
+
agent.run("How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) are in BERT base encoder compared to the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?")
|
| 161 |
+
```
|
| 162 |
+
|
| 163 |
+
### Manage your agent's toolbox
|
| 164 |
+
|
| 165 |
+
You can manage an agent's toolbox by adding or replacing a tool in attribute `agent.tools`, since it is a standard dictionary.
|
| 166 |
+
|
| 167 |
+
Let's add the `model_download_tool` to an existing agent initialized with only the default toolbox.
|
| 168 |
+
|
| 169 |
+
```python
|
| 170 |
+
from smolagents import InferenceClientModel
|
| 171 |
+
|
| 172 |
+
model = InferenceClientModel(model_id="Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct")
|
| 173 |
+
|
| 174 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
|
| 175 |
+
agent.tools[model_download_tool.name] = model_download_tool
|
| 176 |
+
```
|
| 177 |
+
Now we can leverage the new tool:
|
| 178 |
+
|
| 179 |
+
```python
|
| 180 |
+
agent.run(
|
| 181 |
+
"Can you give me the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub but reverse the letters?"
|
| 182 |
+
)
|
| 183 |
+
```
|
| 184 |
+
|
| 185 |
+
|
| 186 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 187 |
+
> Beware of not adding too many tools to an agent: this can overwhelm weaker LLM engines.
|
| 188 |
+
|
| 189 |
+
|
| 190 |
+
### Use a collection of tools
|
| 191 |
+
|
| 192 |
+
You can leverage tool collections by using [`ToolCollection`]. It supports loading either a collection from the Hub or an MCP server tools.
|
| 193 |
+
|
| 194 |
+
#### Tool Collection from a collection in the Hub
|
| 195 |
+
|
| 196 |
+
You can leverage it with the slug of the collection you want to use.
|
| 197 |
+
Then pass them as a list to initialize your agent, and start using them!
|
| 198 |
+
|
| 199 |
+
```py
|
| 200 |
+
from smolagents import ToolCollection, CodeAgent
|
| 201 |
+
|
| 202 |
+
image_tool_collection = ToolCollection.from_hub(
|
| 203 |
+
collection_slug="huggingface-tools/diffusion-tools-6630bb19a942c2306a2cdb6f",
|
| 204 |
+
token="<YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>"
|
| 205 |
+
)
|
| 206 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[*image_tool_collection.tools], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
|
| 207 |
+
|
| 208 |
+
agent.run("Please draw me a picture of rivers and lakes.")
|
| 209 |
+
```
|
| 210 |
+
|
| 211 |
+
To speed up the start, tools are loaded only if called by the agent.
|
| 212 |
+
|
| 213 |
+
#### Tool Collection from any MCP server
|
| 214 |
+
|
| 215 |
+
Leverage tools from the hundreds of MCP servers available on [glama.ai](https://glama.ai/mcp/servers) or [smithery.ai](https://smithery.ai/).
|
| 216 |
+
|
| 217 |
+
> [!WARNING]
|
| 218 |
+
> **Security Warning:** Using MCP servers comes with security risks:
|
| 219 |
+
> - **Trust is essential:** Only use MCP servers from trusted sources. Malicious servers can execute harmful code on your machine.
|
| 220 |
+
> - **Stdio-based MCP servers** will always execute code on your machine (that's their intended functionality).
|
| 221 |
+
> - **SSE-based MCP servers** while the remote MCP servers will not be able to execute code on your machine, still proceed with caution.
|
| 222 |
+
>
|
| 223 |
+
> Always verify the source and integrity of any MCP server before connecting to it, especially for production environments.
|
| 224 |
+
|
| 225 |
+
The MCP servers tools can be loaded with [`ToolCollection.from_mcp`].
|
| 226 |
+
|
| 227 |
+
For stdio-based MCP servers, pass the server parameters as an instance of `mcp.StdioServerParameters`:
|
| 228 |
+
```py
|
| 229 |
+
from smolagents import ToolCollection, CodeAgent
|
| 230 |
+
from mcp import StdioServerParameters
|
| 231 |
+
|
| 232 |
+
server_parameters = StdioServerParameters(
|
| 233 |
+
command="uvx",
|
| 234 |
+
args=["--quiet", "[email protected]"],
|
| 235 |
+
env={"UV_PYTHON": "3.12", **os.environ},
|
| 236 |
+
)
|
| 237 |
+
|
| 238 |
+
with ToolCollection.from_mcp(server_parameters, trust_remote_code=True) as tool_collection:
|
| 239 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[*tool_collection.tools], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
|
| 240 |
+
agent.run("Please find a remedy for hangover.")
|
| 241 |
+
```
|
| 242 |
+
|
| 243 |
+
For SSE-based MCP servers, simply pass a dict with parameters to `mcp.client.sse.sse_client`:
|
| 244 |
+
```py
|
| 245 |
+
from smolagents import ToolCollection, CodeAgent
|
| 246 |
+
|
| 247 |
+
with ToolCollection.from_mcp({"url": "http://127.0.0.1:8000/sse"}, trust_remote_code=True) as tool_collection:
|
| 248 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[*tool_collection.tools], add_base_tools=True)
|
| 249 |
+
agent.run("Please find a remedy for hangover.")
|
| 250 |
+
```
|
| 251 |
+
|
| 252 |
+
### Use MCP tools with MCPClient directly
|
| 253 |
+
|
| 254 |
+
You can also work with MCP tools by using the `MCPClient` directly, which gives you more control over the connection and tool management:
|
| 255 |
+
|
| 256 |
+
For stdio-based MCP servers:
|
| 257 |
+
```python
|
| 258 |
+
from smolagents import MCPClient, CodeAgent
|
| 259 |
+
from mcp import StdioServerParameters
|
| 260 |
+
import os
|
| 261 |
+
|
| 262 |
+
server_parameters = StdioServerParameters(
|
| 263 |
+
command="uvx", # Using uvx ensures dependencies are available
|
| 264 |
+
args=["--quiet", "[email protected]"],
|
| 265 |
+
env={"UV_PYTHON": "3.12", **os.environ},
|
| 266 |
+
)
|
| 267 |
+
|
| 268 |
+
with MCPClient(server_parameters) as tools:
|
| 269 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=tools, model=model, add_base_tools=True)
|
| 270 |
+
agent.run("Please find the latest research on COVID-19 treatment.")
|
| 271 |
+
```
|
| 272 |
+
|
| 273 |
+
For SSE-based MCP servers:
|
| 274 |
+
```python
|
| 275 |
+
from smolagents import MCPClient, CodeAgent
|
| 276 |
+
|
| 277 |
+
with MCPClient({"url": "http://127.0.0.1:8000/sse"}) as tools:
|
| 278 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=tools, model=model, add_base_tools=True)
|
| 279 |
+
agent.run("Please find a remedy for hangover.")
|
| 280 |
+
```
|
| 281 |
+
|
| 282 |
+
You can also manually manage the connection lifecycle with the try...finally pattern:
|
| 283 |
+
|
| 284 |
+
```python
|
| 285 |
+
from smolagents import MCPClient, CodeAgent
|
| 286 |
+
from mcp import StdioServerParameters
|
| 287 |
+
import os
|
| 288 |
+
|
| 289 |
+
# Initialize server parameters
|
| 290 |
+
server_parameters = StdioServerParameters(
|
| 291 |
+
command="uvx",
|
| 292 |
+
args=["--quiet", "[email protected]"],
|
| 293 |
+
env={"UV_PYTHON": "3.12", **os.environ},
|
| 294 |
+
)
|
| 295 |
+
|
| 296 |
+
# Manually manage the connection
|
| 297 |
+
try:
|
| 298 |
+
mcp_client = MCPClient(server_parameters)
|
| 299 |
+
tools = mcp_client.get_tools()
|
| 300 |
+
|
| 301 |
+
# Use the tools with your agent
|
| 302 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=tools, model=model, add_base_tools=True)
|
| 303 |
+
result = agent.run("What are the recent therapeutic approaches for Alzheimer's disease?")
|
| 304 |
+
|
| 305 |
+
# Process the result as needed
|
| 306 |
+
print(f"Agent response: {result}")
|
| 307 |
+
finally:
|
| 308 |
+
# Always ensure the connection is properly closed
|
| 309 |
+
mcp_client.disconnect()
|
| 310 |
+
```
|
| 311 |
+
|
| 312 |
+
You can also connect to multiple MCP servers at once by passing a list of server parameters:
|
| 313 |
+
```python
|
| 314 |
+
from smolagents import MCPClient, CodeAgent
|
| 315 |
+
from mcp import StdioServerParameters
|
| 316 |
+
import os
|
| 317 |
+
|
| 318 |
+
server_params1 = StdioServerParameters(
|
| 319 |
+
command="uvx",
|
| 320 |
+
args=["--quiet", "[email protected]"],
|
| 321 |
+
env={"UV_PYTHON": "3.12", **os.environ},
|
| 322 |
+
)
|
| 323 |
+
|
| 324 |
+
server_params2 = {"url": "http://127.0.0.1:8000/sse"}
|
| 325 |
+
|
| 326 |
+
with MCPClient([server_params1, server_params2]) as tools:
|
| 327 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=tools, model=model, add_base_tools=True)
|
| 328 |
+
agent.run("Please analyze the latest research and suggest remedies for headaches.")
|
| 329 |
+
```
|
| 330 |
+
|
| 331 |
+
> [!WARNING]
|
| 332 |
+
> **Security Warning:** The same security warnings mentioned for `ToolCollection.from_mcp` apply when using `MCPClient` directly.
|
smolagents/docs/source/hi/_config.py
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# docstyle-ignore
|
| 2 |
+
INSTALL_CONTENT = """
|
| 3 |
+
# Installation
|
| 4 |
+
! pip install smolagents
|
| 5 |
+
# To install from source instead of the last release, comment the command above and uncomment the following one.
|
| 6 |
+
# ! pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/smolagents.git
|
| 7 |
+
"""
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
notebook_first_cells = [{"type": "code", "content": INSTALL_CONTENT}]
|
| 10 |
+
black_avoid_patterns = {
|
| 11 |
+
"{processor_class}": "FakeProcessorClass",
|
| 12 |
+
"{model_class}": "FakeModelClass",
|
| 13 |
+
"{object_class}": "FakeObjectClass",
|
| 14 |
+
}
|
smolagents/docs/source/hi/_toctree.yml
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
- title: Get started
|
| 2 |
+
sections:
|
| 3 |
+
- local: index
|
| 4 |
+
title: 🤗 Agents
|
| 5 |
+
- local: guided_tour
|
| 6 |
+
title: गाइडेड टूर
|
| 7 |
+
- title: Tutorials
|
| 8 |
+
sections:
|
| 9 |
+
- local: tutorials/building_good_agents
|
| 10 |
+
title: ✨ अच्छे Agents का निर्माण
|
| 11 |
+
- local: tutorials/inspect_runs
|
| 12 |
+
title: 📊 OpenTelemetry के साथ runs का निरीक्षण
|
| 13 |
+
- local: tutorials/tools
|
| 14 |
+
title: 🛠️ Tools - in-depth guide
|
| 15 |
+
- local: tutorials/secure_code_execution
|
| 16 |
+
title: 🛡️ E2B के साथ अपने कोड एक्जीक्यूशन को सुरक्षित करें
|
| 17 |
+
- title: Conceptual guides
|
| 18 |
+
sections:
|
| 19 |
+
- local: conceptual_guides/intro_agents
|
| 20 |
+
title: 🤖 Agentic सिस्टम का परिचय
|
| 21 |
+
- local: conceptual_guides/react
|
| 22 |
+
title: 🤔 मल्टी-स्टेप एजेंट कैसे काम करते हैं?
|
| 23 |
+
- title: Examples
|
| 24 |
+
sections:
|
| 25 |
+
- local: examples/text_to_sql
|
| 26 |
+
title: सेल्फ करेक्टिंग Text-to-SQL
|
| 27 |
+
- local: examples/rag
|
| 28 |
+
title: एजेंटिक RAG के साथ अपनी ज्ञान आधारित को मास्टर करें
|
| 29 |
+
- local: examples/multiagents
|
| 30 |
+
title: एक बहु-एजेंट प्रणाली का आयोजन करें
|
| 31 |
+
- title: Reference
|
| 32 |
+
sections:
|
| 33 |
+
- local: reference/agents
|
| 34 |
+
title: एजेंट से संबंधित ऑब्जेक्ट्स
|
| 35 |
+
- local: reference/tools
|
| 36 |
+
title: टूल्स से संबंधित ऑब्जेक्ट्स
|
smolagents/docs/source/hi/conceptual_guides/intro_agents.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Agents का परिचय
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
## 🤔 Agents क्या हैं?
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
AI का उपयोग करने वाली किसी भी कुशल प्रणाली को LLM को वास्तविक दुनिया तक किसी प्रकार की पहुंच प्रदान करने की आवश्यकता होगी: उदाहरण के लिए बाहरी जानकारी प्राप्त करने के लिए एक खोज टूल को कॉल करने की संभावना, या किसी कार्य को हल करने के लिए कुछ प्रोग्राम पर कार्य करने की। दूसरे शब्दों में, LLM में ***agency*** होनी चाहिए। एजेंटिक प्रोग्राम LLM के लिए बाहरी दुनिया का प्रवेश द्वार हैं।
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 8 |
+
> AI Agents वे **प्रोग्राम हैं जहां LLM आउटपुट वर्कफ़्लो को नियंत्रित करते हैं**।
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
LLM का उपयोग करने वाली कोई भी प्रणाली LLM आउटपुट को कोड में एकीकृत करेगी। कोड वर्कफ़्लो पर LLM के इनपुट का प्रभाव सिस्टम में LLM की एजेंसी का स्तर है।
|
| 11 |
+
|
| 12 |
+
ध्यान दें कि इस परिभाषा के साथ, "agent" एक अलग, 0 या 1 परिभाषा नहीं है: इसके बजाय, "agency" एक निरंतर स्पेक्ट्रम पर विकसित होती है, जैसे-जैसे आप अपने वर्कफ़्लो पर LLM को अधिक या कम शक्ति देते हैं।
|
| 13 |
+
|
| 14 |
+
नीचे दी गई तालिका में देखें कि कैसे एजेंसी विभिन्न प्रणालियों में भिन्न हो सकती है:
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
| एजेंसी स्तर | विवरण | इसे क्या कहा जाता है | उदाहरण पैटर्न |
|
| 17 |
+
|------------|---------|-------------------|----------------|
|
| 18 |
+
| ☆☆☆ | LLM आउटपुट का प्रोग्राम प्रवाह पर कोई प्रभाव नहीं | सरल प्रोसेसर | `process_llm_output(llm_response)` |
|
| 19 |
+
| ★☆☆ | LLM आउटपुट if/else स्विच निर्धारित करता है | राउटर | `if llm_decision(): path_a() else: path_b()` |
|
| 20 |
+
| ★★☆ | LLM आउटपुट फंक्शन एक्जीक्यूशन निर्धारित करता है | टूल कॉलर | `run_function(llm_chosen_tool, llm_chosen_args)` |
|
| 21 |
+
| ★★★ | LLM आउटपुट पुनरावृत्ति और प्रोग्राम की निरंतरता को नियंत्रित करता है | मल्टी-स्टेप एजेंट | `while llm_should_continue(): execute_next_step()` |
|
| 22 |
+
| ★★★ | एक एजेंटिक वर्कफ़्लो दूसरे एजेंटिक वर्कफ़्लो को शुरू कर सकता है | मल्टी-एजेंट | `if llm_trigger(): execute_agent()` |
|
| 23 |
+
|
| 24 |
+
मल्टी-स्टेप agent की यह कोड संरचना है:
|
| 25 |
+
|
| 26 |
+
```python
|
| 27 |
+
memory = [user_defined_task]
|
| 28 |
+
while llm_should_continue(memory): # यह लूप मल्टी-स्टेप भाग है
|
| 29 |
+
action = llm_get_next_action(memory) # यह टूल-कॉलिंग भाग है
|
| 30 |
+
observations = execute_action(action)
|
| 31 |
+
memory += [action, observations]
|
| 32 |
+
```
|
| 33 |
+
|
| 34 |
+
यह एजेंटिक सिस्टम एक लूप में चलता है, प्रत्येक चरण में एक नई क्रिया को शुरू करता है (क्रिया में कुछ पूर्व-निर्धारित *tools* को कॉल करना शामिल हो सकता है जो केवल फंक्शंस हैं), जब तक कि उसके अवलोकन से यह स्पष्ट न हो जाए कि दिए गए कार्य को हल करने के लिए एक संतोषजनक स्थिति प्राप्त कर ली गई है।
|
| 35 |
+
|
| 36 |
+
## ✅ Agents का उपयोग कब करें / ⛔ कब उनसे बचें
|
| 37 |
+
|
| 38 |
+
Agents तब उपयोगी होते हैं जब आपको किसी ऐप के वर्कफ़्लो को निर्धारित करने के लिए LLM की आवश्यकता होती है। लेकिन वे अक्सर जरूरत से ज्यादा होते हैं। सवाल यह है कि, क्या मुझे वास्तव में दिए गए कार्य को कुशलतापूर्वक हल करने के लिए वर्कफ़्लो में लचीलेपन की आवश्यकता है?
|
| 39 |
+
यदि पूर्व-निर्धारित वर्कफ़्लो बहुत बार विफल होता है, तो इसका मतलब है कि आपको अधिक लचीलेपन की आवश्यकता है।
|
| 40 |
+
|
| 41 |
+
आइए एक उदाहरण लेते हैं: मान लीजिए आप एक ऐप बना रहे हैं जो एक सर्फिंग ट्रिप वेबसाइट पर ग्राहक अनुरोधों को संभालता है।
|
| 42 |
+
|
| 43 |
+
आप पहले से जान सकते हैं कि अनुरोध 2 में से किसी एक श्रेणी में आएंगे (उपयोगकर्ता की पसंद के आधार पर), और आपके पास इन 2 मामलों में से प्रत्येक के लिए एक पूर्व-निर्धारित वर्कफ़्लो है।
|
| 44 |
+
|
| 45 |
+
1. ट्रिप के बारे में कुछ जानकारी चाहिए? ⇒ उन्हें अपने नॉलेज बेस में खोज करने के लिए एक सर्च बार तक पहुंच दें
|
| 46 |
+
2. सेल्स टीम से बात करना चाहते हैं? ⇒ उन्हें एक संपर्क फॉर्म में टाइप करने दें।
|
| 47 |
+
|
| 48 |
+
यदि वह निर्धारणात्मक वर्कफ़्लो सभी प्रश्नों के लिए फिट बैठता है, तो बेशक बस सब कुछ कोड करें! यह आपको एक 100% विश्वसनीय सिस्टम देगा और एलएलएम द्वारा अनपेक्षित कार्यप्रवाह में हस्तक्षेप करने से त्रुटियों का कोई जोखिम नहीं होगा। साधारणता और मजबूती के लिए, सलाह दी जाती है कि एजेंटिक व्यवहार का उपयोग न किया जाए।
|
| 49 |
+
|
| 50 |
+
लेकिन क्या होगा अगर वर्कफ़्लो को पहले से इतनी अच्छी तरह से निर्धारित नहीं किया जा सकता?
