Llama-3.3-Nemotron-Super-49B-v1
Model Overview
Llama-3.3-Nemotron-Super-49B-v1 is a large language model (LLM) which is a derivative of Meta Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct (AKA the reference model). It is a reasoning model that is post trained for reasoning, human chat preferences, and tasks, such as RAG and tool calling. The model supports a context length of 128K tokens.
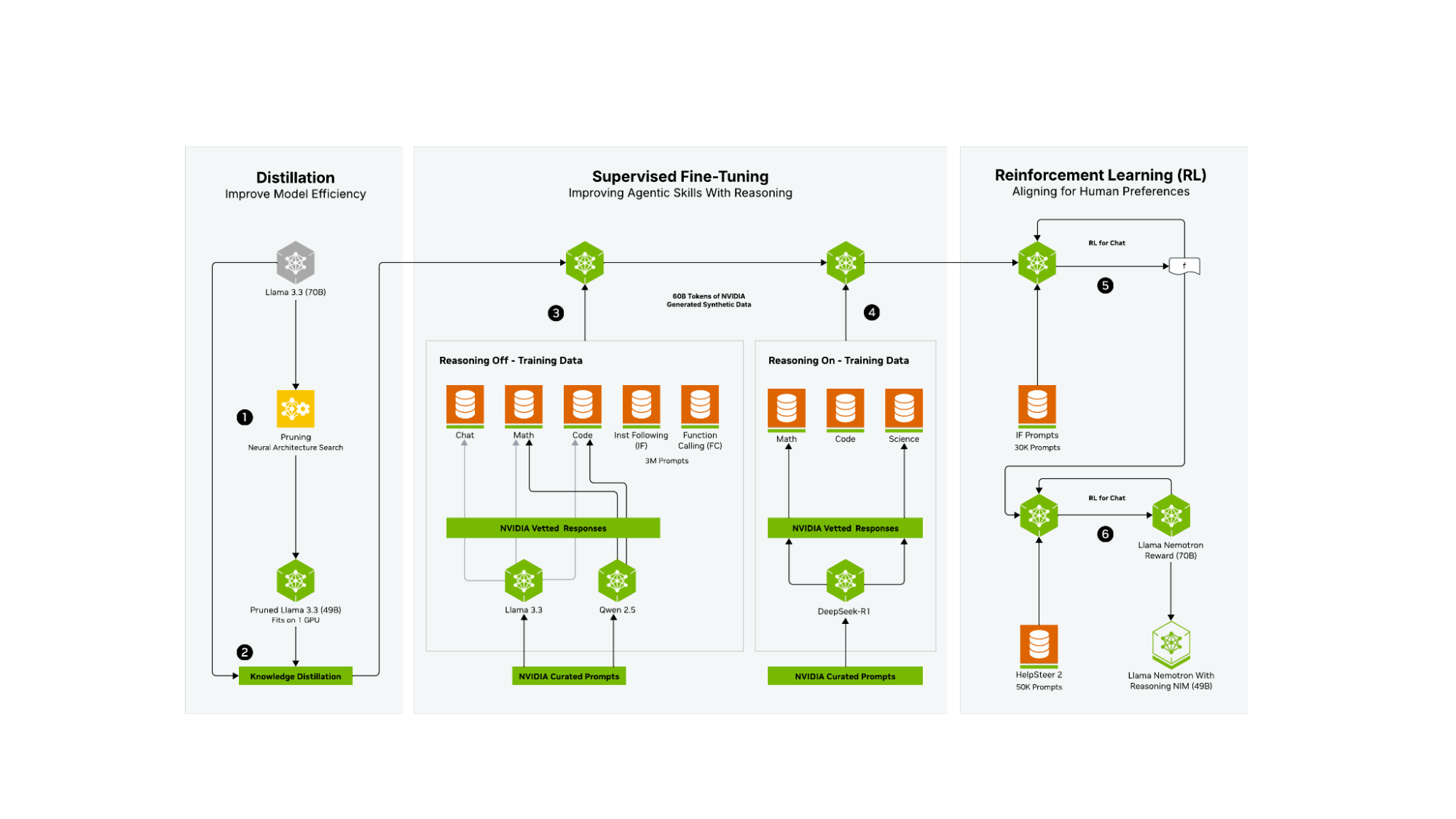
Llama-3.3-Nemotron-Super-49B-v1 is a model which offers a great tradeoff between model accuracy and efficiency. Efficiency (throughput) directly translates to savings. Using a novel Neural Architecture Search (NAS) approach, we greatly reduce the model’s memory footprint, enabling larger workloads, as well as fitting the model on a single GPU at high workloads (H200). This NAS approach enables the selection of a desired point in the accuracy-efficiency tradeoff. For more information on the NAS approach, please refer to this paper.