|
| 51 |
+
|
| 52 |
+
उदाहरण के लिए, एक उपयोगकर्ता पूछना चाहता है: `"मैं सोमवार को आ सकता हूं, लेकिन मैं अपना पासपोर्ट भूल गया जिससे मुझे बुधवार तक देर हो सकती है, क्या आप मुझे और मेरी चीजों को मंगलवार सुबह सर्फ करने ले जा सकते हैं, क्या मुझे कैंसलेशन इंश्योरेंस मिल सकता है?"` यह प्रश्न कई कारकों पर निर्भर करता है, और शायद ऊपर दिए गए पूर्व-निर्धारित मानदंडों में से कोई भी इस अनुरोध के लिए पर्याप्त नहीं होगा।
|
| 53 |
+
|
| 54 |
+
यदि पूर्व-निर्धारित वर्कफ़्लो बहुत बार विफल होता है, तो इसका मतलब है कि आपको अधिक लचीलेपन की आवश्यकता है।
|
| 55 |
+
|
| 56 |
+
यहीं पर एक एजेंटिक सेटअप मदद करता है।
|
| 57 |
+
|
| 58 |
+
ऊपर दिए गए उदाहरण में, आप बस एक मल्टी-स्टेप agent बना सकते हैं जिसके पास मौसम पूर्वानुमान के लिए एक मौसम API, यात्रा की दूरी जानने के लिए के लिए Google Maps API, एक कर्मचारी उपलब्धता डैशबोर्ड और आपके नॉलेज बेस पर एक RAG सिस्टम तक पहुंच है।
|
| 59 |
+
|
| 60 |
+
हाल ही तक, कंप्यूटर प्रोग्राम पूर्व-निर्धारित वर्कफ़्लो तक सीमित थे, if/else स्विच का
|
| 61 |
+
ढेर लगाकार जटिलता को संभालने का प्रयास कर रहे थे। वे बेहद संकीर्ण कार्यों पर केंद्रित थे, जैसे "इन संख्याओं का योग निकालें" या "इस ग्राफ़ में सबसे छोटा रास्ता खोजें"। लेकिन वास्तव में, अधिकांश वास्तविक जीवन के कार्य, जैसे ऊपर दिया गया हमारा यात्रा उदाहरण, पूर्व-निर्धारित वर्कफ़्लो में फिट नहीं होते हैं। एजेंटिक सिस्टम प्रोग्राम के लिए वास्तविक दुनिया के कार्यों की विशाल दुनिया खोलते हैं!
|
| 62 |
+
|
| 63 |
+
## क्यों `smolagents`?
|
| 64 |
+
|
| 65 |
+
कुछ लो-लेवल एजेंटिक उपयोग के मामलों के लिए, जैसे चेन या राउटर, आप सभी कोड खुद लिख सकते हैं। आप इस तरह से बहुत बेहतर होंगे, क्योंकि यह आपको अपने सिस्टम को बेहतर ढंग से नियंत्रित और समझने की अनुमति देगा।
|
| 66 |
+
|
| 67 |
+
लेकिन जैसे ही आप अधिक जटिल व्यवहारों की ओर बढ़ते हैं जैसे कि LLM को एक फ़ंक्शन कॉल करने देना (यह "tool calling" है) या LLM को एक while लूप चलाने देना ("multi-step agent"), कुछ एब्सट्रैक्शन्स की आवश्यकता होती है:
|
| 68 |
+
- टूल कॉलिंग के लिए, आपको एजेंट के आउटपुट को पार्स करने की आवश्यकता होती है, इसलिए इस आउटपुट को एक पूर्व-निर्धारित प्रारूप की आवश्यकता होती है जैसे "विचार: मुझे 'get_weather' टूल कॉल करना चाहिए। क्रिया: get_weather(Paris)।", जिसे आप एक पूर्व-निर्धारित फ़ंक्शन के साथ पार्स करते हैं, और LLM को दिए गए सिस्टम प्रॉम्प्ट को इस प्रारूप के बारे में सूचित करना चाहिए।
|
| 69 |
+
- एक मल्टी-स्टेप एजेंट के लिए जहां LLM आउटपुट लूप को निर्धारित करता है, आपको पिछले लूप इटरेशन में क्या हुआ इसके आधार पर LLM को एक अलग प्रॉम्प्ट देने की आवश्यकता होती है: इसलिए आपको किसी प्रकार की मेमोरी की आवश्यकता होती है।
|
| 70 |
+
|
| 71 |
+
इन दो उदाहरणों के साथ, हमने पहले ही कुछ चीजों की आवश्यकता का पता लगा लिया:
|
| 72 |
+
|
| 73 |
+
- बेशक, एक LLM जो सिस्टम को पावर देने वाले इंजन के रूप में कार्य करता है
|
| 74 |
+
- एजेंट द्वारा एक्सेस किए जा सकने वाले टूल्स की एक सूची
|
| 75 |
+
- एक पार्सर जो LLM आउटपुट से टूल कॉल को निकालता है
|
| 76 |
+
- एक सिस्टम प्रोम्प्ट जो पार्सर के साथ सिंक्रनाइज़ होता है
|
| 77 |
+
- एक मेमोरी
|
| 78 |
+
|
| 79 |
+
लेकिन रुकिए, चूंकि हम निर्णयों में LLM को जगह देते हैं, निश्चित रूप से वे गलतियां करेंगे: इसलिए हमें एरर लॉगिंग और पुनः प्रयास तंत्र की आवश्यकता है।
|
| 80 |
+
|
| 81 |
+
ये सभी तत्व एक अच्छे कामकाजी सिस्टम बनाने के लिए एक-दूसरे से घनिष्ठ रूप से जुड़े हुए हैं। यही कारण है कि हमने तय किया कि इन सभी चीजों को एक सा��� काम करने के लिए बुनियादी निर्माण ब्लॉक्स की आवश्यकता है।
|
| 82 |
+
|
| 83 |
+
## कोड Agents
|
| 84 |
+
|
| 85 |
+
एक मल्टी-स्टेप एजेंट में, प्रत्येक चरण पर, LLM बाहरी टूल्स को कुछ कॉल के रूप में एक क्रिया लिख सकता है। इन क्रियाओं को लिखने के लिए एक सामान्य स्वरूप (Anthropic, OpenAI और कई अन्य द्वारा उपयोग किया जाता है) आमतौर पर "टूल्स के नाम और उपयोग करने के लिए तर्कों के JSON के रूप में क्रियाएं लिखने" के विभिन्न रूप होते हैं, जिन्हें आप फिर पार्स करते हैं यह जानने के लिए कि कौन सा टूल किन तर्कों के साथ निष्पादित करना है"।
|
| 86 |
+
|
| 87 |
+
[कई](https://huggingface.co/papers/2402.01030) [शोध](https://huggingface.co/papers/2411.01747) [पत्रों](https://huggingface.co/papers/2401.00812) ने दिखाया है कि कोड में टूल कॉलिंग LLM का होना बहुत बेहतर है।
|
| 88 |
+
|
| 89 |
+
इसका कारण बस यह है कि *हमने अपनी कोड भाषाओं को विशेष रूप से कंप्यूटर द्वारा किए गए कार्यों को व्यक्त करने का सर्वोत्तम संभव तरीका बनाने के लिए तैयार किया*। यदि JSON स्निपेट्स बेहतर अभिव्यक्ति होते, तो JSON शीर्ष प्रोग्रामिंग भाषा होती और प्रोग्रामिंग नरक में होती।
|
| 90 |
+
|
| 91 |
+
नीचे दी गई छवि, [Executable Code Actions Elicit Better LLM Agents](https://huggingface.co/papers/2402.01030) से ली गई है, जो कोड में क्रियाएं लिखने के कुछ फायदे दर्शाती है:
|
| 92 |
+
|
| 93 |
+
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/code_vs_json_actions.png">
|
| 94 |
+
|
| 95 |
+
JSON जैसे स्निपेट्स की बजाय कोड में क्रियाएं लिखने से बेहतर प्राप्त होता है:
|
| 96 |
+
|
| 97 |
+
- **कम्पोजेबिलिटी:** क्या आप JSON क्रियाओं को एक-दूसरे के भीतर नेस्ट कर सकते हैं, या बाद में पुन: उपयोग करने के लिए JSON क्रियाओं का एक सेट परिभाषित कर सकते हैं, उसी तरह जैसे आप बस एक पायथन फंक्शन परिभाषित कर सकते हैं?
|
| 98 |
+
- **ऑब्जेक्ट प्रबंधन:** आप `generate_image` जैसी क्रिया के आउटपुट को JSON में कैसे स्टोर करते हैं?
|
| 99 |
+
- **सामान्यता:** कोड को सरल रूप से कुछ भी व्यक्त करने के लिए बनाया गया है जो आप कंप्यूटर से करवा सकते हैं।
|
| 100 |
+
- **LLM प्रशिक्षण डेटा में प्रतिनिधित्व:** बहुत सारी गुणवत्तापूर्ण कोड क्रियाएं पहले से ही LLM के ट्रेनिंग डेटा में शामिल हैं जिसका मतलब है कि वे इसके लिए पहले से ही प्रशिक्षित हैं!
|
smolagents/docs/source/hi/conceptual_guides/react.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# मल्टी-स्टेप एजेंट्स कैसे काम करते हैं?
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
ReAct फ्रेमवर्क ([Yao et al., 2022](https://huggingface.co/papers/2210.03629)) वर्तमान में एजेंट्स बनाने का मुख्य दृष्टिकोण है।
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
नाम दो शब्दों, "Reason" (तर्क) और "Act" (क्रिया) के संयोजन पर आधारित है। वास्तव में, इस आर्किटेक्चर का पालन करने वाले एजेंट अपने कार्य को उतने चरणों में हल करेंगे जितने आवश्यक हों, प्रत्येक चरण में एक Reasoning कदम होगा, फिर एक Action कदम होगा, जहाँ यह टूल कॉल्स तैयार करेगा जो उसे कार्य को हल करने के करीब ले जाएंगे।
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
ReAct प्रक्रिया में पिछले चरणों की मेमोरी रखना शामिल है।
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 10 |
+
> मल्टी-स्टेप एजेंट्स के बारे में अधिक जानने के लिए [Open-source LLMs as LangChain Agents](https://huggingface.co/blog/open-source-llms-as-agents) ब्लॉग पोस्ट पढ़ें।
|
| 11 |
+
|
| 12 |
+
यहाँ एक वीडियो ओवरव्यू है कि यह कैसे काम करता है:
|
| 13 |
+
|
| 14 |
+
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
| 15 |
+
<img
|
| 16 |
+
class="block dark:hidden"
|
| 17 |
+
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/Agent_ManimCE.gif"
|
| 18 |
+
/>
|
| 19 |
+
<img
|
| 20 |
+
class="hidden dark:block"
|
| 21 |
+
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/Agent_ManimCE.gif"
|
| 22 |
+
/>
|
| 23 |
+
</div>
|
| 24 |
+
|
| 25 |
+
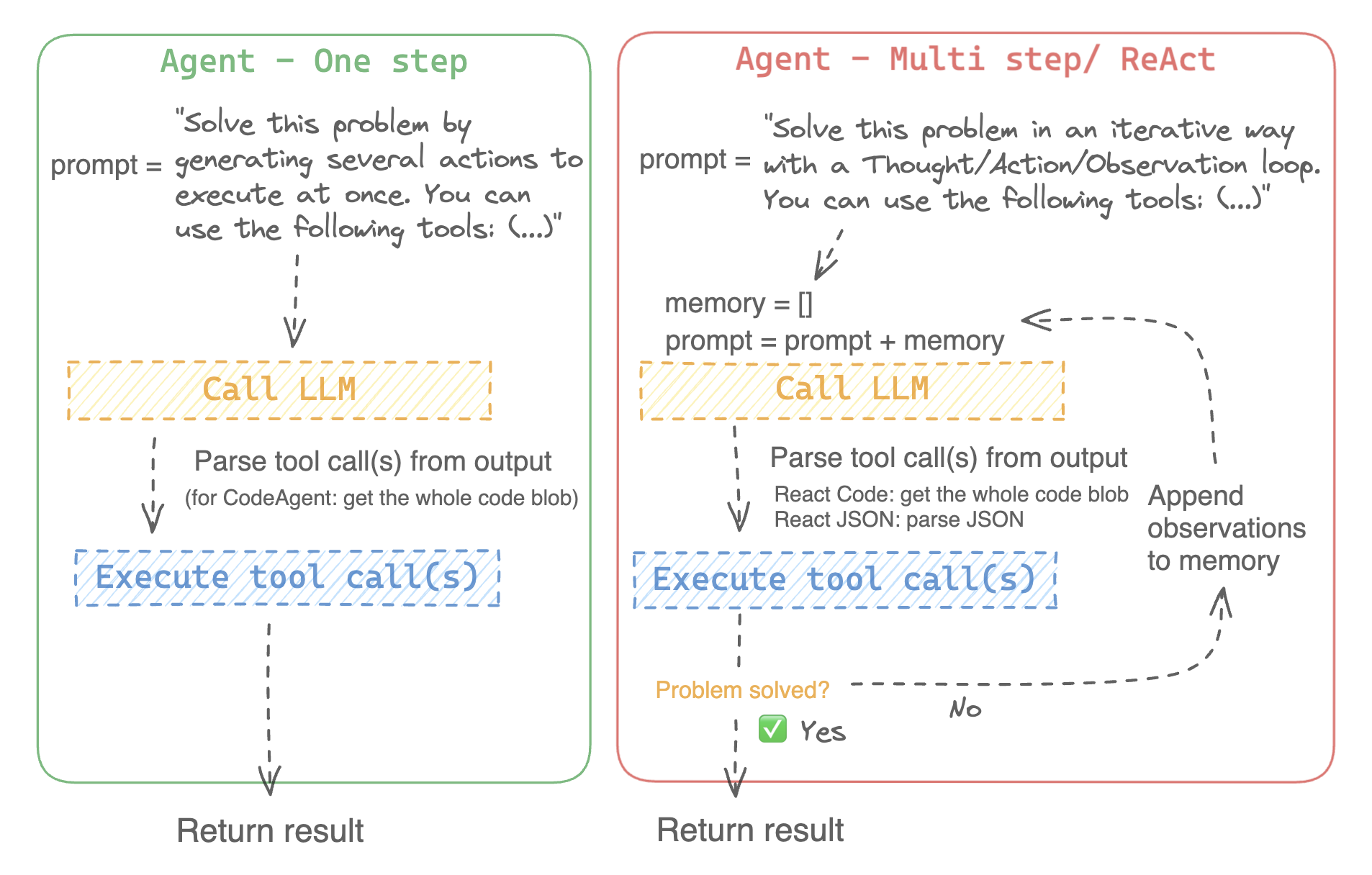
|
| 26 |
+
|
| 27 |
+
हम दो प्रकार के ToolCallingAgent को लागू करते हैं:
|
| 28 |
+
- [`ToolCallingAgent`] अपने आउटपुट में टूल कॉल को JSON के रूप में जनरेट करता है।
|
| 29 |
+
- [`CodeAgent`] ToolCallingAgent का एक नया प्रकार है जो अपने टूल कॉल को कोड के ब्लॉब्स के रूप में जनरेट करता है, जो उन LLM के लिए वास्तव में अच्छी तरह काम करता है जिनका कोडिंग प्रदर्शन मजबूत है।
|
smolagents/docs/source/hi/examples/multiagents.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,184 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# मल्टी-एजेंट सिस्टम का आयोजन करें 🤖🤝🤖
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
[[open-in-colab]]
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
इस नोटबुक में हम एक **मल्टी-एजेंट वेब ब्राउज़र बनाएंगे: एक एजेंटिक सिस्टम जिसमें कई एजेंट वेब का उपयोग करके समस्याओं को हल करने के लिए सहयोग करते हैं!**
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
यह एक सरल संरचना होगी, जो प्रबंधित वेब खोज एजेंट को रैप करने के लिए `ManagedAgent` ऑब्जेक्ट का उपयोग करता है:
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
```
|
| 10 |
+
+----------------+
|
| 11 |
+
| Manager agent |
|
| 12 |
+
+----------------+
|
| 13 |
+
|
|
| 14 |
+
_______________|______________
|
| 15 |
+
| |
|
| 16 |
+
Code interpreter +--------------------------------+
|
| 17 |
+
tool | Managed agent |
|
| 18 |
+
| +------------------+ |
|
| 19 |
+
| | Web Search agent | |
|
| 20 |
+
| +------------------+ |
|
| 21 |
+
| | | |
|
| 22 |
+
| Web Search tool | |
|
| 23 |
+
| Visit webpage tool |
|
| 24 |
+
+--------------------------------+
|
| 25 |
+
```
|
| 26 |
+
आइए इस सिस्टम को सेट करें।
|
| 27 |
+
|
| 28 |
+
आवश्यक डिपेंडेंसी इंस्टॉल करने के लिए नीचे दी गई लाइन चलाएं:
|
| 29 |
+
|
| 30 |
+
```
|
| 31 |
+
!pip install markdownify duckduckgo-search smolagents --upgrade -q
|
| 32 |
+
```
|
| 33 |
+
|
| 34 |
+
HF Inference API को कॉल करने के लिए लॉगिन करें:
|
| 35 |
+
|
| 36 |
+
```
|
| 37 |
+
from huggingface_hub import login
|
| 38 |
+
|
| 39 |
+
login()
|
| 40 |
+
```
|
| 41 |
+
|
| 42 |
+
⚡️ हमारा एजेंट [Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct](https://huggingface.co/Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct) द्वारा संचालित होगा जो `InferenceClientModel` क्लास का उपयोग करता है जो HF के Inference API का उपयोग करता है: Inference API किसी भी OS मॉडल को जल्दी और आसानी से चलाने की अनुमति देता है।
|
| 43 |
+
|
| 44 |
+
_नोट:_ The Inference API विभिन्न मानदंडों के आधार पर मॉडल होस्ट करता है, और डिप्लॉय किए गए मॉडल बिना पूर्व सूचना के अपडेट या बदले जा सकते हैं। इसके बारे में अधिक जानें [यहां](https://huggingface.co/docs/api-inference/supported-models)।
|
| 45 |
+
|
| 46 |
+
```py
|
| 47 |
+
model_id = "Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct"
|
| 48 |
+
```
|
| 49 |
+
|
| 50 |
+
## 🔍 एक वेब सर्च टूल बनाएं
|
| 51 |
+
|
| 52 |
+
वेब ब्राउज़िंग के लिए, हम पहले से मौजूद [`DuckDuckGoSearchTool`](https://github.com/huggingface/smolagents/blob/main/src/smolagents/default_tools.py#L151-L176) टूल का उपयोग कर सकते हैं जो Google search के समान सुविधा प्रदान करता है।
|
| 53 |
+
|
| 54 |
+
लेकिन फिर हमें `DuckDuckGoSearchTool` द्वारा खोजे गए पेज को देखने में भी सक्षम होने की आवश्यकता होगी।
|
| 55 |
+
ऐसा करने के लिए, हम लाइब्रेरी के बिल्ट-इन `VisitWebpageTool` को इम्पोर्ट कर सकते हैं, लेकिन हम इसे फिर से बनाएंगे यह देखने के लिए कि यह कैसे किया जाता है।
|
| 56 |
+
|
| 57 |
+
तो आइए `markdownify` का उपयोग करके शुरू से अपना `VisitWebpageTool` टूल बनाएं।
|
| 58 |
+
|
| 59 |
+
```py
|
| 60 |
+
import re
|
| 61 |
+
import requests
|
| 62 |
+
from markdownify import markdownify
|
| 63 |
+
from requests.exceptions import RequestException
|
| 64 |
+
from smolagents import tool
|
| 65 |
+
|
| 66 |
+
|
| 67 |
+
@tool
|
| 68 |
+
def visit_webpage(url: str) -> str:
|
| 69 |
+
"""Visits a webpage at the given URL and returns its content as a markdown string.
|
| 70 |
+
|
| 71 |
+
Args:
|
| 72 |
+
url: The URL of the webpage to visit.
|
| 73 |
+
|
| 74 |
+
Returns:
|
| 75 |
+
The content of the webpage converted to Markdown, or an error message if the request fails.
|
| 76 |
+
"""
|
| 77 |
+
try:
|
| 78 |
+
# Send a GET request to the URL
|
| 79 |
+
response = requests.get(url)
|
| 80 |
+
response.raise_for_status() # Raise an exception for bad status codes
|
| 81 |
+
|
| 82 |
+
# Convert the HTML content to Markdown
|
| 83 |
+
markdown_content = markdownify(response.text).strip()
|
| 84 |
+
|
| 85 |
+
# Remove multiple line breaks
|
| 86 |
+
markdown_content = re.sub(r"\n{3,}", "\n\n", markdown_content)
|
| 87 |
+
|
| 88 |
+
return markdown_content
|
| 89 |
+
|
| 90 |
+
except RequestException as e:
|
| 91 |
+
return f"Error fetching the webpage: {str(e)}"
|
| 92 |
+
except Exception as e:
|
| 93 |
+
return f"An unexpected error occurred: {str(e)}"
|
| 94 |
+
```
|
| 95 |
+
|
| 96 |
+
ठीक है, अब चलिए हमारे टूल को टेस्ट करें!
|
| 97 |
+
|
| 98 |
+
```py
|
| 99 |
+
print(visit_webpage("https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hugging_Face")[:500])
|
| 100 |
+
```
|
| 101 |
+
|
| 102 |
+
## हमारी मल्टी-एजेंट सिस्टम का निर्माण करें 🤖🤝🤖
|
| 103 |
+
|
| 104 |
+
अब जब हमारे पास सभी टूल्स `search` और `visit_webpage` हैं, हम उनका उपयोग वेब एजेंट बनाने के लिए कर सकते हैं।
|
| 105 |
+
|
| 106 |
+
इस एजेंट के लिए कौन सा कॉन्फ़िगरेशन चुनें?
|
| 107 |
+
- वेब ब्राउज़िंग एक सिंगल-टाइमलाइन टास्क है जिसे समानांतर टूल कॉल की आवश्यकता नहीं है, इसलिए JSON टूल कॉलिंग इसके लिए अच्छी तरह काम करती है। इसलिए हम `ToolCallingAgent` चुनते हैं।
|
| 108 |
+
- साथ ही, चूंकि कभी-कभी वेब सर्च में सही उत्तर खोजने से पहले कई पेजों की सर्च करने की आवश्यकता होती है, हम `max_steps` को बढ़ाकर 10 करना पसंद करते हैं।
|
| 109 |
+
|
| 110 |
+
```py
|
| 111 |
+
from smolagents import (
|
| 112 |
+
CodeAgent,
|
| 113 |
+
ToolCallingAgent,
|
| 114 |
+
InferenceClientModel,
|
| 115 |
+
ManagedAgent,
|
| 116 |
+
DuckDuckGoSearchTool,
|
| 117 |
+
LiteLLMModel,
|
| 118 |
+
)
|
| 119 |
+
|
| 120 |
+
model = InferenceClientModel(model_id=model_id)
|
| 121 |
+
|
| 122 |
+
web_agent = ToolCallingAgent(
|
| 123 |
+
tools=[DuckDuckGoSearchTool(), visit_webpage],
|
| 124 |
+
model=model,
|
| 125 |
+
max_steps=10,
|
| 126 |
+
)
|
| 127 |
+
```
|
| 128 |
+
|
| 129 |
+
फिर हम इस एजेंट को एक `ManagedAgent` में रैप करते हैं जो इसे इसके मैनेजर एजेंट द्वारा कॉल करने योग्य बनाएगा।
|
| 130 |
+
|
| 131 |
+
```py
|
| 132 |
+
managed_web_agent = ManagedAgent(
|
| 133 |
+
agent=web_agent,
|
| 134 |
+
name="search",
|
| 135 |
+
description="Runs web searches for you. Give it your query as an argument.",
|
| 136 |
+
)
|
| 137 |
+
```
|
| 138 |
+
|
| 139 |
+
अंत में हम एक मैनेजर एजेंट बनाते हैं, और इनिशियलाइजेशन पर हम अपने मैनेज्ड एजेंट को इसके `managed_agents` आर्गुमेंट में पास करते हैं।
|
| 140 |
+
|
| 141 |
+
चूंकि यह एजेंट योजना बनाने और सोचने का काम करता है, उन्नत तर्क लाभदायक होगा, इसलिए `CodeAgent` सबसे अच्छा विकल्प होगा।
|
| 142 |
+
|
| 143 |
+
साथ ही, हम एक ऐसा प्रश्न पूछना चाहते हैं जिसमें वर्तमान वर्ष और अतिरिक्त डेटा गणना शामिल है: इसलिए आइए `additional_authorized_imports=["time", "numpy", "pandas"]` जोड़ें, यदि एजेंट को इन पैकेजों की आवश्यकता हो।
|
| 144 |
+
|
| 145 |
+
```py
|
| 146 |
+
manager_agent = CodeAgent(
|
| 147 |
+
tools=[],
|
| 148 |
+
model=model,
|
| 149 |
+
managed_agents=[managed_web_agent],
|
| 150 |
+
additional_authorized_imports=["time", "numpy", "pandas"],
|
| 151 |
+
)
|
| 152 |
+
```
|
| 153 |
+
|
| 154 |
+
बस इतना ही! अब चलिए हमारे सिस्टम को चलाते हैं! हम एक ऐसा प्रश्न चुनते हैं जिसमें गणना और शोध दोनों की आवश्यकता है।
|
| 155 |
+
|
| 156 |
+
```py
|
| 157 |
+
answer = manager_agent.run("If LLM training continues to scale up at the current rhythm until 2030, what would be the electric power in GW required to power the biggest training runs by 2030? What would that correspond to, compared to some countries? Please provide a source for any numbers used.")
|
| 158 |
+
```
|
| 159 |
+
|
| 160 |
+
We get this report as the answer:
|
| 161 |
+
```
|
| 162 |
+
Based on current growth projections and energy consumption estimates, if LLM trainings continue to scale up at the
|
| 163 |
+
current rhythm until 2030:
|
| 164 |
+
|
| 165 |
+
1. The electric power required to power the biggest training runs by 2030 would be approximately 303.74 GW, which
|
| 166 |
+
translates to about 2,660,762 GWh/year.
|
| 167 |
+
|
| 168 |
+
2. Comparing this to countries' electricity consumption:
|
| 169 |
+
- It would be equivalent to about 34% of China's total electricity consumption.
|
| 170 |
+
- It would exceed the total electricity consumption of India (184%), Russia (267%), and Japan (291%).
|
| 171 |
+
- It would be nearly 9 times the electricity consumption of countries like Italy or Mexico.
|
| 172 |
+
|
| 173 |
+
3. Source of numbers:
|
| 174 |
+
- The initial estimate of 5 GW for future LLM training comes from AWS CEO Matt Garman.
|
| 175 |
+
- The growth projection used a CAGR of 79.80% from market research by Springs.
|
| 176 |
+
- Country electricity consumption data is from the U.S. Energy Information Administration, primarily for the year
|
| 177 |
+
2021.
|
| 178 |
+
```
|
| 179 |
+
|
| 180 |
+
लगता है कि यदि [स्केलिंग हाइपोथिसिस](https://gwern.net/scaling-hypothesis) सत्य बनी रहती है तो हमें कुछ बड़े पावरप्लांट्स की आवश्यकता होगी।
|
| 181 |
+
|
| 182 |
+
हमारे एजेंट्स ने कार्य को हल करने के लिए कुशलतापूर्वक सहयोग किया! ✅
|
| 183 |
+
|
| 184 |
+
💡 आप इस ऑर्केस्ट्रेशन को आसानी से अधिक एजेंट्स में विस्तारित कर सकते हैं: एक कोड एक्जीक्यूशन करता है, एक वेब सर्च करता है, एक फाइल लोडिंग को संभालता है।
|
smolagents/docs/source/hi/examples/rag.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# एजेंटिक RAG
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
[[open-in-colab]]
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
रिट्रीवल-ऑगमेंटेड-जनरेशन (RAG) है "एक यूजर के प्रश्न का उत्तर देने के लिए LLM का उपयोग करना, लेकिन उत्तर को एक नॉलेज बेस से प्राप्त जानकारी पर आधारित करना"। इसमें वैनिला या फाइन-ट्यून्ड LLM का उपयोग करने की तुलना में कई फायदे हैं: कुछ नाम लेने के लिए, यह उत्तर को सत्य तथ्यों पर आधारित करने और काल्पनिक बातों को कम करने की अनुमति देता है, यह LLM को डोमेन-विशिष्ट ज्ञान प्रदान करने की अनुमति देता है, और यह नॉलेज बेस से जानकारी तक पहुंच का सूक्ष्म नियंत्रण प्रदान करता है।
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
लेकिन वैनिला RAG की सीमाएं हैं, सबसे महत्वपूर्ण ये दो:
|
| 8 |
+
- यह केवल एक रिट्रीवल स्टेप करता है: यदि परिणाम खराब हैं, तो जनरेशन भी बदले में खराब होगा।
|
| 9 |
+
- सिमेंटिक समानता की गणना यूजर के प्रश्न को संदर्भ के रूप में करके की जाती है, जो अनुकूल नहीं हो सकती: उदाहरण के लिए, यूजर का प्रश्न अक्सर एक सवाल होगा, जबकि सही उत्तर देने वाला डॉक्यूमेंट सकारात्मक स्वर में हो सकता है, और इसका समानता स्कोर अन्य स्रोत दस्तावेज़ों की तुलना में कम हो सकता है, जो प्रश्नवाचक स्वर में हो सकते हैं। इससे संबंधित जानकारी को चूकने का जोखिम होता है।
|
| 10 |
+
|
| 11 |
+
हम एक RAG एजेंट बनाकर इन समस्याओं को कम कर सकते हैं: बहुत सरल तरीके से, एक रिट्रीवर टूल से लैस एजेंट!
|
| 12 |
+
|
| 13 |
+
यह एजेंट करेगा: ✅ स्वयं क्वेरी तैयार करेगा और ✅ आवश्यकता पड़ने पर पुनः-प्राप्ति के लिए समीक्षा करेगा।
|
| 14 |
+
|
| 15 |
+
इसलिए यह सहज रूप से कुछ उन्नत RAG तकनीकों को प्राप्त कर लेना चाहिए!
|
| 16 |
+
- सिमेंटिक खोज में सीधे यूजर क्वेरी का संदर्भ के रूप में उपयोग करने के बजाय, एजेंट स्वयं एक संदर्भ वाक्य तैयार करता है जो लक्षित डॉक्यूमेंट्स के करीब हो सकता है, जैसा कि [HyDE](https://huggingface.co/papers/2212.10496) में किया गया है।
|
| 17 |
+
एजेंट जनरेट किए गए स्निपेट्स का उपयोग कर सकता है और आवश्यकता पड़ने पर पुनः-प्राप्ति कर सकता है, जैसा कि [Self-Query](https://docs.llamaindex.ai/en/stable/examples/evaluation/RetryQuery/) में किया गया है।
|
| 18 |
+
|
| 19 |
+
चलिए इस सिस्टम को बनाते हैं। 🛠️
|
| 20 |
+
|
| 21 |
+
आवश्यक डिपेंडेंसी इंस्टॉल करने के लिए नीचे दी गई लाइन चलाएं।
|
| 22 |
+
```bash
|
| 23 |
+
!pip install smolagents pandas langchain langchain-community sentence-transformers rank_bm25 --upgrade -q
|
| 24 |
+
```
|
| 25 |
+
HF Inference API को कॉल करने के लिए, आपको अपने एनवायरनमेंट वेरिएबल `HF_TOKEN` के रूप में एक वैध टोकन की आवश्यकता होगी।
|
| 26 |
+
हम इसे लोड करने के लिए python-dotenv का उपयोग करते हैं।
|
| 27 |
+
```py
|
| 28 |
+
from dotenv import load_dotenv
|
| 29 |
+
load_dotenv()
|
| 30 |
+
```
|
| 31 |
+
|
| 32 |
+
हम पहले एक नॉलेज बेस लोड करते हैं जि��� पर हम RAG को लागू करना चाहते हैं: यह डेटा सेट Hugging Face के कई लाइब्रेरी के डॉक्यूमेंट पृष्ठों का संकलन है, जिन्हें Markdown में स्टोर किया गया है। हम केवल `transformers` लाइब्रेरी के दस्तावेज़ों को रखेंगे।
|
| 33 |
+
|
| 34 |
+
फिर डेटासेट को प्रोसेस करके और इसे एक वेक्टर डेटाबेस में स्टोर करके नॉलेज बेस तैयार करें जिसे रिट्रीवर द्वारा उपयोग किया जाएगा।
|
| 35 |
+
|
| 36 |
+
हम [LangChain](https://python.langchain.com/docs/introduction/) का उपयोग करते हैं क्योंकि इसमें उत्कृष्ट वेक्टर डेटाबेस उपयोगिताएं हैं।
|
| 37 |
+
|
| 38 |
+
```py
|
| 39 |
+
import datasets
|
| 40 |
+
from langchain.docstore.document import Document
|
| 41 |
+
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
|
| 42 |
+
from langchain_community.retrievers import BM25Retriever
|
| 43 |
+
|
| 44 |
+
knowledge_base = datasets.load_dataset("m-ric/huggingface_doc", split="train")
|
| 45 |
+
knowledge_base = knowledge_base.filter(lambda row: row["source"].startswith("huggingface/transformers"))
|
| 46 |
+
|
| 47 |
+
source_docs = [
|
| 48 |
+
Document(page_content=doc["text"], metadata={"source": doc["source"].split("/")[1]})
|
| 49 |
+
for doc in knowledge_base
|
| 50 |
+
]
|
| 51 |
+
|
| 52 |
+
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
|
| 53 |
+
chunk_size=500,
|
| 54 |
+
chunk_overlap=50,
|
| 55 |
+
add_start_index=True,
|
| 56 |
+
strip_whitespace=True,
|
| 57 |
+
separators=["\n\n", "\n", ".", " ", ""],
|
| 58 |
+
)
|
| 59 |
+
docs_processed = text_splitter.split_documents(source_docs)
|
| 60 |
+
```
|
| 61 |
+
|
| 62 |
+
अब डॉक्यूमेंट्स तैयार हैं।
|
| 63 |
+
|
| 64 |
+
तो चलिए अपना एजेंटिक RAG सिस्टम बनाएं!
|
| 65 |
+
|
| 66 |
+
👉 हमें केवल एक RetrieverTool की आवश्यकता है जिसका उपयोग हमारा एजेंट नॉलेज बेस से जानकारी प्राप्त करने के लिए कर सकता है।
|
| 67 |
+
|
| 68 |
+
चूंकि हमें टूल के एट्रीब्यूट के रूप में एक vectordb जोड़ने की आवश्यकता है, हम सरल टूल कंस्ट्रक्टर को `@tool` डेकोरेटर के साथ सीधे उपयोग नहीं कर सकते: इसलिए हम [tools tutorial](../tutorials/tools) में हाइलाइट किए गए सेटअप का पालन करेंगे।
|
| 69 |
+
|
| 70 |
+
```py
|
| 71 |
+
from smolagents import Tool
|
| 72 |
+
|
| 73 |
+
class RetrieverTool(Tool):
|
| 74 |
+
name = "retriever"
|
| 75 |
+
description = "Uses semantic search to retrieve the parts of transformers documentation that could be most relevant to answer your query."
|
| 76 |
+
inputs = {
|
| 77 |
+
"query": {
|
| 78 |
+
"type": "string",
|
| 79 |
+
"description": "The query to perform. This should be semantically close to your target documents. Use the affirmative form rather than a question.",
|
| 80 |
+
}
|
| 81 |
+
}
|
| 82 |
+
output_type = "string"
|
| 83 |
+
|
| 84 |
+
def __init__(self, docs, **kwargs):
|
| 85 |
+
super().__init__(**kwargs)
|
| 86 |
+
self.retriever = BM25Retriever.from_documents(
|
| 87 |
+
docs, k=10
|
| 88 |
+
)
|
| 89 |
+
|
| 90 |
+
def forward(self, query: str) -> str:
|
| 91 |
+
assert isinstance(query, str), "Your search query must be a string"
|
| 92 |
+
|
| 93 |
+
docs = self.retriever.invoke(
|
| 94 |
+
query,
|
| 95 |
+
)
|
| 96 |
+
return "\nRetrieved documents:\n" + "".join(
|
| 97 |
+
[
|
| 98 |
+
f"\n\n===== Document {str(i)} =====\n" + doc.page_content
|
| 99 |
+
for i, doc in enumerate(docs)
|
| 100 |
+
]
|
| 101 |
+
)
|
| 102 |
+
|
| 103 |
+
retriever_tool = RetrieverTool(docs_processed)
|
| 104 |
+
```
|
| 105 |
+
हमने BM25 का उपयोग किया है, जो एक क्लासिक रिट्रीवल विधि है, क्योंकि इसे सेटअप करना बहुत आसान है।
|
| 106 |
+
रिट्रीवल सटीकता में सुधार करने के लिए, आप BM25 को डॉक्यूमेंट्स के लिए वेक्टर प्रतिनिधित्व का उपयोग करके सिमेंटिक खोज से बदल सकते हैं: इस प्रकार आप एक अच्छा एम्बेडिंग मॉडल चुनने के लिए [MTEB Leaderboard](https://huggingface.co/spaces/mteb/leaderboard) पर जा सकते हैं।
|
| 107 |
+
|
| 108 |
+
अब यह सीधा है कि एक एजेंट बनाया जाए जो इस `retriever_tool` का उपयोग करेगा!
|
| 109 |
+
|
| 110 |
+
|
| 111 |
+
एजेंट को इनिशियलाइजेशन पर इन आर्गुमेंट्स की आवश्यकता होगी:
|
| 112 |
+
- `tools`: टूल्स की एक सूची जिन्हें एजेंट कॉल कर सकेगा।
|
| 113 |
+
- `model`: LLM जो एजेंट को पावर देता है।
|
| 114 |
+
हमारा `model` एक कॉलेबल होना चाहिए जो इनपुट के रूप में संदेशों की एक सूची लेता है और टेक्स्ट लौटाता है। इसे एक stop_sequences आर्गुमेंट भी स्वीकार करने की आवश्यकता है जो बताता है कि जनरेशन कब रोकनी है। सुविधा के लिए, हम सीधे पैकेज में प्रदान की गई HfEngine क्लास का उपयोग करते हैं ताकि एक LLM इंजन मिल सके जो Hugging Face के Inference API को कॉल करता है।
|
| 115 |
+
|
| 116 |
+
और हम [meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct](meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct) का उपयोग llm इंजन के रूप में करते हैं क्योंकि:
|
| 117 |
+
- इसमें लंबा 128k कॉन्टेक्स्ट है, जो लंबे स्रोत दस्तावेजों को प्रोसेस करने में मददगार है
|
| 118 |
+
- यह हर समय HF के Inference API पर मुफ्त में उपलब्ध है!
|
| 119 |
+
|
| 120 |
+
_नोट:_ Inference API विभिन्न मानदंडों के आधार पर मॉडल होस्ट करता है, और डिप्लॉय किए गए मॉडल बिना पूर्व सूचना के अपडेट या बदले जा सकते हैं। इसके बारे में अधिक जानें [यहां](https://huggingface.co/docs/api-inference/supported-models) पढ़ें।
|
| 121 |
+
|
| 122 |
+
```py
|
| 123 |
+
from smolagents import InferenceClientModel, CodeAgent
|
| 124 |
+
|
| 125 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(
|
| 126 |
+
tools=[retriever_tool], model=InferenceClientModel(model_id="meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct"), max_steps=4, verbosity_level=2
|
| 127 |
+
)
|
| 128 |
+
```
|
| 129 |
+
|
| 130 |
+
CodeAgent को इनिशियलाइज करने पर, इसे स्वचालित रूप से एक डिफ़ॉल्ट सिस्टम प्रॉम्प्ट दिया गया है जो LLM इंजन को चरण-दर-चरण प्रोसेस करने और कोड स्निपेट्स के रूप में टूल कॉल जनरेट करने के लिए कहता है, लेकिन आप आवश्यकतानुसार इस प्रॉम्प्ट टेम्पलेट को अपने से बदल सकते हैं।
|
| 131 |
+
|
| 132 |
+
जब CodeAgent का `.run()` मेथड लॉन्च किया जाता है, तो एजेंट LLM इंजन को कॉल करने का कार्य करता है, और टूल कॉल्स को निष्पादित करता है, यह सब एक लूप में होता है, जो तब तक चलता है जब तक टूल final_answer के साथ अंतिम उत्तर के रूप में नहीं बुलाया जाता।
|
| 133 |
+
|
| 134 |
+
```py
|
| 135 |
+
agent_output = agent.run("For a transformers model training, which is slower, the forward or the backward pass?")
|
| 136 |
+
|
| 137 |
+
print("Final output:")
|
| 138 |
+
print(agent_output)
|
| 139 |
+
```
|
| 140 |
+
|
| 141 |
+
|
smolagents/docs/source/hi/examples/text_to_sql.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,188 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Text-to-SQL
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
[[open-in-colab]]
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
इस ट्यूटोरियल में, हम देखेंगे कि कैसे `smolagents` का उपयोग करके एक एजेंट को SQL का उपयोग करने के लिए लागू किया जा सकता है।
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
> आइए सबसे महत्वपूर्ण प्रश्न से शुरू करें: इसे साधारण क्यों नहीं रखें और एक सामान्य text-to-SQL पाइपलाइन का उपयोग करें?