The model underwent a multi-phase post-training process to enhance both its reasoning and non-reasoning capabilities. This includes a supervised fine-tuning stage for Math, Code, Reasoning, and Tool Calling as well as multiple reinforcement learning (RL) stages using REINFORCE (RLOO) and Online Reward-aware Preference Optimization (RPO) algorithms for both chat and instruction-following. The final model checkpoint is obtained after merging the final SFT and Online RPO checkpoints. For more details on how the model was trained, please see our technical report and blog.
This model is part of the Llama Nemotron Collection. You can find the other model(s) in this family here:
This model is ready for commercial use.
License/Terms of Use
GOVERNING TERMS: Your use of this model is governed by the NVIDIA Open Model License.
Additional Information: Llama 3.3 Community License Agreement. Built with Llama.
Model Developer: NVIDIA
Model Dates: Trained between November 2024 and February 2025
Data Freshness: The pretraining data has a cutoff of 2023 per Meta Llama 3.3 70B
Use Case:
Developers designing AI Agent systems, chatbots, RAG systems, and other AI-powered applications. Also suitable for typical instruction-following tasks.
Release Date:
3/18/2025
References
- [2505.00949] Llama-Nemotron: Efficient Reasoning Models
- [2411.19146] Puzzle: Distillation-Based NAS for Inference-Optimized LLMs
- [2502.00203] Reward-aware Preference Optimization: A Unified Mathematical Framework for Model Alignment
Model Architecture
Architecture Type: Dense decoder-only Transformer model
Network Architecture: Llama 3.3 70B Instruct, customized through Neural Architecture Search (NAS)
The model is a derivative of Meta’s Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct, using Neural Architecture Search (NAS). The NAS algorithm results in non-standard and non-repetitive blocks. This includes the following:
- Skip attention: In some blocks, the attention is skipped entirely, or replaced with a single linear layer.
- Variable FFN: The expansion/compression ratio in the FFN layer is different between blocks.
We utilize a block-wise distillation of the reference model, where for each block we create multiple variants providing different tradeoffs of quality vs. computational complexity, discussed in more depth below. We then search over the blocks to create a model which meets the required throughput and memory (optimized for a single H100-80GB GPU) while minimizing the quality degradation. The model then undergoes knowledge distillation (KD), with a focus on English single and multi-turn chat use-cases. The KD step included 40 billion tokens consisting of a mixture of 3 datasets - FineWeb, Buzz-V1.2 and Dolma.
Intended use
Llama-3.3-Nemotron-Super-49B-v1 is a general purpose reasoning and chat model intended to be used in English and coding languages. Other non-English languages (German, French, Italian, Portuguese, Hindi, Spanish, and Thai) are also supported.
Input
- Input Type: Text
- Input Format: String
- Input Parameters: One-Dimensional (1D)
- Other Properties Related to Input: Context length up to 131,072 tokens
Output
- Output Type: Text
- Output Format: String
- Output Parameters: One-Dimensional (1D)
- Other Properties Related to Output: Context length up to 131,072 tokens
Model Version
1.0 (3/18/2025)
Software Integration
- Runtime Engine: Transformers
- Recommended Hardware Microarchitecture Compatibility:
- NVIDIA Hopper
- NVIDIA Ampere
Quick Start and Usage Recommendations:
- Reasoning mode (ON/OFF) is controlled via the system prompt, which must be set as shown in the example below. All instructions should be contained within the user prompt
- We recommend setting temperature to
0.6, and Top P to0.95for Reasoning ON mode - We recommend using greedy decoding for Reasoning OFF mode
- We have provided a list of prompts to use for evaluation for each benchmark where a specific template is required
- The model will include
<think></think>if no reasoning was necessary in Reasoning ON model, this is expected behaviour
You can try this model out through the preview API, using this link: Llama-3_3-Nemotron-Super-49B-v1.