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
एक सामान्य text-to-SQL पाइपलाइन कमजोर होती है, क्योंकि उत्पन्न SQL क्वेरी गलत हो सकती है। इससे भी बुरी बात यह है कि क्वेरी गलत हो सकती है, लेकिन कोई एरर नहीं दिखाएगी, बल्कि बिना किसी अलार्म के गलत/बेकार आउटपुट दे सकती है।
|
| 10 |
+
|
| 11 |
+
|
| 12 |
+
👉 इसके बजाय, एक एजेंट सिस्टम आउटपुट का गंभीरता से निरीक्षण कर सकता है और तय कर सकता है कि क्वेरी को बदलने की जरूरत है या नहीं, इस प्रकार इसे बेहतर प्रदर्शन में मदद मिलती है।
|
| 13 |
+
|
| 14 |
+
आइए इस एजेंट को बनाएं! 💪
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
पहले, हम SQL एनवायरनमेंट सेटअप करते हैं:
|
| 17 |
+
```py
|
| 18 |
+
from sqlalchemy import (
|
| 19 |
+
create_engine,
|
| 20 |
+
MetaData,
|
| 21 |
+
Table,
|
| 22 |
+
Column,
|
| 23 |
+
String,
|
| 24 |
+
Integer,
|
| 25 |
+
Float,
|
| 26 |
+
insert,
|
| 27 |
+
inspect,
|
| 28 |
+
text,
|
| 29 |
+
)
|
| 30 |
+
|
| 31 |
+
engine = create_engine("sqlite:///:memory:")
|
| 32 |
+
metadata_obj = MetaData()
|
| 33 |
+
|
| 34 |
+
# create city SQL table
|
| 35 |
+
table_name = "receipts"
|
| 36 |
+
receipts = Table(
|
| 37 |
+
table_name,
|
| 38 |
+
metadata_obj,
|
| 39 |
+
Column("receipt_id", Integer, primary_key=True),
|
| 40 |
+
Column("customer_name", String(16), primary_key=True),
|
| 41 |
+
Column("price", Float),
|
| 42 |
+
Column("tip", Float),
|
| 43 |
+
)
|
| 44 |
+
metadata_obj.create_all(engine)
|
| 45 |
+
|
| 46 |
+
rows = [
|
| 47 |
+
{"receipt_id": 1, "customer_name": "Alan Payne", "price": 12.06, "tip": 1.20},
|
| 48 |
+
{"receipt_id": 2, "customer_name": "Alex Mason", "price": 23.86, "tip": 0.24},
|
| 49 |
+
{"receipt_id": 3, "customer_name": "Woodrow Wilson", "price": 53.43, "tip": 5.43},
|
| 50 |
+
{"receipt_id": 4, "customer_name": "Margaret James", "price": 21.11, "tip": 1.00},
|
| 51 |
+
]
|
| 52 |
+
for row in rows:
|
| 53 |
+
stmt = insert(receipts).values(**row)
|
| 54 |
+
with engine.begin() as connection:
|
| 55 |
+
cursor = connection.execute(stmt)
|
| 56 |
+
```
|
| 57 |
+
|
| 58 |
+
### Agent बनाएं
|
| 59 |
+
|
| 60 |
+
अब आइए हमारी SQL टेबल को एक टूल द्वारा पुनर्प्राप्त करने योग्य बनाएं।
|
| 61 |
+
|
| 62 |
+
टूल का विवरण विशेषता एजेंट सिस्टम द्वारा LLM के prompt में एम्बेड किया जाएगा: यह LLM को टूल का उपयोग करने के बारे में जानकारी देता है। यहीं पर हम SQL टेबल का वर्णन करना चाहते हैं।
|
| 63 |
+
|
| 64 |
+
```py
|
| 65 |
+
inspector = inspect(engine)
|
| 66 |
+
columns_info = [(col["name"], col["type"]) for col in inspector.get_columns("receipts")]
|
| 67 |
+
|
| 68 |
+
table_description = "Columns:\n" + "\n".join([f" - {name}: {col_type}" for name, col_type in columns_info])
|
| 69 |
+
print(table_description)
|
| 70 |
+
```
|
| 71 |
+
|
| 72 |
+
```text
|
| 73 |
+
Columns:
|
| 74 |
+
- receipt_id: INTEGER
|
| 75 |
+
- customer_name: VARCHAR(16)
|
| 76 |
+
- price: FLOAT
|
| 77 |
+
- tip: FLOAT
|
| 78 |
+
```
|
| 79 |
+
|
| 80 |
+
अब आइए हमारा टूल बनाएं। इसे निम्नलिखित की आवश्यकता है: (अधिक जानकारी के लिए [टूल doc](../tutorials/tools) पढ़ें)
|
| 81 |
+
- एक डॉकस्ट्रिंग जिसमें आर्ग्युमेंट्स की सूची वाला `Args:` भाग हो।
|
| 82 |
+
- इनपुट और आउटपुट दोनों पर टाइप हिंट्स।
|
| 83 |
+
|
| 84 |
+
```py
|
| 85 |
+
from smolagents import tool
|
| 86 |
+
|
| 87 |
+
@tool
|
| 88 |
+
def sql_engine(query: str) -> str:
|
| 89 |
+
"""
|
| 90 |
+
Allows you to perform SQL queries on the table. Returns a string representation of the result.
|
| 91 |
+
The table is named 'receipts'. Its description is as follows:
|
| 92 |
+
Columns:
|
| 93 |
+
- receipt_id: INTEGER
|
| 94 |
+
- customer_name: VARCHAR(16)
|
| 95 |
+
- price: FLOAT
|
| 96 |
+
- tip: FLOAT
|
| 97 |
+
|
| 98 |
+
Args:
|
| 99 |
+
query: The query to perform. This should be correct SQL.
|
| 100 |
+
"""
|
| 101 |
+
output = ""
|
| 102 |
+
with engine.connect() as con:
|
| 103 |
+
rows = con.execute(text(query))
|
| 104 |
+
for row in rows:
|
| 105 |
+
output += "\n" + str(row)
|
| 106 |
+
return output
|
| 107 |
+
```
|
| 108 |
+
|
| 109 |
+
अब आइए एक ���जेंट बनाएं जो इस टूल का लाभ उठाता है।
|
| 110 |
+
|
| 111 |
+
हम `CodeAgent` का उपयोग करते हैं, जो smolagents का मुख्य एजेंट क्लास है: एक एजेंट जो कोड में एक्शन लिखता है और ReAct फ्रेमवर्क के अनुसार पिछले आउटपुट पर पुनरावृत्ति कर सकता है।
|
| 112 |
+
|
| 113 |
+
मॉडल वह LLM है जो एजेंट सिस्टम को संचालित करता है। `InferenceClientModel` आपको HF के Inference API का उपयोग करके LLM को कॉल करने की अनुमति देता है, या तो सर्वरलेस या डेडिकेटेड एंडपॉइंट के माध्यम से, लेकिन आप किसी भी प्रोप्राइटरी API का भी उपयोग कर सकते हैं।
|
| 114 |
+
|
| 115 |
+
```py
|
| 116 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel
|
| 117 |
+
|
| 118 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(
|
| 119 |
+
tools=[sql_engine],
|
| 120 |
+
model=InferenceClientModel(model_id="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct"),
|
| 121 |
+
)
|
| 122 |
+
agent.run("Can you give me the name of the client who got the most expensive receipt?")
|
| 123 |
+
```
|
| 124 |
+
|
| 125 |
+
### लेवल 2: टेबल जॉइन्स
|
| 126 |
+
|
| 127 |
+
अब आइए इसे और चुनौतीपूर्ण बनाएं! हम चाहते हैं कि हमारा एजेंट कई टेबल्स के बीच जॉइन को संभाल सके।
|
| 128 |
+
|
| 129 |
+
तो आइए हम प्रत्येक receipt_id के लिए वेटर्स के नाम रिकॉर्ड करने वाली एक दूसरी टेबल बनाते हैं!
|
| 130 |
+
|
| 131 |
+
```py
|
| 132 |
+
table_name = "waiters"
|
| 133 |
+
receipts = Table(
|
| 134 |
+
table_name,
|
| 135 |
+
metadata_obj,
|
| 136 |
+
Column("receipt_id", Integer, primary_key=True),
|
| 137 |
+
Column("waiter_name", String(16), primary_key=True),
|
| 138 |
+
)
|
| 139 |
+
metadata_obj.create_all(engine)
|
| 140 |
+
|
| 141 |
+
rows = [
|
| 142 |
+
{"receipt_id": 1, "waiter_name": "Corey Johnson"},
|
| 143 |
+
{"receipt_id": 2, "waiter_name": "Michael Watts"},
|
| 144 |
+
{"receipt_id": 3, "waiter_name": "Michael Watts"},
|
| 145 |
+
{"receipt_id": 4, "waiter_name": "Margaret James"},
|
| 146 |
+
]
|
| 147 |
+
for row in rows:
|
| 148 |
+
stmt = insert(receipts).values(**row)
|
| 149 |
+
with engine.begin() as connection:
|
| 150 |
+
cursor = connection.execute(stmt)
|
| 151 |
+
```
|
| 152 |
+
चूंकि हमने टेबल को बदल दिया है, हम LLM को इस टेबल की जानकारी का उचित उपयोग करने देने के लिए इस टेबल के विवरण के साथ `SQLExecutorTool` को अपडेट करते हैं।
|
| 153 |
+
|
| 154 |
+
```py
|
| 155 |
+
updated_description = """Allows you to perform SQL queries on the table. Beware that this tool's output is a string representation of the execution output.
|
| 156 |
+
It can use the following tables:"""
|
| 157 |
+
|
| 158 |
+
inspector = inspect(engine)
|
| 159 |
+
for table in ["receipts", "waiters"]:
|
| 160 |
+
columns_info = [(col["name"], col["type"]) for col in inspector.get_columns(table)]
|
| 161 |
+
|
| 162 |
+
table_description = f"Table '{table}':\n"
|
| 163 |
+
|
| 164 |
+
table_description += "Columns:\n" + "\n".join([f" - {name}: {col_type}" for name, col_type in columns_info])
|
| 165 |
+
updated_description += "\n\n" + table_description
|
| 166 |
+
|
| 167 |
+
print(updated_description)
|
| 168 |
+
```
|
| 169 |
+
चूंकि यह रिक्वेस्ट पिछले वाले से थोड़ी कठिन है, हम LLM इंजन को अधिक शक्तिशाली [Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct](https://huggingface.co/Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct) का उपयोग करने के लिए स्विच करेंगे!
|
| 170 |
+
|
| 171 |
+
```py
|
| 172 |
+
sql_engine.description = updated_description
|
| 173 |
+
|
| 174 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(
|
| 175 |
+
tools=[sql_engine],
|
| 176 |
+
model=InferenceClientModel(model_id="Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct"),
|
| 177 |
+
)
|
| 178 |
+
|
| 179 |
+
agent.run("Which waiter got more total money from tips?")
|
| 180 |
+
```
|
| 181 |
+
यह सीधे काम करता है! सेटअप आश्चर्यजनक रूप से सरल था, है ना?
|
| 182 |
+
|
| 183 |
+
यह उदाहरण पूरा हो गया! हमने इन अवधारणाओं को छुआ है:
|
| 184 |
+
- नए टूल्स का निर्माण।
|
| 185 |
+
- टूल के विवरण को अपडेट करना।
|
| 186 |
+
- एक मजबूत LLM में स्विच करने से एजेंट की तर्कशक्ति में मदद मिलती है।
|
| 187 |
+
|
| 188 |
+
✅ अब आप वह text-to-SQL सिस्टम बना सकते हैं जिसका आपने हमेशा सपना देखा है! ✨
|
smolagents/docs/source/hi/guided_tour.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,345 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Agents - गाइडेड टूर
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
[[open-in-colab]]
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
इस गाइडेड विजिट में, आप सीखेंगे कि एक एजेंट कैसे बनाएं, इसे कैसे चलाएं, और अपने यूज-केस के लिए बेहतर काम करने के लिए इसे कैसे कस्टमाइज़ करें।
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
### अपना Agent बनाना
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
एक मिनिमल एजेंट को इनिशियलाइज़ करने के लिए, आपको कम से कम इन दो आर्ग्यूमेंट्स की आवश्यकता है:
|
| 10 |
+
|
| 11 |
+
- `model`, आपके एजेंट को पावर देने के लिए एक टेक्स्ट-जनरेशन मॉडल - क्योंकि एजेंट एक सिंपल LLM से अलग है, यह एक सिस्टम है जो LLM को अपने इंजन के रूप में उपयोग करता है। आप इनमें से कोई भी विकल्प उपयोग कर सकते हैं:
|
| 12 |
+
- [`TransformersModel`] `transformers` पाइपलाइन को पहले से इनिशियलाइज़ करता है जो `transformers` का उपयोग करके आपकी लोकल मशीन पर इन्फरेंस चलाने के लिए होता है।
|
| 13 |
+
- [`InferenceClientModel`] अंदर से `huggingface_hub.InferenceClient` का लाभ उठाता है।
|
| 14 |
+
- [`LiteLLMModel`] आपको [LiteLLM](https://docs.litellm.ai/) के माध्यम से 100+ अलग-अलग मॉडल्स को कॉल करने देता है!
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
- `tools`, `Tools` की एक लिस्ट जिसे एजेंट टास्क को हल करने के लिए उपयोग कर सकता है। यह एक खाली लिस्ट हो सकती है। आप ऑप्शनल आर्ग्यूमेंट `add_base_tools=True` को परिभाषित करके अपनी `tools` लिस्ट के ऊपर डिफ़ॉल्ट टूलबॉक्स भी जोड़ सकते हैं।
|
| 17 |
+
|
| 18 |
+
एक बार जब आपके पास ये दो आर्ग्यूमेंट्स, `tools` और `model` हैं, तो आप एक एजेंट बना सकते हैं और इसे चला सकते हैं। आप कोई भी LLM उपयोग कर सकते हैं, या तो [Hugging Face API](https://huggingface.co/docs/api-inference/en/index), [transformers](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/), [ollama](https://ollama.com/), या [LiteLLM](https://www.litellm.ai/) के माध्यम से।
|
| 19 |
+
|
| 20 |
+
<hfoptions id="एक LLM चुनें">
|
| 21 |
+
<hfoption id="Hugging Face API">
|
| 22 |
+
|
| 23 |
+
Hugging Face API टोकन के बिना उपयोग करने के लिए मुफ्त है, लेकिन फिर इसमें रेट लिमिटेशन होगी।
|
| 24 |
+
|
| 25 |
+
गेटेड मॉडल्स तक पहुंचने या PRO अकाउंट के साथ अपनी रेट लिमिट्स बढ़ाने के लिए, आपको एनवायरनमेंट वेरिएबल `HF_TOKEN` सेट करना होगा या `InferenceClientModel` के इनिशियलाइजेशन पर `token` वेरिएबल पास करना होगा।
|
| 26 |
+
|
| 27 |
+
```python
|
| 28 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel
|
| 29 |
+
|
| 30 |
+
model_id = "meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct"
|
| 31 |
+
|
| 32 |
+
model = InferenceClientModel(model_id=model_id, token="<YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>")
|
| 33 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
|
| 34 |
+
|
| 35 |
+
agent.run(
|
| 36 |
+
"Could you give me the 118th number in the Fibonacci sequence?",
|
| 37 |
+
)
|
| 38 |
+
```
|
| 39 |
+
</hfoption>
|
| 40 |
+
<hfoption id="Local Transformers Model">
|
| 41 |
+
|
| 42 |
+
```python
|
| 43 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, TransformersModel
|
| 44 |
+
|
| 45 |
+
model_id = "meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct"
|
| 46 |
+
|
| 47 |
+
model = TransformersModel(model_id=model_id)
|
| 48 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
|
| 49 |
+
|
| 50 |
+
agent.run(
|
| 51 |
+
"Could you give me the 118th number in the Fibonacci sequence?",
|
| 52 |
+
)
|
| 53 |
+
```
|
| 54 |
+
</hfoption>
|
| 55 |
+
<hfoption id="OpenAI या Anthropic API">
|
| 56 |
+
|
| 57 |
+
`LiteLLMModel` का उपयोग करने के लिए, आपको एनवायरनमेंट वेरिएबल `ANTHROPIC_API_KEY` या `OPENAI_API_KEY` सेट करना होगा, या इनिशियलाइजेशन पर `api_key` वेरिएबल पास करना होगा।
|
| 58 |
+
|
| 59 |
+
```python
|
| 60 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, LiteLLMModel
|
| 61 |
+
|
| 62 |
+
model = LiteLLMModel(model_id="anthropic/claude-3-5-sonnet-latest", api_key="YOUR_ANTHROPIC_API_KEY") # Could use 'gpt-4o'
|
| 63 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
|
| 64 |
+
|
| 65 |
+
agent.run(
|
| 66 |
+
"Could you give me the 118th number in the Fibonacci sequence?",
|
| 67 |
+
)
|
| 68 |
+
```
|
| 69 |
+
</hfoption>
|
| 70 |
+
<hfoption id="Ollama">
|
| 71 |
+
|
| 72 |
+
```python
|
| 73 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, LiteLLMModel
|
| 74 |
+
|
| 75 |
+
model = LiteLLMModel(
|
| 76 |
+
model_id="ollama_chat/llama3.2", # This model is a bit weak for agentic behaviours though
|
| 77 |
+
api_base="http://localhost:11434", # replace with 127.0.0.1:11434 or remote open-ai compatible server if necessary
|
| 78 |
+
api_key="YOUR_API_KEY" # replace with API key if necessary
|
| 79 |
+
num_ctx=8192 # ollama default is 2048 which will fail horribly. 8192 works for easy tasks, more is better. Check https://huggingface.co/spaces/NyxKrage/LLM-Model-VRAM-Calculator to calculate how much VRAM this will need for the selected model.
|
| 80 |
+
)
|
| 81 |
+
|
| 82 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
|
| 83 |
+
|
| 84 |
+
agent.run(
|
| 85 |
+
"Could you give me the 118th number in the Fibonacci sequence?",
|
| 86 |
+
)
|
| 87 |
+
```
|
| 88 |
+
</hfoption>
|
| 89 |
+
</hfoptions>
|
| 90 |
+
|
| 91 |
+
#### CodeAgent और ToolCallingAgent
|
| 92 |
+
|
| 93 |
+
[`CodeAgent`] हमारा डिफ़ॉल्ट एजेंट है। यह हर स्टेप पर पायथन कोड स्निपेट्स लिखेगा और एक्जीक्यूट करेगा।
|
| 94 |
+
|
| 95 |
+
डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से, एक्जीक्यूशन आपके लोकल एनवायरनमेंट में किया जाता है।
|
| 96 |
+
यह सुरक्षित होना चाहिए क्योंकि केवल वही फ़ंक्शंस कॉल किए जा सकते हैं जो आपने प्रदान किए हैं (विशेष रूप से यदि यह केवल Hugging Face टूल्स हैं) और पूर्व-परिभाषित सुरक्षित फ़ंक्शंस जैसे `print` या `math` मॉड्यूल से फ़ंक्शंस, इसलिए आप पहले से ही सीमित हैं कि क्या एक्जीक्यूट किया जा सकता है।
|
| 97 |
+
|
| 98 |
+
पायथन इंटरप्रेटर डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से सेफ लिस्ट के बाहर इम्पोर्ट की अनुमति नहीं देता है, इसलिए सबसे स्पष्ट अटैक समस्या नहीं होनी चाहिए।
|
| 99 |
+
आप अपने [`CodeAgent`] के इनिशियलाइजेशन पर आर्ग्यूमेंट `additional_authorized_imports` में स्ट्रिंग्स की लिस्ट के रूप में अतिरिक्त मॉड्यूल्स को अधिकृत कर सकते हैं।
|
| 100 |
+
|
| 101 |
+
```py
|
| 102 |
+
model = InferenceClientModel()
|
| 103 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, additional_authorized_imports=['requests', 'bs4'])
|
| 104 |
+
agent.run("Could you get me the title of the page at url 'https://huggingface.co/blog'?")
|
| 105 |
+
```
|
| 106 |
+
|
| 107 |
+
> [!WARNING]
|
| 108 |
+
> LLM आर्बिट्ररी कोड जनरेट कर सकता है जो फिर एक्जीक्यूट किया जाएगा: कोई असुरक्षित इम्पोर्ट न जोड़ें!
|
| 109 |
+
|
| 110 |
+
एक्जीक्यूशन किसी भी कोड पर रुक जाएगा जो एक अवैध ऑपरेशन करने का प्रयास करता है या यदि एजेंट द्वारा जनरेट किए गए कोड में एक रेगुलर पायथन एरर है।
|
| 111 |
+
|
| 112 |
+
आप [E2B कोड एक्जीक्यूटर](https://e2b.dev/docs#what-is-e2-b) या Docker का उपयोग लोकल पायथन इंटरप्रेटर के बजाय कर सकते हैं। E2B के लिए, पहले [`E2B_API_KEY` एनवायरनमेंट वेरिएबल सेट करें](https://e2b.dev/dashboard?tab=keys) और फिर एजेंट इनिशियलाइजेशन पर `executor_type="e2b"` पास करें। Docker के लिए, इनिशियलाइजेशन के दौरान `executor_type="docker"` पास करें।
|
| 113 |
+
|
| 114 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 115 |
+
> कोड एक्जीक्यूशन के बारे में और जानें [इस ट्यूटोरियल में](tutorials/secure_code_execution)।
|
| 116 |
+
|
| 117 |
+
हम JSON-जैसे ब्लॉब्स के रूप में एक्शन लिखने के व्यापक रूप से उपयोग किए जाने वाले तरीके का भी समर्थन करते हैं: यह [`ToolCallingAgent`] है, यह बहुत कुछ [`CodeAgent`] की तरह ही काम करता है, बेशक `additional_authorized_imports` के बिना ��्योंकि यह कोड एक्जीक्यूट नहीं करता।
|
| 118 |
+
|
| 119 |
+
```py
|
| 120 |
+
from smolagents import ToolCallingAgent
|
| 121 |
+
|
| 122 |
+
agent = ToolCallingAgent(tools=[], model=model)
|
| 123 |
+
agent.run("Could you get me the title of the page at url 'https://huggingface.co/blog'?")
|
| 124 |
+
```
|
| 125 |
+
|
| 126 |
+
### एजेंट रन का निरीक्षण
|
| 127 |
+
|
| 128 |
+
रन के बाद क्या हुआ यह जांचने के लिए यहाँ कुछ उपयोगी एट्रिब्यूट्स हैं:
|
| 129 |
+
- `agent.logs` एजेंट के फाइन-ग्रेन्ड लॉग्स को स्टोर करता है। एजेंट के रन के हर स्टेप पर, सब कुछ एक डिक्शनरी में स्टोर किया जाता है जो फिर `agent.logs` में जोड़ा जाता है।
|
| 130 |
+
- `agent.write_memory_to_messages()` चलाने से LLM के लिए एजेंट के लॉग्स की एक इनर मेमोरी बनती है, चैट मैसेज की लिस्ट के रूप में। यह मेथड लॉग के प्रत्येक स्टेप पर जाता है और केवल वही स्टोर करता है जिसमें यह एक मैसेज के रूप में रुचि रखता है: उदाहरण के लिए, यह सिस्टम प्रॉम्प्ट और टास्क को अलग-अलग मैसेज के रूप में सेव करेगा, फिर प्रत्येक स्टेप के लिए यह LLM आउटपुट को एक मैसेज के रूप में और टूल कॉल आउटपुट को दूसरे मैसेज के रूप में स्टोर करेगा।
|
| 131 |
+
|
| 132 |
+
## टूल्स
|
| 133 |
+
|
| 134 |
+
टूल एक एटॉमिक फ़ंक्शन है जिसे एजेंट द्वारा उपयोग किया जाता है। LLM द्वारा उपयोग किए जाने के लिए, इसे कुछ एट्रिब्यूट्स की भी आवश्यकता होती है जो इसकी API बनाते हैं और LLM को यह बताने के लिए उपयोग किए जाएंगे कि इस टूल को कैसे कॉल करें:
|
| 135 |
+
- एक नाम
|
| 136 |
+
- एक विवरण
|
| 137 |
+
- इनपुट प्रकार और विवरण
|
| 138 |
+
- एक आउटपुट प्रकार
|
| 139 |
+
|
| 140 |
+
आप उदाहरण के लिए [`PythonInterpreterTool`] को चेक कर सकते हैं: इसमें एक नाम, विवरण, इनपुट विवरण, एक आउटपुट प्रकार, और एक्शन करने के लिए एक `forward` मेथड है।
|
| 141 |
+
|
| 142 |
+
जब एजेंट इनिशियलाइज़ किया जाता है, टूल एट्रिब्यूट्स का उपयोग एक टूल विवरण जनरेट करने के लिए किया जाता है जो एजेंट के सिस्टम प्रॉम्प्ट में बेक किया जाता है। यह एजेंट को बताता है कि वह कौन से टूल्स उपयोग कर सकता है और क्यों।
|
| 143 |
+
|
| 144 |
+
### डिफ़ॉल्ट टूलबॉक्स
|
| 145 |
+
|
| 146 |
+
`smolagents` एजेंट्स को सशक्त बनाने के लिए एक डिफ़ॉल्ट टूलबॉक्स के साथ आता है, जिसे आप आर्ग्यूमेंट `add_base_tools=True` के साथ अपने एजेंट में इनिशियलाइजेशन पर जोड़ सकते हैं:
|
| 147 |
+
|
| 148 |
+
- **DuckDuckGo वेब सर्च**: DuckDuckGo ब्राउज़र का उपयोग करके वेब सर्च करता है।
|
| 149 |
+
- **पायथन कोड इंटरप्रेटर**: आपका LLM जनरेटेड पायथन कोड एक सुरक्षित एनवायरनमेंट में चलाता है। यह टूल [`ToolCallingAgent`] में केवल तभी जोड़ा जाएगा जब आप इसे `add_base_tools=True` के साथ इनिशियलाइज़ करते हैं, क्योंकि कोड-बेस्ड एजेंट पहले से ही नेटिव रूप से पायथन कोड एक्जीक्यूट कर सकता है
|
| 150 |
+
- **ट्रांसक्राइबर**: Whisper-Turbo पर बनाया गया एक स्पीच-टू-टेक्स्ट पाइपल��इन जो ऑडियो को टेक्स्ट में ट्रांसक्राइब करता है।
|
| 151 |
+
|
| 152 |
+
आप मैन्युअल रूप से एक टूल का उपयोग उसके आर्ग्यूमेंट्स के साथ कॉल करके कर सकते हैं।
|
| 153 |
+
|
| 154 |
+
```python
|
| 155 |
+
from smolagents import DuckDuckGoSearchTool
|
| 156 |
+
|
| 157 |
+
search_tool = DuckDuckGoSearchTool()
|
| 158 |
+
print(search_tool("Who's the current president of Russia?"))
|
| 159 |
+
```
|
| 160 |
+
|
| 161 |
+
### अपने कस्टम टूल बनाएं
|
| 162 |
+
|
| 163 |
+
आप ऐसे उपयोग के मामलों के लिए अपने खुद के टूल बना सकते हैं जो Hugging Face के डिफ़ॉल्ट टूल्स द्वारा कवर नहीं किए गए हैं।
|
| 164 |
+
उदाहरण के लिए, चलिए एक टूल बनाते हैं जो दिए गए कार्य (task) के लिए हब से सबसे अधिक डाउनलोड किए गए मॉडल को रिटर्न करता है।
|
| 165 |
+
|
| 166 |
+
आप नीचे दिए गए कोड से शुरुआत करेंगे।
|
| 167 |
+
|
| 168 |
+
```python
|
| 169 |
+
from huggingface_hub import list_models
|
| 170 |
+
|
| 171 |
+
task = "text-classification"
|
| 172 |
+
|
| 173 |
+
most_downloaded_model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
| 174 |
+
print(most_downloaded_model.id)
|
| 175 |
+
```
|
| 176 |
+
|
| 177 |
+
यह कोड आसानी से टूल में बदला जा सकता है, बस इसे एक फ़ंक्शन में रैप करें और `tool` डेकोरेटर जोड़ें:
|
| 178 |
+
यह टूल बनाने का एकमात्र तरीका नहीं है: आप इसे सीधे [`Tool`] का सबक्लास बनाकर भी परिभाषित कर सकते हैं, जो आपको अधिक लचीलापन प्रदान करता है, जैसे भारी क्लास एट्रिब्यूट्स को इनिशियलाइज़ करने की संभावना।
|
| 179 |
+
|
| 180 |
+
चलो देखते हैं कि यह दोनों विकल्पों के लिए कैसे काम करता है:
|
| 181 |
+
|
| 182 |
+
<hfoptions id="build-a-tool">
|
| 183 |
+
<hfoption id="@tool के साथ एक फ़ंक्शन को डेकोरेट करें">
|
| 184 |
+
|
| 185 |
+
```py
|
| 186 |
+
from smolagents import tool
|
| 187 |
+
|
| 188 |
+
@tool
|
| 189 |
+
def model_download_tool(task: str) -> str:
|
| 190 |
+
"""
|
| 191 |
+
This is a tool that returns the most downloaded model of a given task on the Hugging Face Hub.
|
| 192 |
+
It returns the name of the checkpoint.
|
| 193 |
+
|
| 194 |
+
Args:
|
| 195 |
+
task: The task for which to get the download count.
|
| 196 |
+
"""
|
| 197 |
+
most_downloaded_model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
| 198 |
+
return most_downloaded_model.id
|
| 199 |
+
```
|
| 200 |
+
|
| 201 |
+
फ़ंक्शन को चाहिए:
|
| 202 |
+
- एक स्पष्ट नाम: नाम टूल के कार्य को स्पष्ट रूप से बताने वाला होना चाहिए ताकि इसे चलाने वाले LLM को आसानी हो। चूंकि यह टूल कार्य के लिए सबसे अधिक डाउनलोड किए गए मॉडल को लौटाता है, इसका नाम `model_download_tool` रखा गया है।
|
| 203 |
+
- इनपुट और आउटपुट पर टाइप हिंट्स।
|
| 204 |
+
- एक विवरण: इसमें 'Args:' भाग शामिल होना चाहिए, जिसमें प्रत्येक आर्ग्युमेंट का वर्णन (बिना टाइप संकेत के) किया गया हो। यह विवरण एक निर्देश मैनुअल की तरह होता है जो LLM को टूल चलाने में मदद करता है। इसे अनदेखा न करें।
|
| 205 |
+
इन सभी तत्वों को एजेंट की सिस्टम प्रॉम्प्ट में स्वचालित रूप से शामिल किया जाएगा: इसलिए इन्हें यथासंभव स्पष्ट बनाने का प्रयास करें!
|
| 206 |
+
|
| 207 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 208 |
+
> यह परिभाषा प्रारूप `apply_chat_template` में उपयोग की गई टूल स्कीमा जैसा ही है, केवल अतिरिक्त `tool` डेकोरेटर जोड़ा गया है: हमारे टूल उपयोग API के बारे में अधिक पढ़ें [यहाँ](https://huggingface.co/blog/unified-tool-use#passing-tools-to-a-chat-template)।
|
| 209 |
+
</hfoption>
|
| 210 |
+
<hfoption id="सबक्लास टूल">
|
| 211 |
+
|
| 212 |
+
```py
|
| 213 |
+
from smolagents import Tool
|
| 214 |
+
|
| 215 |
+
class ModelDownloadTool(Tool):
|
| 216 |
+
name = "model_download_tool"
|
| 217 |
+
description = "This is a tool that returns the most downloaded model of a given task on the Hugging Face Hub. It returns the name of the checkpoint."
|
| 218 |
+
inputs = {"task": {"type": "string", "description": "The task for which to get the download count."}}
|
| 219 |
+
output_type = "string"
|
| 220 |
+
|
| 221 |
+
def forward(self, task: str) -> str:
|
| 222 |
+
most_downloaded_model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
| 223 |
+
return most_downloaded_model.id
|
| 224 |
+
```
|
| 225 |
+
|
| 226 |
+
सबक्लास को निम्नलिखित एट्रिब्यूट्स की आवश्यकता होती है:
|
| 227 |
+
- एक स्पष्ट `name`: नाम टूल के कार्य को स्पष्ट रूप से बताने वाला होना चाहिए।
|
| 228 |
+
- एक `description`: यह भी LLM के लिए निर्देश मैनुअल की तरह काम करता है।
|
| 229 |
+
- इनपुट प्रकार और उनके विवरण।
|
| 230 |
+
- आउटपुट प्रकार।
|
| 231 |
+
इन सभी एट्रिब्यूट्स को एजेंट की सिस्टम प्रॉम्प्ट में स्वचालित रूप से शामिल किया जाएगा, इन्हें स्पष्ट और विस्तृत बनाएं।
|
| 232 |
+
</hfoption>
|
| 233 |
+
</hfoptions>
|
| 234 |
+
|
| 235 |
+
|
| 236 |
+
आप सीधे अपने एजेंट को इनिशियलाइज़ कर सकते हैं:
|
| 237 |
+
```py
|
| 238 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel
|
| 239 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[model_download_tool], model=InferenceClientModel())
|
| 240 |
+
agent.run(
|
| 241 |
+
"Can you give me the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub?"
|
| 242 |
+
)
|
| 243 |
+
```
|
| 244 |
+
|
| 245 |
+
लॉग्स इस प्रकार होंगे:
|
| 246 |
+
```text
|
| 247 |
+
╭──────────────────────────────────────── New run ─────────────────────────────────────────╮
|
| 248 |
+
│ │
|
| 249 |
+
│ Can you give me the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' │
|
| 250 |
+
│ task on the Hugging Face Hub? │
|
| 251 |
+
│ │
|
| 252 |
+
╰─ InferenceClientModel - Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct ───────────────────────────────────────────╯
|
| 253 |
+
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ Step 0 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
|
| 254 |
+
╭─ Executing this code: ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
|
| 255 |
+
│ 1 model_name = model_download_tool(task="text-to-video") │
|
| 256 |
+
│ 2 print(model_name) │
|
| 257 |
+
╰──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
|
| 258 |
+
Execution logs:
|
| 259 |
+
ByteDance/AnimateDiff-Lightning
|
| 260 |
+
|
| 261 |
+
Out: None
|
| 262 |
+
[Step 0: Duration 0.27 seconds| Input tokens: 2,069 | Output tokens: 60]
|
| 263 |
+
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ Step 1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
|
| 264 |
+
╭─ Executing this code: ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
|
| 265 |
+
│ 1 final_answer("ByteDance/AnimateDiff-Lightning") │
|
| 266 |
+
╰──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
|
| 267 |
+
Out - Final answer: ByteDance/AnimateDiff-Lightning
|
| 268 |
+
[Step 1: Duration 0.10 seconds| Input tokens: 4,288 | Output tokens: 148]
|
| 269 |
+
Out[20]: 'ByteDance/AnimateDiff-Lightning'
|
| 270 |
+
```
|
| 271 |
+
|
| 272 |
+
[!TIP]
|
| 273 |
+
> टूल्स के बारे में अधिक प���़ें [dedicated tutorial](./tutorials/tools#टूल-क्या-है-और-इसे-कैसे-बनाएं) में।
|
| 274 |
+
|
| 275 |
+
## मल्टी-एजेंट्स
|
| 276 |
+
|
| 277 |
+
Microsoft के फ्रेमवर्क [Autogen](https://huggingface.co/papers/2308.08155) के साथ मल्टी-एजेंट सिस्टम्स की शुरुआत हुई।
|
| 278 |
+
|
| 279 |
+
इस प्रकार के फ्रेमवर्क में, आपके कार्य को हल करने के लिए कई एजेंट्स एक साथ काम करते हैं, न कि केवल एक।
|
| 280 |
+
यह अधिकांश बेंचमार्क्स पर बेहतर प्रदर्शन देता है। इसका कारण यह है कि कई कार्यों के लिए, एक सर्व-समावेशी प्रणाली के बजाय, आप उप-कार्यों पर विशेषज्ञता रखने वाली इकाइयों को पसंद करेंगे। इस तरह, अलग-अलग टूल सेट्स और मेमोरी वाले एजेंट्स के पास विशेषकरण की अधिक कुशलता होती है। उदाहरण के लिए, कोड उत्पन्न करने वाले एजेंट की मेमोरी को वेब सर्च एजेंट द्वारा देखे गए वेबपेजों की सभी सामग्री से क्यों भरें? इन्हें अलग रखना बेहतर है।
|
| 281 |
+
|
| 282 |
+
आप `smolagents` का उपयोग करके आसानी से श्रेणीबद्ध मल्टी-एजेंट सिस्टम्स बना सकते हैं।
|
| 283 |
+
|
| 284 |
+
ऐसा करने के लिए, एजेंट को [`ManagedAgent`] ऑब्जेक्ट में समाहित करें। यह ऑब्जेक्ट `agent`, `name`, और एक `description` जैसे तर्कों की आवश्यकता होती है, जो फिर मैनेजर एजेंट की सिस्टम प्रॉम्प्ट में एम्बेड किया जाता है
|
| 285 |
+
|
| 286 |
+
यहां एक एजेंट बनाने का उदाहरण दिया गया है जो हमारे [`DuckDuckGoSearchTool`] का उपयोग करके एक विशिष्ट वेब खोज एजेंट को प्रबंधित करता है।
|
| 287 |
+
|
| 288 |
+
```py
|
| 289 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel, DuckDuckGoSearchTool, ManagedAgent
|
| 290 |
+
|
| 291 |
+
model = InferenceClientModel()
|
| 292 |
+
|
| 293 |
+
web_agent = CodeAgent(tools=[DuckDuckGoSearchTool()], model=model)
|
| 294 |
+
|
| 295 |
+
managed_web_agent = ManagedAgent(
|
| 296 |
+
agent=web_agent,
|
| 297 |
+
name="web_search",
|
| 298 |
+
description="Runs web searches for you. Give it your query as an argument."
|
| 299 |
+
)
|
| 300 |
+
|
| 301 |
+
manager_agent = CodeAgent(
|
| 302 |
+
tools=[], model=model, managed_agents=[managed_web_agent]
|
| 303 |
+
)
|
| 304 |
+
|
| 305 |
+
manager_agent.run("Who is the CEO of Hugging Face?")
|
| 306 |
+
```
|
| 307 |
+
|
| 308 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 309 |
+
> कुशल मल्टी-एजेंट इंप्लीमेंटेशन का एक विस्तृत उदाहरण देखने के लिए, [कैसे हमने अपने मल्टी-एजेंट सिस्टम को GAIA लीडरबोर्ड के शीर्ष पर पहुंचाया](https://huggingface.co/blog/beating-gaia) पर जाएं।
|
| 310 |
+
|
| 311 |
+
|
| 312 |
+
## अपने एजेंट से बात करें और उसके विचारों को एक शानदार Gradio इंटरफेस में विज़ुअलाइज़ करें
|
| 313 |
+
|
| 314 |
+
आप `GradioUI` का उपयोग करके अपने एजेंट को इंटरैक्टिव तरीके से कार्य सौंप सकते हैं और उसके सोचने और निष्पादन की प्रक्रिया को देख सकते हैं। नीचे एक उदाहरण दिया गया है:
|
| 315 |
+
|
| 316 |
+
```py
|
| 317 |
+
from smolagents import (
|
| 318 |
+
load_tool,
|
| 319 |
+
CodeAgent,
|
| 320 |
+
InferenceClientModel,
|
| 321 |
+
GradioUI
|
| 322 |
+
)
|
| 323 |
+
|
| 324 |
+
# Import tool from Hub
|
| 325 |
+
image_generation_tool = load_tool("m-ric/text-to-image", trust_remote_code=True)
|
| 326 |
+
|
| 327 |
+
model = InferenceClientModel(model_id=model_id)
|
| 328 |
+
|
| 329 |
+
# Initialize the agent with the image generation tool
|
| 330 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[image_generation_tool], model=model)
|
| 331 |
+
|
| 332 |
+
GradioUI(agent).launch()
|
| 333 |
+
```
|
| 334 |
+
|
| 335 |
+
अंदरूनी तौर पर, जब यूजर एक नया उत्तर टाइप करता है, तो एजेंट को `agent.run(user_request, reset=False)` के साथ लॉन्च किया जाता है।
|
| 336 |
+
यहाँ `reset=False` फ���लैग का मतलब है कि एजेंट की मेमोरी इस नए कार्य को लॉन्च करने से पहले क्लियर नहीं होती, जिससे बातचीत जारी रहती है।
|
| 337 |
+
|
| 338 |
+
आप इस `reset=False` आर्ग्युमेंट का उपयोग किसी भी अन्य एजेंटिक एप्लिकेशन में बातचीत जारी रखने के लिए कर सकते हैं।
|
| 339 |
+
|
| 340 |
+
## अगले कदम
|
| 341 |
+
|
| 342 |
+
अधिक गहन उपयोग के लिए, आप हमारे ट्यूटोरियल्स देख सकते हैं:
|
| 343 |
+
- [हमारे कोड एजेंट्स कैसे काम करते हैं इसका विवरण](./tutorials/secure_code_execution)
|
| 344 |
+
- [अच्छे एजेंट्स बनाने के लिए यह गाइड](./tutorials/building_good_agents)
|
| 345 |
+
- [टूल उपयोग के लिए इन-डेप्थ गाइड ](./tutorials/building_good_agents)।
|
smolagents/docs/source/hi/index.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# `smolagents`
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
| 4 |
+
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/smolagents/license_to_call.png" width=100%/>
|
| 5 |
+
</div>
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
यह लाइब्रेरी पावरफुल एजेंट्स बनाने के लिए सबसे सरल फ्रेमवर्क है! वैसे, "एजेंट्स" हैं क्या? हम अपनी परिभाषा [इस पेज पर](conceptual_guides/intro_agents) प्रदान करते हैं, जहाँ आपको यह भी पता चलेगा कि इन्हें कब उपयोग करें या न करें (स्पॉइलर: आप अक्सर एजेंट्स के बिना बेहतर काम कर सकते हैं)।
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
यह लाइब्रेरी प्रदान करती है:
|
| 10 |
+
|
| 11 |
+
✨ **सरलता**: Agents का लॉजिक लगभग एक हजार लाइन्स ऑफ़ कोड में समाहित है। हमने रॉ कोड के ऊपर एब्स्ट्रैक्शन को न्यूनतम आकार में रखा है!
|
| 12 |
+
|
| 13 |
+
🌐 **सभी LLM के लिए सपोर्ट**: यह हब पर होस्ट किए गए मॉडल्स को उनके `transformers` वर्जन में या हमारे इन्फरेंस API के माध्यम से सपोर्ट करता है, साथ ही OpenAI, Anthropic से भी... किसी भी LLM से एजेंट को पावर करना वास्तव में आसान है।
|
| 14 |
+
|
| 15 |
+
🧑💻 **कोड Agents के लिए फर्स्ट-क्लास सपोर्ट**, यानी ऐसे एजेंट्स जो अपनी एक्शन्स को कोड में लिखते हैं (कोड लिखने के लिए उपयोग किए जाने वाले एजेंट्स के विपरीत), [यहाँ और पढ़ें](tutorials/secure_code_execution)।
|
| 16 |
+
|
| 17 |
+
🤗 **हब इंटीग्रेशन**: आप टूल्स को हब पर शेयर और लोड कर सकते हैं, और आगे और भी बहुत कुछ आने वाला है!
|
| 18 |
+
!
|
| 19 |
+
|
| 20 |
+
<div class="mt-10">
|
| 21 |
+
<div class="w-full flex flex-col space-y-4 md:space-y-0 md:grid md:grid-cols-2 md:gap-y-4 md:gap-x-5">
|
| 22 |
+
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="./guided_tour"
|
| 23 |
+
><div class="w-full text-center bg-gradient-to-br from-blue-400 to-blue-500 rounded-lg py-1.5 font-semibold mb-5 text-white text-lg leading-relaxed">गाइडेड टूर</div>
|
| 24 |
+
<p class="text-gray-700">बेसिक्स सीखें और एजेंट्स का उपयोग करने में परिचित हों। यदि आप पहली बार एजेंट्स का उपयोग कर रहे हैं तो यहाँ से शुरू करें!</p>
|
| 25 |
+
</a>
|
| 26 |
+
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="./examples/text_to_sql"
|
| 27 |
+
><div class="w-full text-center bg-gradient-to-br from-indigo-400 to-indigo-500 rounded-lg py-1.5 font-semibold mb-5 text-white text-lg leading-relaxed">हाउ-टू गाइड्स</div>
|
| 28 |
+
<p class="text-gray-700">एक विशिष्ट लक्ष्य प्राप्त करने में मदद के लिए गाइड: SQL क्वेरी जनरेट और टेस्ट करने के लिए एजेंट बनाएं!</p>
|
| 29 |
+
</a>
|
| 30 |
+
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="./conceptual_guides/intro_agents"
|
| 31 |
+
><div class="w-full text-center bg-gradient-to-br from-pink-400 to-pink-500 rounded-lg py-1.5 font-semibold mb-5 text-white text-lg leading-relaxed">कॉन्सेप्चुअल गाइड्स</div>
|
| 32 |
+
<p class="text-gray-700">महत्वपूर्ण विषयों की बेहतर समझ बनाने के लिए उच्च-स्तरीय व्याख्याएं।</p>
|
| 33 |
+
</a>
|
| 34 |
+
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="./tutorials/building_good_agents"
|
| 35 |
+
><div class="w-full text-center bg-gradient-to-br from-purple-400 to-purple-500 rounded-lg py-1.5 font-semibold mb-5 text-white text-lg leading-relaxed">ट्यूटोरियल्स</div>
|
| 36 |
+
<p class="text-gray-700">एजेंट्स बनाने के महत्वपूर्ण पहलुओं को कवर करने वाले क्ट्यूटोरियल्स।</p>
|
| 37 |
+
</a>
|
| 38 |
+
</div>
|
| 39 |
+
</div>
|
smolagents/docs/source/hi/reference/agents.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,151 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Agents
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
<Tip warning={true}>
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
Smolagents एक experimental API है जो किसी भी समय बदल सकता है। एजेंट्स द्वारा लौटाए गए परिणाम भिन्न हो सकते हैं क्योंकि APIs या underlying मॉडल बदलने की संभावना रखते हैं।
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
</Tip>
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
Agents और tools के बारे में अधिक जानने के लिए [introductory guide](../index) पढ़ना सुनिश्चित करें।
|
| 10 |
+
यह पेज underlying क्लासेज के लिए API docs को शामिल करता है।
|
| 11 |
+
|
| 12 |
+
## Agents
|
| 13 |
+
|
| 14 |
+
हमारे एजेंट्स [`MultiStepAgent`] से इनहेरिट करते हैं, जिसका अर्थ है कि वे कई चरणों में कार्य कर सकते हैं, प्रत्येक चरण में एक विचार, फिर एक टूल कॉल और एक्जीक्यूशन शामिल होता है। [इस कॉन्सेप्चुअल गाइड](../conceptual_guides/react) में अधिक पढ़ें।
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
हम मुख्य [`Agent`] क्लास पर आधारित दो प्रकार के एजेंट्स प्रदान करते हैं।
|
| 17 |
+
- [`CodeAgent`] डिफ़ॉल्ट एजेंट है, यह अपने टूल कॉल्स को Python कोड में लिखता है।
|
| 18 |
+
- [`ToolCallingAgent`] अपने टूल कॉल्स को JSON में लिखता है।
|
| 19 |
+
|
| 20 |
+
दोनों को इनिशियलाइजेशन पर `model` और टूल्स की सूची `tools` आर्गुमेंट्स की आवश्यकता होती है।
|
| 21 |
+
|
| 22 |
+
### Agents की क्लासेज
|
| 23 |
+
|
| 24 |
+
[[autodoc]] MultiStepAgent
|
| 25 |
+
|
| 26 |
+
[[autodoc]] CodeAgent
|
| 27 |
+
|
| 28 |
+
[[autodoc]] ToolCallingAgent
|
| 29 |
+
|
| 30 |
+
### ManagedAgent
|
| 31 |
+
|
| 32 |
+
_This class is deprecated since 1.8.0: now you just need to pass name and description attributes to an agent to directly use it as previously done with a ManagedAgent._
|
| 33 |
+
|
| 34 |
+
### stream_to_gradio
|
| 35 |
+
|
| 36 |
+
[[autodoc]] stream_to_gradio
|
| 37 |
+
|
| 38 |
+
### GradioUI
|
| 39 |
+
|
| 40 |
+
[[autodoc]] GradioUI
|
| 41 |
+
|
| 42 |
+
## मॉडल्स
|
| 43 |
+
|
| 44 |
+
आप स्वतंत्र रूप से अपने स्वयं के मॉडल बना सकते हैं और उनका उपयोग कर सकते हैं।
|
| 45 |
+
|
| 46 |
+
आप अपने एजेंट के लिए कोई भी `model` कॉल करने योग्य उपयोग कर सकते हैं, जब तक कि:
|
| 47 |
+
1. यह अपने इनपुट `messages` के लिए [messages format](./chat_templating) (`List[Dict[str, str]]`) का पालन करता है, और यह एक `str` लौटाता है।
|
| 48 |
+
2. यह आर्गुमेंट `stop_sequences` में पास किए गए सीक्वेंस से *पहले* आउटपुट जनरेट करना बंद कर देता है।
|
| 49 |
+
|
| 50 |
+
अपने LLM को परिभाषित करने के लिए, आप एक `custom_model` मेथड बना सकते हैं जो [messages](./chat_templating) की एक सूची स्वीकार करता है और टेक्स्ट युक्त .content विशेषता वाला एक ऑब्जेक्ट लौटाता है। इस कॉलेबल को एक `stop_sequences` आर्गुमेंट भी स्वीकार करने की आवश्यकता होती है जो बताता है कि कब जनरेट करना और बंद करना है।
|
| 51 |
+
|
| 52 |
+
```python
|
| 53 |
+
from huggingface_hub import login, InferenceClient
|
| 54 |
+
|
| 55 |
+
login("<YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>")
|
| 56 |
+
|
| 57 |
+
model_id = "meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct"
|
| 58 |
+
|
| 59 |
+
client = InferenceClient(model=model_id)
|
| 60 |
+
|
| 61 |
+
def custom_model(messages, stop_sequences=["Task"]):
|
| 62 |
+
response = client.chat_completion(messages, stop=stop_sequences, max_tokens=1000)
|
| 63 |
+
answer = response.choices[0].message
|
| 64 |
+
return answer
|
| 65 |
+
```
|
| 66 |
+
|
| 67 |
+
इसके अतिरिक्त, `custom_model` एक `grammar` आर्गुमेंट भी ले सकता है। जिस स्थिति में आप एजेंट इनिशियलाइजेशन पर एक `grammar` निर्दिष्ट करते हैं, यह आर्गुमेंट मॉडल के कॉल्स को आपके द्वारा इनिशियलाइजेशन पर परिभाषित `grammar` के साथ पास किया जाएगा, ताकि [constrained generation](https://huggingface.co/docs/text-generation-inference/conceptual/guidance) की अनुमति ���िल सके जिससे उचित-फॉर्मेटेड एजेंट आउटपुट को फोर्स किया जा सके।
|
| 68 |
+
|
| 69 |
+
### TransformersModel
|
| 70 |
+
|
| 71 |
+
सुविधा के लिए, हमने एक `TransformersModel` जोड़ा है जो इनिशियलाइजेशन पर दिए गए model_id के लिए एक लोकल `transformers` पाइपलाइन बनाकर ऊपर के बिंदुओं को लागू करता है।
|
| 72 |
+
|
| 73 |
+
```python
|
| 74 |
+
from smolagents import TransformersModel
|
| 75 |
+
|
| 76 |
+
model = TransformersModel(model_id="HuggingFaceTB/SmolLM-135M-Instruct")
|
| 77 |
+
|
| 78 |
+
print(model([{"role": "user", "content": "Ok!"}], stop_sequences=["great"]))
|
| 79 |
+
```
|
| 80 |
+
```text
|
| 81 |
+
>>> What a
|
| 82 |
+
```
|
| 83 |
+
|
| 84 |
+
[[autodoc]] TransformersModel
|
| 85 |
+
|
| 86 |
+
### InferenceClientModel
|
| 87 |
+
|
| 88 |
+
`InferenceClientModel` LLM के एक्जीक्यूशन के लिए [HF Inference API](https://huggingface.co/docs/api-inference/index) क्लाइंट को रैप करता है।
|
| 89 |
+
|
| 90 |
+
```python
|
| 91 |
+
from smolagents import InferenceClientModel
|
| 92 |
+
|
| 93 |
+
messages = [
|
| 94 |
+
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello, how are you?"},
|
| 95 |
+
{"role": "assistant", "content": "I'm doing great. How can I help you today?"},
|
| 96 |
+
{"role": "user", "content": "No need to help, take it easy."},
|
| 97 |
+
]
|
| 98 |
+
|
| 99 |
+
model = InferenceClientModel()
|
| 100 |
+
print(model(messages))
|
| 101 |
+
```
|
| 102 |
+
```text
|
| 103 |
+
>>> Of course! If you change your mind, feel free to reach out. Take care!
|
| 104 |
+
```
|
| 105 |
+
[[autodoc]] InferenceClientModel
|
| 106 |
+
|
| 107 |
+
### LiteLLMModel
|
| 108 |
+
|
| 109 |
+
`LiteLLMModel` विभिन्न प्रदाताओं से 100+ LLMs को सपोर्ट करने के लिए [LiteLLM](https://www.litellm.ai/) का लाभ उठाता है।
|
| 110 |
+
आप मॉडल इनिशियलाइजेशन पर kwargs पास कर सकते हैं जो तब मॉडल का उपयोग करते समय प्रयोग किए जाएंगे, उदाहरण के लिए नीचे हम `temperature` पास करते हैं।
|
| 111 |
+
|
| 112 |
+
```python
|
| 113 |
+
from smolagents import LiteLLMModel
|
| 114 |
+
|
| 115 |
+
messages = [
|
| 116 |
+
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello, how are you?"},
|
| 117 |
+
{"role": "assistant", "content": "I'm doing great. How can I help you today?"},
|
| 118 |
+
{"role": "user", "content": "No need to help, take it easy."},
|
| 119 |
+
]
|
| 120 |
+
|
| 121 |
+
model = LiteLLMModel(model_id="anthropic/claude-3-5-sonnet-latest", temperature=0.2, max_tokens=10)
|
| 122 |
+
print(model(messages))
|
| 123 |
+
```
|
| 124 |
+
|
| 125 |
+
[[autodoc]] LiteLLMModel
|
| 126 |
+
|
| 127 |
+
### OpenAiServerModel
|
| 128 |
+
|
| 129 |
+
|
| 130 |
+
यह क्लास आपको किसी भी OpenAIServer कम्पैटिबल मॉडल को कॉल करने देती है।
|
| 131 |
+
यहाँ बताया गया है कि आप इसे कैसे सेट कर सकते हैं (आप दूसरे सर्वर को पॉइंट करने के लिए `api_base` url को कस्टमाइज़ कर सकते हैं):
|
| 132 |
+
```py
|
| 133 |
+
import os
|
| 134 |
+
from smolagents import OpenAIServerModel
|
| 135 |
+
|
| 136 |
+
model = OpenAIServerModel(
|
| 137 |
+
model_id="gpt-4o",
|
| 138 |
+
api_base="https://api.openai.com/v1",
|
| 139 |
+
api_key=os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"],
|
| 140 |
+
)
|
| 141 |
+
```
|
| 142 |
+
|
| 143 |
+
## Prompts
|
| 144 |
+
|
| 145 |
+
[[autodoc]] smolagents.agents.PromptTemplates
|
| 146 |
+
|
| 147 |
+
[[autodoc]] smolagents.agents.PlanningPromptTemplate
|
| 148 |
+
|
| 149 |
+
[[autodoc]] smolagents.agents.ManagedAgentPromptTemplate
|
| 150 |
+
|
| 151 |
+
[[autodoc]] smolagents.agents.FinalAnswerPromptTemplate
|
smolagents/docs/source/hi/reference/tools.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Tools
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
<Tip warning={true}>
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
Smolagents एक experimental API है जो किसी भी समय बदल सकता है। एजेंट्स द्वारा लौटाए गए परिणाम भिन्न हो सकते हैं क्योंकि APIs या underlying मॉडल बदलने की संभावना रखते हैं।
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
</Tip>
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
एजेंट्स और टूल्स के बारे में अधिक जानने के लिए [introductory guide](../index) पढ़ना सुनिश्चित करें।
|
| 10 |
+
यह पेज underlying क्लासेज के लिए API docs को शामिल करता है।
|
| 11 |
+
|
| 12 |
+
## Tools
|
| 13 |
+
|
| 14 |
+
### load_tool
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
[[autodoc]] load_tool
|
| 17 |
+
|
| 18 |
+
### tool
|
| 19 |
+
|
| 20 |
+
[[autodoc]] tool
|
| 21 |
+
|
| 22 |
+
### Tool
|
| 23 |
+
|
| 24 |
+
[[autodoc]] Tool
|
| 25 |
+
|
| 26 |
+
### launch_gradio_demo
|
| 27 |
+
|
| 28 |
+
[[autodoc]] launch_gradio_demo
|
| 29 |
+
|
| 30 |
+
## Default Tools
|
| 31 |
+
|
| 32 |
+
### PythonInterpreterTool
|
| 33 |
+
|
| 34 |
+
[[autodoc]] PythonInterpreterTool
|
| 35 |
+
|
| 36 |
+
### DuckDuckGoSearchTool
|
| 37 |
+
|
| 38 |
+
[[autodoc]] DuckDuckGoSearchTool
|
| 39 |
+
|
| 40 |
+
### VisitWebpageTool
|
| 41 |
+
|
| 42 |
+
[[autodoc]] VisitWebpageTool
|
| 43 |
+
|
| 44 |
+
### UserInputTool
|
| 45 |
+
|
| 46 |
+
[[autodoc]] UserInputTool
|
| 47 |
+
|
| 48 |
+
## ToolCollection
|
| 49 |
+
|
| 50 |
+
[[autodoc]] ToolCollection
|
| 51 |
+
|
| 52 |
+
## Agent टाइप्स
|
| 53 |
+
|
| 54 |
+
एजेंट्स टूल्स के बीच किसी भी प्रकार की ऑब्जेक्ट को संभाल सकते हैं; टूल्स, पूरी तरह से मल्टीमोडल होने के कारण, टेक्स्ट, इमेज, ऑडियो, वीडियो सहित अन्य प्रकारों को स्वीकार और रिटर्न कर सकते हैं।
|
| 55 |
+
टूल्स के बीच अनुकूलता बढ़ाने के साथ-साथ इन रिटर्न्स को ipython (jupyter, colab, ipython notebooks, ...) में सही ढंग से रेंडर करने के लिए, हम इन टाइप्स के आसपास रैपर क्लासेज को लागू करते हैं।
|
| 56 |
+
|
| 57 |
+
रैप किए गए ऑब्जेक्ट्स को प्रारंभ में जैसा व्यवहार करना चाहिए वैसा ही करना जारी रखना चाहिए; एक टेक्स्ट ऑब्जेक्ट को अभी भी स्ट्रिंग की तरह व्यवहार करना चाहिए|
|
| 58 |
+
एक इमेज ऑब्जेक्ट को अभी भी `PIL.Image` की तरह व्यवहार करना चाहिए।
|
| 59 |
+
|
| 60 |
+
इन टाइप्स के तीन विशिष्ट उद्देश्य हैं:
|
| 61 |
+
|
| 62 |
+
- टाइप पर `to_raw` को कॉल करने से अंतर्निहित ऑब्जेक्ट रिटर्न होना चाहिए
|
| 63 |
+
- टाइप पर `to_string` को कॉल करने से ऑब्जेक्ट को स्ट्रिंग के रूप में रिटर्न होना चाहिए: वह `AgentText` के मामले में स्ट्रिंग हो सकती है लेकिन अन्य उदाहरणों में ऑब्जेक्ट के सीरियलाइज्ड वर्जन का पाथ होगा
|
| 64 |
+
- इसे एक ipython kernel में प्रदर्शित करने पर ऑब्जेक्ट को सही ढंग से प्रदर्शित करना चाहिए
|
| 65 |
+
|
| 66 |
+
### AgentText
|
| 67 |
+
|
| 68 |
+
[[autodoc]] smolagents.agent_types.AgentText
|
| 69 |
+
|
| 70 |
+
### AgentImage
|
| 71 |
+
|
| 72 |
+
[[autodoc]] smolagents.agent_types.AgentImage
|
| 73 |
+
|
| 74 |
+
### AgentAudio
|
| 75 |
+
|
| 76 |
+
[[autodoc]] smolagents.agent_types.AgentAudio
|
smolagents/docs/source/hi/tutorials/building_good_agents.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,420 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# अच्छे Agents का निर्माण
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
[[open-in-colab]]
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
एक ऐसा एजेंट बनाने में जो काम करता है और जो काम नहीं करता है, इसमें ज़मीन-आसमान का अंतर है।
|
| 6 |
+
हम कैसे ऐसे एजेंट्स बना सकते हैं जो बाद वाली श्रेणी में आते हैं?
|
| 7 |
+
इस गाइड में, हम एजेंट्स बनाने के लिए सर्वोत्तम प्रक्रियाएँ के बारे में बात करेंगे।
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 10 |
+
> यदि आप एजेंट्स बनाने में नए हैं, तो पहले [एजेंट्स का परिचय](../conceptual_guides/intro_agents) और [smolagents की गाइडेड टूर](../guided_tour) पढ़ना सुनिश्चित करें।
|
| 11 |
+
|
| 12 |
+
### सर्वश्रेष्ठ एजेंटिक सिस्टम सबसे सरल होते हैं: वर्कफ़्लो को जितना हो सके उतना सरल बनाएं
|
| 13 |
+
|
| 14 |
+
अपने वर्कफ़्लो में एक LLM को कुछ एजेंसी देने से त्रुटियों का जोखिम होता है।
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
अच्छी तरह से प्रोग्राम किए गए एजेंटिक सिस्टम में वैसे भी अच्छी एरर लॉगिंग और रीट्राई मैकेनिज्म होते हैं, जिससे LLM इंजन अपनी गलतियों को सुधारने का मौका मिलता है। लेकिन LLM त्रुटि के जोखिम को अधिकतम कम करने के लिए, आपको अपना वर्कफ़्लो सरल बनाना चाहिए!
|
| 17 |
+
|
| 18 |
+
आइए [एजेंट्स का परिचय](../conceptual_guides/intro_agents) से उदाहरण पर फिर से विचार करें: एक सर्फ ट्रिप कंपनी के लिए उपयोगकर्ता प्रश्नों का उत्तर देने वाला बॉट।
|
| 19 |
+
एजेंट को हर बार जब एक नए सर्फ स्पॉट के बारे में पूछा जाता है तो "travel distance API" और "weather API" के लिए 2 अलग-अलग कॉल करने देने के बजाय, आप केवल एक एकीकृत टूल "return_spot_information" बना सकते हैं, एक फंक्शन जो दोनों APIs को एक साथ कॉल करता है और उनके संयोजित आउटपुट को उपयोगकर्ता को वापस करता है।
|
| 20 |
+
|
| 21 |
+
यह लागत, देरी और त्रुटि जोखिम को कम करेगा!
|
| 22 |
+
|
| 23 |
+
मुख्य दिशानिर्देश है: LLM कॉल्स की संख्या को जितना हो सके उतना कम करें।
|
| 24 |
+
|
| 25 |
+
इससे कुछ निष्कर्ष निकलते हैं:
|
| 26 |
+
- जब भी संभव हो, दो APIs के हमारे उदाहरण की तरह 2 टूल्स को एक में समूहित करें।
|
| 27 |
+
- जब भी संभव हो, लॉजिक एजेंटिक निर्णयों के बजाय डिटरमिनिस्टिक फंक्शंस पर आधारित होनी चाहिए।
|
| 28 |
+
|
| 29 |
+
### LLM इंजन को जानकारी के प्रवाह में सुधार करें
|
| 30 |
+
|
| 31 |
+
याद रखें कि आपका LLM इंजन एक *बुद्धिमान* रोबोट की तरह है, जो एक कमरे में बंद है, और बाहरी दुनिया के साथ इसका एकमात्र संचार दरवाजे के नीचे से नोट्स पास करना है।
|
| 32 |
+
|
| 33 |
+
यह किसी भी ऐसी चीज के बारे में नहीं जानेगा जिसे आप स्पष्ट रूप से अपने प्रॉम्प्ट में नहीं डालते हैं।
|
| 34 |
+
|
| 35 |
+
इसलिए पहले अपने कार्य को बहुत स्पष्ट बनाने से शुरू करें!
|
| 36 |
+
चूंकि एक एजेंट LLM द्वारा संचालित होता है, आपके कार्य के निर्माण में छोटे बदलाव भी पूरी तरह से ���लग परिणाम दे सकते हैं।
|
| 37 |
+
|
| 38 |
+
फिर, टूल के उपयोग में अपने एजेंट की ओर जानकारी के प्रवाह में सुधार करें।
|
| 39 |
+
|
| 40 |
+
पालन करने के लिए विशेष दिशानिर्देश:
|
| 41 |
+
- प्रत्येक टूल को वह सब कुछ लॉग करना चाहिए (टूल की `forward` मेथड के अंदर केवल `print` स्टेटमेंट्स का उपयोग करके) जो LLM इंजन के लिए उपयोगी हो सकता है।
|
| 42 |
+
- विशेष रूप से, टूल एक्जीक्यूशन गलतियों पर विस्तृत लॉगिंग बहुत मदद करेगी!
|
| 43 |
+
|
| 44 |
+
उदाहरण के लिए, यहाँ एक टूल है जो लोकेशन और डेट-टाइम के आधार पर मौसम डेटा प्राप्त करता है:
|
| 45 |
+
|
| 46 |
+
पहले, यहाँ एक खराब रूप है:
|
| 47 |
+
```python
|
| 48 |
+
import datetime
|
| 49 |
+
from smolagents import tool
|
| 50 |
+
|
| 51 |
+
def get_weather_report_at_coordinates(coordinates, date_time):
|
| 52 |
+
# Dummy function, returns a list of [temperature in °C, risk of rain on a scale 0-1, wave height in m]
|
| 53 |
+
return [28.0, 0.35, 0.85]
|
| 54 |
+
|
| 55 |
+
def convert_location_to_coordinates(location):
|
| 56 |
+
# Returns dummy coordinates
|
| 57 |
+
return [3.3, -42.0]
|
| 58 |
+
|
| 59 |
+
@tool
|
| 60 |
+
def get_weather_api(location: str, date_time: str) -> str:
|
| 61 |
+
"""
|
| 62 |
+
Returns the weather report.
|
| 63 |
+
|
| 64 |
+
Args:
|
| 65 |
+
location: the name of the place that you want the weather for.
|
| 66 |
+
date_time: the date and time for which you want the report.
|
| 67 |
+
"""
|
| 68 |
+
lon, lat = convert_location_to_coordinates(location)
|
| 69 |
+
date_time = datetime.strptime(date_time)
|
| 70 |
+
return str(get_weather_report_at_coordinates((lon, lat), date_time))
|
| 71 |
+
```
|
| 72 |
+
|
| 73 |
+
# यह खराब क्यों है?
|
| 74 |
+
- `date_time` के लिए उपयोग किए जाने वाले फॉर्मेट की सटीकता का कोई उल्लेख नहीं है।
|
| 75 |
+
- यह स्पष्ट नहीं है कि स्थान (location) को किस प्रकार निर्दिष्ट किया जाना चाहिए।
|
| 76 |
+
- त्रुटियों को स्पष्ट रूप से इंगित करने के लिए कोई लॉगिंग मेकैनिज्म मौजूद नहीं है, जैसे कि स्थान गलत फॉर्मेट में होना या `date_time` का सही ढंग से फॉर्मेट न होना।
|
| 77 |
+
- आउटपुट फॉर्मेट समझने में कठिन है।
|
| 78 |
+
|
| 79 |
+
यदि टूल कॉल विफल हो जाती है, तो मेमोरी में लॉग की गई एरर ट्रेस LLM को टूल की समस्याओं को ठीक करने के लिए रिवर्स इंजीनियरिंग में मदद कर सकती है। लेकिन इतना सारा काम LLM को ही क्यों करने देना?
|
| 80 |
+
|
| 81 |
+
इस टूल को बेहतर तरीके से बनाने का एक उदाहरण इस प्रकार हो सकता है:
|
| 82 |
+
|
| 83 |
+
```python
|
| 84 |
+
@tool
|
| 85 |
+
def get_weather_api(location: str, date_time: str) -> str:
|
| 86 |
+
"""
|
| 87 |
+
Returns the weather report.
|
| 88 |
+
|
| 89 |
+
Args:
|
| 90 |
+
location: the name of the place that you want the weather for. Should be a place name, followed by possibly a city name, then a country, like "Anchor Point, Taghazout, Morocco".
|
| 91 |
+
date_time: the date and time for which you want the report, formatted as '%m/%d/%y %H:%M:%S'.
|
| 92 |
+
"""
|
| 93 |
+
lon, lat = convert_location_to_coordinates(location)
|
| 94 |
+
try:
|
| 95 |
+
date_time = datetime.strptime(date_time)
|
| 96 |
+
except Exception as e:
|
| 97 |
+
raise ValueError("Conversion of `date_time` to datetime format failed, make sure to provide a string in format '%m/%d/%y %H:%M:%S'. Full trace:" + str(e))
|
| 98 |
+
temperature_celsius, risk_of_rain, wave_height = get_weather_report_at_coordinates((lon, lat), date_time)
|
| 99 |
+
return f"Weather report for {location}, {date_time}: Temperature will be {temperature_celsius}°C, risk of rain is {risk_of_rain*100:.0f}%, wave height is {wave_height}m."
|
| 100 |
+
```
|
| 101 |
+
|
| 102 |
+
सामान्य तौर पर, अपने LLM का बोझ को कम करने के लिए, खुद से यह अच्छा सवाल पूछें: "यदि मैं नया और अनुभवहीन हूं और इस टूल का पहली बार उपयोग कर रहा हूं, तो इस टूल के साथ प्रोग्रामिंग करना और अपनी गलति��ों को ठीक करना मेरे लिए कितना आसान होगा?"
|
| 103 |
+
|
| 104 |
+
### एजेंट को अधिक तर्क (arguments) दें
|
| 105 |
+
|
| 106 |
+
अपने एजेंट को कार्य का वर्णन करने वाले साधारण स्ट्रिंग से आगे बढ़कर कुछ अतिरिक्त ऑब्जेक्ट्स देने के लिए, आप `additional_args` का उपयोग कर सकते हैं। यह आपको किसी भी प्रकार का ऑब्जेक्ट पास करने की सुविधा देता है:
|
| 107 |
+
|
| 108 |
+
|
| 109 |
+
```py
|
| 110 |
+
from smolagents import CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel
|
| 111 |
+
|
| 112 |
+
model_id = "meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct"
|
| 113 |
+
|
| 114 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=InferenceClientModel(model_id=model_id), add_base_tools=True)
|
| 115 |
+
|
| 116 |
+
agent.run(
|
| 117 |
+
"Why does Mike not know many people in New York?",
|
| 118 |
+
additional_args={"mp3_sound_file_url":'https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/recording.mp3'}
|
| 119 |
+
)
|
| 120 |
+
```
|
| 121 |
+
उदाहरण के लिए, आप इस `additional_args` आर्ग्यूमेंट का उपयोग उन इमेजेज़ या स्ट्रिंग्स को पास करने के लिए कर सकते हैं जिन्हें आप चाहते हैं कि आपका एजेंट उपयोग करे।
|
| 122 |
+
|
| 123 |
+
|
| 124 |
+
|
| 125 |
+
## अपने एजेंट को डिबग कैसे करें
|
| 126 |
+
|
| 127 |
+
### 1. एक अधिक शक्तिशाली LLM का उपयोग करें
|
| 128 |
+
|
| 129 |
+
एजेंटिक वर्कफ़्लो में, कुछ त्रुटियां वास्तविक होती हैं, जबकि कुछ अन्य त्रुटियां आपके LLM इंजन के सही तरीके से तर्क न कर पाने की वजह से होती हैं।
|
| 130 |
+
उदाहरण के लिए, इस ट्रेस को देखें, जहां मैंने एक `CodeAgent` से एक कार की तस्वीर बनाने के लिए कहा:
|
| 131 |
+
```
|
| 132 |
+
==================================================================================================== New task ====================================================================================================
|
| 133 |
+
Make me a cool car picture
|
| 134 |
+
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── New step ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
|
| 135 |
+
Agent is executing the code below: ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
|
| 136 |
+
image_generator(prompt="A cool, futuristic sports car with LED headlights, aerodynamic design, and vibrant color, high-res, photorealistic")
|
| 137 |
+
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
|
| 138 |
+
|
| 139 |
+
Last output from code snippet: ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
|
| 140 |
+
/var/folders/6m/9b1tts6d5w960j80wbw9tx3m0000gn/T/tmpx09qfsdd/652f0007-3ee9-44e2-94ac-90dae6bb89a4.png
|
| 141 |
+
Step 1:
|
| 142 |
+
|
| 143 |
+
- Time taken: 16.35 seconds
|
| 144 |
+
- Input tokens: 1,383
|
| 145 |
+
- Output tokens: 77
|
| 146 |
+
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── New step ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
|
| 147 |
+
Agent is executing the code below: ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
|
| 148 |
+
final_answer("/var/folders/6m/9b1tts6d5w960j80wbw9tx3m0000gn/T/tmpx09qfsdd/652f0007-3ee9-44e2-94ac-90dae6bb89a4.png")
|
| 149 |
+
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
|
| 150 |
+
Print outputs:
|
| 151 |
+
|
| 152 |
+
Last output from code snippet: ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
|
| 153 |
+
/var/folders/6m/9b1tts6d5w960j80wbw9tx3m0000gn/T/tmpx09qfsdd/652f0007-3ee9-44e2-94ac-90dae6bb89a4.png
|
| 154 |
+
Final answer:
|
| 155 |
+
/var/folders/6m/9b1tts6d5w960j80wbw9tx3m0000gn/T/tmpx09qfsdd/652f0007-3ee9-44e2-94ac-90dae6bb89a4.png
|
| 156 |
+
```
|
| 157 |
+
उपयोगकर्ता को, एक इमेज लौटाए जाने के बजाय, उन्हें एक पाथ लौटाया जाता है।
|
| 158 |
+
यह सिस्टम से एक बग की तरह दिख सकता है, लेकिन वास्तव में एजेंटिक सिस्टम ने त्रुटि नहीं की: यह केवल इसलिए है कि LLM ब्रेन ने इमेज आउटपुट को एक वेरिएबल में सेव करने की गलती की।
|
| 159 |
+
इस प्रकार यह इमेज को फिर से एक्सेस नहीं कर सकता है सिवाय इमेज को सेव करते समय लॉग किए गए पाथ का उपयोग करके, इसलिए यह इमेज के बजाय पाथ लौटाता है।
|
| 160 |
+
|
| 161 |
+
अपने एजेंट को डीबग करने का पहला कदम इस प्रकार है "एक अधिक शक्तिशाली LLM का उपयोग करें"। `Qwen2/5-72B-Instruct` जैसे विकल्प वह गलती नहीं करते।
|
| 162 |
+
|
| 163 |
+
### 2. अधिक मार्गदर्शन / अधिक जानकारी प्रदान करें
|
| 164 |
+
|
| 165 |
+
आप कम शक्तिशाली मॉडल्स का भी उपयोग कर सकते हैं, बशर्ते आप उन्हें अधिक प्रभावी ढंग से मार्गदर्शन करें।
|
| 166 |
+
|
| 167 |
+
अपने आप को अपने मॉडल की जगह रखें: यदि आप कार्य को हल करने वाला मॉडल होते, तो क्या आप उपलब्ध जानकारी (सिस्टम प्रॉम्प्ट + कार्य निर्माण + टूल विवरण से) के साथ संघर्ष करते?
|
| 168 |
+
|
| 169 |
+
क्या आपको कुछ अतिरिक्त स्पष्टी��रण की आवश्यकता होती?
|
| 170 |
+
|
| 171 |
+
अतिरिक्त जानकारी प्रदान करने के लिए, हम तुरंत सिस्टम प्रॉम्प्ट को बदलने की सलाह नहीं देते हैं: डिफ़ॉल्ट सिस्टम प्रॉम्प्ट में कई समायोजन हैं जिन्हें आप तब तक नहीं बिगाड़ना चाहते जब तक आप प्रॉम्प्ट को बहुत अच्छी तरह से नहीं समझते।
|
| 172 |
+
अपने LLM इंजन को मार्गदर्शन करने के बेहतर तरीके हैं:
|
| 173 |
+
- यदि यह कार्य को हल करने के बारे में है: इन सभी विवरणों को कार्य में जोड़ें। यह कार्य 100 पेज लंबा हो सकता है
|
| 174 |
+
- यदि यह टूल्स के उपयोग के बारे में है: आपके टूल्स की विवरण विशेषता।
|
| 175 |
+
|
| 176 |
+
### 3. सिस्टम प्रॉम्प्ट बदलें (आमतौर पर यह सलाह नहीं दी जाती)
|
| 177 |
+
|
| 178 |
+
यदि उपरोक्त स्पष्टीकरण पर्याप्त नहीं हैं, तो आप सिस्टम प्रॉम्प्ट बदल सकते हैं।
|
| 179 |
+
|
| 180 |
+
आइए देखें कि यह कैसे काम करता है। उदाहरण के लिए, आइए [`CodeAgent`] के लिए डिफ़ॉल्ट सिस्टम प्रॉम्प्ट की जाँच करें (नीचे दिया गया वर्जन जीरो-शॉट उदाहरणों को छोड़कर छोटा किया गया है)।
|
| 181 |
+
|
| 182 |
+
```python
|
| 183 |
+
print(agent.prompt_templates["system_prompt"])
|
| 184 |
+
```
|
| 185 |
+
Here is what you get:
|
| 186 |
+
```text
|
| 187 |
+
You are an expert assistant who can solve any task using code blobs. You will be given a task to solve as best you can.
|
| 188 |
+
To do so, you have been given access to a list of tools: these tools are basically Python functions which you can call with code.
|
| 189 |
+
To solve the task, you must plan forward to proceed in a series of steps, in a cycle of 'Thought:', 'Code:', and 'Observation:' sequences.
|
| 190 |
+
|
| 191 |
+
At each step, in the 'Thought:' sequence, you should first explain your reasoning towards solving the task and the tools that you want to use.
|
| 192 |
+
Then in the 'Code:' sequence, you should write the code in simple Python. The code sequence must end with '<end_code>' sequence.
|
| 193 |
+
During each intermediate step, you can use 'print()' to save whatever important information you will then need.
|
| 194 |
+
These print outputs will then appear in the 'Observation:' field, which will be available as input for the next step.
|
| 195 |
+
In the end you have to return a final answer using the `final_answer` tool.
|
| 196 |
+
|
| 197 |
+
Here are a few examples using notional tools:
|
| 198 |
+
---
|
| 199 |
+
Task: "Generate an image of the oldest person in this document."
|
| 200 |
+
|
| 201 |
+
Thought: I will proceed step by step and use the following tools: `document_qa` to find the oldest person in the document, then `image_generator` to generate an image according to the answer.
|
| 202 |
+
Code:
|
| 203 |
+
```py
|
| 204 |
+
answer = document_qa(document=document, question="Who is the oldest person mentioned?")
|
| 205 |
+
print(answer)
|
| 206 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 207 |
+
Observation: "The oldest person in the document is John Doe, a 55 year old lumberjack living in Newfoundland."
|
| 208 |
+
|
| 209 |
+
Thought: I will now generate an image showcasing the oldest person.
|
| 210 |
+
Code:
|
| 211 |
+
```py
|
| 212 |
+
image = image_generator("A portrait of John Doe, a 55-year-old man living in Canada.")
|
| 213 |
+
final_answer(image)
|
| 214 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 215 |
+
|
| 216 |
+
---
|
| 217 |
+
Task: "What is the result of the following operation: 5 + 3 + 1294.678?"
|
| 218 |
+
|
| 219 |
+
Thought: I will use python code to compute the result of the operation and then return the final answer using the `final_answer` tool
|
| 220 |
+
Code:
|
| 221 |
+
```py
|
| 222 |
+
result = 5 + 3 + 1294.678
|
| 223 |
+
final_answer(result)
|
| 224 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 225 |
+
|
| 226 |
+
---
|
| 227 |
+
Task:
|
| 228 |
+
"Answer the question in the variable `question` about the image stored in the variable `image`. The question is in French.
|
| 229 |
+
You have been provided with these additional arguments, that you can access using the keys as variables in your python code:
|
| 230 |
+
{'question': 'Quel est l'animal sur l'image?', 'image': 'path/to/image.jpg'}"
|
| 231 |
+
|
| 232 |
+
Thought: I will use the following tools: `translator` to translate the question into English and then `image_qa` to answer the question on the input image.
|
| 233 |
+
Code:
|
| 234 |
+
```py
|
| 235 |
+
translated_question = translator(question=question, src_lang="French", tgt_lang="English")
|
| 236 |
+
print(f"The translated question is {translated_question}.")
|
| 237 |
+
answer = image_qa(image=image, question=translated_question)
|
| 238 |
+
final_answer(f"The answer is {answer}")
|
| 239 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 240 |
+
|
| 241 |
+
---
|
| 242 |
+
Task:
|
| 243 |
+
In a 1979 interview, Stanislaus Ulam discusses with Martin Sherwin about other great physicists of his time, including Oppenheimer.
|
| 244 |
+
What does he say was the consequence of Einstein learning too much math on his creativity, in one word?
|
| 245 |
+
|
| 246 |
+
Thought: I need to find and read the 1979 interview of Stanislaus Ulam with Martin Sherwin.
|
| 247 |
+
Code:
|
| 248 |
+
```py
|
| 249 |
+
pages = search(query="1979 interview Stanislaus Ulam Martin Sherwin physicists Einstein")
|
| 250 |
+
print(pages)
|
| 251 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 252 |
+
Observation:
|
| 253 |
+
No result found for query "1979 interview Stanislaus Ulam Martin Sherwin physicists Einstein".
|
| 254 |
+
|
| 255 |
+
Thought: The query was maybe too restrictive and did not find any results. Let's try again with a broader query.
|
| 256 |
+
Code:
|
| 257 |
+
```py
|
| 258 |
+
pages = search(query="1979 interview Stanislaus Ulam")
|
| 259 |
+
print(pages)
|
| 260 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 261 |
+
Observation:
|
| 262 |
+
Found 6 pages:
|
| 263 |
+
[Stanislaus Ulam 1979 interview](https://ahf.nuclearmuseum.org/voices/oral-histories/stanislaus-ulams-interview-1979/)
|
| 264 |
+
|
| 265 |
+
[Ulam discusses Manhattan Project](https://ahf.nuclearmuseum.org/manhattan-project/ulam-manhattan-project/)
|
| 266 |
+
|
| 267 |
+
(truncated)
|
| 268 |
+
|
| 269 |
+
Thought: I will read the first 2 pages to know more.
|
| 270 |
+
Code:
|
| 271 |
+
```py
|
| 272 |
+
for url in ["https://ahf.nuclearmuseum.org/voices/oral-histories/stanislaus-ulams-interview-1979/", "https://ahf.nuclearmuseum.org/manhattan-project/ulam-manhattan-project/"]:
|
| 273 |
+
whole_page = visit_webpage(url)
|
| 274 |
+
print(whole_page)
|
| 275 |
+
print("\n" + "="*80 + "\n") # Print separator between pages
|
| 276 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 277 |
+
Observation:
|
| 278 |
+
Manhattan Project Locations:
|
| 279 |
+
Los Alamos, NM
|
| 280 |
+
Stanislaus Ulam was a Polish-American mathematician. He worked on the Manhattan Project at Los Alamos and later helped design the hydrogen bomb. In this interview, he discusses his work at
|
| 281 |
+
(truncated)
|
| 282 |
+
|
| 283 |
+
Thought: I now have the final answer: from the webpages visited, Stanislaus Ulam says of Einstein: "He learned too much mathematics and sort of diminished, it seems to me personally, it seems to me his purely physics creativity." Let's answer in one word.
|
| 284 |
+
Code:
|
| 285 |
+
```py
|
| 286 |
+
final_answer("diminished")
|
| 287 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 288 |
+
|
| 289 |
+
---
|
| 290 |
+
Task: "Which city has the highest population: Guangzhou or Shanghai?"
|
| 291 |
+
|
| 292 |
+
Thought: I need to get the populations for both cities and compare them: I will use the tool `search` to get the population of both cities.
|
| 293 |
+
Code:
|
| 294 |
+
```py
|
| 295 |
+
for city in ["Guangzhou", "Shanghai"]:
|
| 296 |
+
print(f"Population {city}:", search(f"{city} population")
|
| 297 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 298 |
+
Observation:
|
| 299 |
+
Population Guangzhou: ['Guangzhou has a population of 15 million inhabitants as of 2021.']
|
| 300 |
+
Population Shanghai: '26 million (2019)'
|
| 301 |
+
|
| 302 |
+
Thought: Now I know that Shanghai has the highest population.
|
| 303 |
+
Code:
|
| 304 |
+
```py
|
| 305 |
+
final_answer("Shanghai")
|
| 306 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 307 |
+
|
| 308 |
+
---
|
| 309 |
+
Task: "What is the current age of the pope, raised to the power 0.36?"
|
| 310 |
+
|
| 311 |
+
Thought: I will use the tool `wiki` to get the age of the pope, and confirm that with a web search.
|
| 312 |
+
Code:
|
| 313 |
+
```py
|
| 314 |
+
pope_age_wiki = wiki(query="current pope age")
|
| 315 |
+
print("Pope age as per wikipedia:", pope_age_wiki)
|
| 316 |
+
pope_age_search = web_search(query="current pope age")
|
| 317 |
+
print("Pope age as per google search:", pope_age_search)
|
| 318 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 319 |
+
Observation:
|
| 320 |
+
Pope age: "The pope Francis is currently 88 years old."
|
| 321 |
+
|
| 322 |
+
Thought: I know that the pope is 88 years old. Let's compute the result using python code.
|
| 323 |
+
Code:
|
| 324 |
+
```py
|
| 325 |
+
pope_current_age = 88 ** 0.36
|
| 326 |
+
final_answer(pope_current_age)
|
| 327 |
+
```<end_code>
|
| 328 |
+
|
| 329 |
+
Above example were using notional tools that might not exist for you. On top of performing computations in the Python code snippets that you create, you only have access to these tools:
|
| 330 |
+
{%- for tool in tools.values() %}
|
| 331 |
+
- {{ tool.name }}: {{ tool.description }}
|
| 332 |
+
Takes inputs: {{tool.inputs}}
|
| 333 |
+
Returns an output of type: {{tool.output_type}}
|
| 334 |
+
{%- endfor %}
|
| 335 |
+
|
| 336 |
+
{%- if managed_agents and managed_agents.values() | list %}
|
| 337 |
+
You can also give tasks to team members.
|
| 338 |
+
Calling a team member works the same as for calling a tool: simply, the only argument you can give in the call is 'task', a long string explaining your task.
|
| 339 |
+
Given that this team member is a real human, you should be very verbose in your task.
|
| 340 |
+
Here is a list of the team members that you can call:
|
| 341 |
+
{%- for agent in managed_agents.values() %}
|
| 342 |
+
- {{ agent.name }}: {{ agent.description }}
|
| 343 |
+
{%- endfor %}
|
| 344 |
+
{%- endif %}
|
| 345 |
+
|
| 346 |
+
Here are the rules you should always follow to solve your task:
|
| 347 |
+
1. Always provide a 'Thought:' sequence, and a 'Code:\n```py' sequence ending with '```<end_code>' sequence, else you will fail.
|
| 348 |
+
2. Use only variables that you have defined!
|
| 349 |
+
3. Always use the right arguments for the tools. DO NOT pass the arguments as a dict as in 'answer = wiki({'query': "What is the place where James Bond lives?"})', but use the arguments directly as in 'answer = wiki(query="What is the place where James Bond lives?")'.
|
| 350 |
+
4. Take care to not chain too many sequential tool calls in the same code block, especially when the output format is unpredictable. For instance, a call to search has an unpredictable return format, so do not have another tool call that depends on its output in the same block: rather output results with print() to use them in the next block.
|
| 351 |
+
5. Call a tool only when needed, and never re-do a tool call that you previously did with the exact same parameters.
|
| 352 |
+
6. Don't name any new variable with the same name as a tool: for instance don't name a variable 'final_answer'.
|
| 353 |
+
7. Never create any notional variables in our code, as having these in your logs will derail you from the true variables.
|
| 354 |
+
8. You can use imports in your code, but only from the following list of modules: {{authorized_imports}}
|
| 355 |
+
9. The state persists between code executions: so if in one step you've created variables or imported modules, these will all persist.
|
| 356 |
+
10. Don't give up! You're in charge of solving the task, not providing directions to solve it.
|
| 357 |
+
|
| 358 |
+
Now Begin! If you solve the task correctly, you will receive a reward of $1,000,000.
|
| 359 |
+
```
|
| 360 |
+
|
| 361 |
+
जैसा कि आप देख सकते हैं, `"{{ tool.description }}"` जैसे प्लेसहोल्डर्स हैं: इनका उपयोग एजेंट इनिशियलाइजेशन के समय टूल्स या मैनेज्ड एजेंट्स के कुछ स्वचालित रूप से जनरेट किए गए विवरणों को डालने के लिए किया जाएगा।
|
| 362 |
+
|
| 363 |
+
इसलिए जबकि आप `system_prompt` पैरामीटर में अपने कस्टम प्रॉम्प्ट को आर्गुमेंट के रूप में पास करके इस सिस्टम प्रॉम्प्ट टेम्पलेट को ओवरराइट कर सकते हैं, आपके नए सिस्टम प्रॉम्प्ट में निम्नलिखित प्लेसहोल्डर्स होने चाहिए:
|
| 364 |
+
- टूल विवरण डालने के लिए।
|
| 365 |
+
```
|
| 366 |
+
{%- for tool in tools.values() %}
|
| 367 |
+
- {{ tool.name }}: {{ tool.description }}
|
| 368 |
+
Takes inputs: {{tool.inputs}}
|
| 369 |
+
Returns an output of type: {{tool.output_type}}
|
| 370 |
+
{%- endfor %}
|
| 371 |
+
```
|
| 372 |
+
- यदि कोई मैनेज्ड एजेंट्स हैं तो उनके लिए विवरण डालने के लिए।
|
| 373 |
+
```
|
| 374 |
+
{%- if managed_agents and managed_agents.values() | list %}
|
| 375 |
+
You can also give tasks to team members.
|
| 376 |
+
Calling a team member works the same as for calling a tool: simply, the only argument you can give in the call is 'task', a long string explaining your task.
|
| 377 |
+
Given that this team member is a real human, you should be very verbose in your task.
|
| 378 |
+
Here is a list of the team members that you can call:
|
| 379 |
+
{%- for agent in managed_agents.values() %}
|
| 380 |
+
- {{ agent.name }}: {{ agent.description }}
|
| 381 |
+
{%- endfor %}
|
| 382 |
+
{%- endif %}
|
| 383 |
+
```
|
| 384 |
+
- केवल `CodeAgent` के लिए: अधिकृत इम्पोर्ट्स की सूची डालने के लिए `"{{authorized_imports}}"`।
|
| 385 |
+
|
| 386 |
+
फिर आप सिस्टम प्रॉम्प्ट को निम्नानुसार बदल सकते हैं:
|
| 387 |
+
|
| 388 |
+
```py
|
| 389 |
+
agent.prompt_templates["system_prompt"] = agent.prompt_templates["system_prompt"] + "\nHere you go!"
|
| 390 |
+
```
|
| 391 |
+
|
| 392 |
+
This also works with the [`ToolCallingAgent`].
|
| 393 |
+
|
| 394 |
+
|
| 395 |
+
### 4. अतिरिक्त योजना
|
| 396 |
+
|
| 397 |
+
हम पूरक योजना चरण के लिए एक मॉडल प्रदान करते हैं, जिसे एजेंट सामान्य क्रियाओं के चरणों के बीच नियमित रूप से चला सकता है। इस चरण में कोई टूल कॉल नहीं होती है, LLM से केवल उन तथ्यों की सूची को अपडेट करने के लिए कहा जाता है जो उसे ज्ञात हैं और इन तथ्यों के आधार पर उसे अगले कदमों के बारे में विचार करना होता है।
|
| 398 |
+
|
| 399 |
+
```py
|
| 400 |
+
from smolagents import load_tool, CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel, DuckDuckGoSearchTool
|
| 401 |
+
from dotenv import load_dotenv
|
| 402 |
+
|
| 403 |
+
load_dotenv()
|
| 404 |
+
|
| 405 |
+
# Import tool from Hub
|
| 406 |
+
image_generation_tool = load_tool("m-ric/text-to-image", trust_remote_code=True)
|
| 407 |
+
|
| 408 |
+
search_tool = DuckDuckGoSearchTool()
|
| 409 |
+
|
| 410 |
+
agent = CodeAgent(
|
| 411 |
+
tools=[search_tool],
|
| 412 |
+
model=InferenceClientModel(model_id="Qwen/Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct"),
|
| 413 |
+
planning_interval=3 # This is where you activate planning!
|
| 414 |
+
)
|
| 415 |
+
|
| 416 |
+
# Run it!
|
| 417 |
+
result = agent.run(
|
| 418 |
+
"How long would a cheetah at full speed take to run the length of Pont Alexandre III?",
|
| 419 |
+
)
|
| 420 |
+
```
|
smolagents/docs/source/hi/tutorials/inspect_runs.mdx
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# OpenTelemetry के साथ runs का निरीक्षण
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
[[open-in-colab]]
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 6 |
+
> यदि आप एजेंट्स बनाने में नए हैं, तो पहले [एजेंट्स का परिचय](../conceptual_guides/intro_agents) और [smolagents की गाइडेड टूर](../guided_tour) पढ़ना सुनिश्चित करें।
|
| 7 |
+
|
| 8 |
+
### Agents runs को लॉग क्यों करें?
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
Agent runs को डीबग करना जटिल होता है।
|
| 11 |
+
|
| 12 |
+
यह सत्यापित करना कठिन है कि एक रन ठीक से चला या नहीं, क्योंकि एजेंट वर्कफ़्लो [डिज़ाइन के अनुसार अप्रत्याशित](../conceptual_guides/intro_agents) होते हैं (यदि वे प्रत्याशित होते, तो आप पुराने अच्छे कोड का ही उपयोग कर रहे होते)।
|
| 13 |
+
|
| 14 |
+
और रन का निरीक्षण करना भी कठिन है: मल्टी-स्टेप एजेंट्स जल्दी ही कंसोल को लॉग से भर देते हैं, और अधिकांश त्रुटियां केवल "LLM dumb" प्रकार की त्रुटियां होती हैं, जिनसे LLM अगले चरण में बेहतर कोड या टूल कॉल लिखकर स्वयं को सुधार लेता है।
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
इसलिए बाद के निरीक्षण और मॉनिटरिंग के लिए प्रोडक्शन में agent runs को रिकॉर्ड करने के लिए इंस्ट्रुमेंटेशन का उपयोग करना आवश्यक है!
|
| 17 |
+
|
| 18 |
+
हमने agent runs को इंस्ट्रुमेंट करने के लिए [OpenTelemetry](https://opentelemetry.io/) मानक को अपनाया है।
|
| 19 |
+
|
| 20 |
+
इसका मतलब है कि आप बस कुछ इंस्ट्रुमेंटेशन कोड चला सकते हैं, फिर अपने एजेंट्स को सामान्य रूप से चला सकते हैं, और सब कुछ आपके प्लेटफॉर्म में लॉग हो जाता है।
|
| 21 |
+
|
| 22 |
+
यह इस प्रकार होता है:
|
| 23 |
+
पहले आवश्यक पैकेज इंस्टॉल करें। यहां हम [Phoenix by Arize AI](https://github.com/Arize-ai/phoenix) इंस्टॉल करते हैं क्योंकि यह लॉग्स को एकत्र और निरीक्षण करने का एक अच्छा समाधान है, लेकिन इस संग्रह और निरीक्षण भाग के लिए आप अन्य OpenTelemetry-कम्पैटिबल प्लेटफॉर्म्स का उपयोग कर सकते हैं।
|
| 24 |
+
|
| 25 |
+
```shell
|
| 26 |
+
pip install smolagents
|
| 27 |
+
pip install arize-phoenix opentelemetry-sdk opentelemetry-exporter-otlp openinference-instrumentation-smolagents
|
| 28 |
+
```
|
| 29 |
+
|
| 30 |
+
फिर कलेक्टर को बैकग्राउंड में चलाएं।
|
| 31 |
+
|
| 32 |
+
```shell
|
| 33 |
+
python -m phoenix.server.main serve
|
| 34 |
+
```
|
| 35 |
+
|
| 36 |
+
अंत में, अपने एजेंट्स को ट्रेस करने और ट्रेस को नीचे परिभाषित एंडपॉइंट पर Phoenix को भेजने के लिए `SmolagentsInstrumentor` को सेट करें।
|
| 37 |
+
|
| 38 |
+
```python
|
| 39 |
+
from opentelemetry import trace
|
| 40 |
+
from opentelemetry.sdk.trace import TracerProvider
|
| 41 |
+
from opentelemetry.sdk.trace.export import BatchSpanProcessor
|
| 42 |
+
|
| 43 |
+
from openinference.instrumentation.smolagents import SmolagentsInstrumentor
|
| 44 |
+
from opentelemetry.exporter.otlp.proto.http.trace_exporter import OTLPSpanExporter
|
| 45 |
+
from opentelemetry.sdk.trace.export import ConsoleSpanExporter, SimpleSpanProcessor
|
| 46 |
+
|
| 47 |
+
endpoint = "http://0.0.0.0:6006/v1/traces"
|
| 48 |
+
trace_provider = TracerProvider()
|
| 49 |
+
trace_provider.add_span_processor(SimpleSpanProcessor(OTLPSpanExporter(endpoint)))
|
| 50 |
+
|
| 51 |
+
SmolagentsInstrumentor().instrument(tracer_provider=trace_provider)
|
| 52 |
+
```
|
| 53 |
+
तब आप अपने एजेंट चला सकते हैं!
|
| 54 |
+
|
| 55 |
+
```py
|
| 56 |
+
from smolagents import (
|
| 57 |
+
CodeAgent,
|
| 58 |
+
ToolCallingAgent,
|
| 59 |
+
DuckDuckGoSearchTool,
|
| 60 |
+
VisitWebpageTool,
|
| 61 |
+
InferenceClientModel,
|
| 62 |
+
)
|
| 63 |
+
|
| 64 |
+
model = InferenceClientModel()
|
| 65 |
+
|
| 66 |
+
managed_agent = ToolCallingAgent(
|
| 67 |
+
tools=[DuckDuckGoSearchTool(), VisitWebpageTool()],
|
| 68 |
+
model=model,
|
| 69 |
+
name="managed_agent",
|
| 70 |
+
description="This is an agent that can do web search.",
|
| 71 |
+
)
|
| 72 |
+
|
| 73 |
+
manager_agent = CodeAgent(
|
| 74 |
+
tools=[],
|
| 75 |
+
model=model,
|
| 76 |
+
managed_agents=[managed_agent],
|
| 77 |
+
)
|
| 78 |
+
manager_agent.run(
|
| 79 |
+
"If the US keeps its 2024 growth rate, how many years will it take for the GDP to double?"
|
| 80 |
+
)
|
| 81 |
+
```
|
| 82 |
+
और फिर आप अपने रन का निरीक्षण करने के लिए `http://0.0.0.0:6006/projects/` पर जा सकते हैं!
|
| 83 |
+
|
| 84 |
+
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/smolagents/inspect_run_phoenix.png">
|
| 85 |
+
|
| 86 |
+
आप देख सकते हैं कि CodeAgent ने अपने मैनेज्ड ToolCallingAgent को (वैसे, मैनेज्ड एजेंट एक CodeAgent भी हो सकता था) U.S. 2024 ग्रोथ रेट के लिए वेब सर्च चलाने के लिए कॉल किया। फिर मैनेज्ड एजेंट ने अपनी रिपोर्ट लौटाई और मैनेजर एजेंट ने अर्थव्यवस्था के दोगुना होने का समय गणना करने के लिए उस पर कार्य किया! अच्छा है, है ना?
|