Use It with Transformers
See the snippet below for usage with Hugging Face Transformers library. Reasoning mode (ON/OFF) is controlled via system prompt. Please see the example below
We recommend using the transformers package with version 4.48.3.
Example of reasoning on:
import torch
import transformers
model_id = "nvidia/Llama-3_3-Nemotron-Super-49B-v1"
model_kwargs = {"torch_dtype": torch.bfloat16, "trust_remote_code": True, "device_map": "auto"}
tokenizer = transformers.AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
tokenizer.pad_token_id = tokenizer.eos_token_id
pipeline = transformers.pipeline(
"text-generation",
model=model_id,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
max_new_tokens=32768,
temperature=0.6,
top_p=0.95,
**model_kwargs
)
thinking = "on"
print(pipeline([{"role": "system", "content": f"detailed thinking {thinking}"},{"role": "user", "content": "Solve x*(sin(x)+2)=0"}]))
Example of reasoning off:
import torch
import transformers
model_id = "nvidia/Llama-3_3-Nemotron-Super-49B-v1"
model_kwargs = {"torch_dtype": torch.bfloat16, "trust_remote_code": True, "device_map": "auto"}
tokenizer = transformers.AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
tokenizer.pad_token_id = tokenizer.eos_token_id
pipeline = transformers.pipeline(
"text-generation",
model=model_id,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
max_new_tokens=32768,
do_sample=False,
**model_kwargs
)
# Thinking can be "on" or "off"
thinking = "off"
print(pipeline([{"role": "system", "content": f"detailed thinking {thinking}"},{"role": "user", "content": "Solve x*(sin(x)+2)=0"}]))
Use It with vLLM
pip install vllm==0.8.3
An example on how to serve with vLLM:
python3 -m vllm.entrypoints.openai.api_server \
--model "nvidia/Llama-3_3-Nemotron-Super-49B-v1" \
--trust-remote-code \
--seed=1 \
--host="0.0.0.0" \
--port=5000 \
--served-model-name "nvidia/Llama-3_3-Nemotron-Super-49B-v1" \
--tensor-parallel-size=8 \
--max-model-len=32768 \
--gpu-memory-utilization 0.95 \
--enforce-eager
Inference:
Engine:
- Transformers
Test Hardware:
- FP8: 1x NVIDIA H100-80GB GPU (Coming Soon!)
- BF16:
- 2x NVIDIA H100-80GB
- 2x NVIDIA A100-80GB GPUs
[Preferred/Supported] Operating System(s): Linux
Training Datasets
A large variety of training data was used for the knowledge distillation phase before post-training pipeline, 3 of which included: FineWeb, Buzz-V1.2, and Dolma.
The data for the multi-stage post-training phases for improvements in Code, Math, and Reasoning is a compilation of SFT and RL data that supports improvements of math, code, general reasoning, and instruction following capabilities of the original Llama instruct model.
In conjunction with this model release, NVIDIA has released 30M samples of post-training data, as public and permissive. Please see Llama-Nemotron-Postraining-Dataset-v1.
Distribution of the domains is as follows:
| Category | Value |
|---|---|
| math | 19,840,970 |
| code | 9,612,677 |
| science | 708,920 |
| instruction following | 56,339 |
| chat | 39,792 |
| safety | 31,426 |
Prompts have been sourced from either public and open corpus or synthetically generated. Responses were synthetically generated by a variety of models, with some prompts containing responses for both reasoning on and off modes, to train the model to distinguish between two modes.
Data Collection for Training Datasets:
- Hybrid: Automated, Human, Synthetic
Data Labeling for Training Datasets:
- Hybrid: Automated, Human, Synthetic
Evaluation Datasets
We used the datasets listed below to evaluate Llama-3.3-Nemotron-Super-49B-v1.
Data Collection for Evaluation Datasets:
- Hybrid: Human/Synthetic
Data Labeling for Evaluation Datasets:
- Hybrid: Human/Synthetic/Automatic
Evaluation Results
These results contain both “Reasoning On”, and “Reasoning Off”. We recommend using temperature=0.6, top_p=0.95 for “Reasoning On” mode, and greedy decoding for “Reasoning Off” mode. All evaluations are done with 32k sequence length. We run the benchmarks up to 16 times and average the scores to be more accurate.
NOTE: Where applicable, a Prompt Template will be provided. While completing benchmarks, please ensure that you are parsing for the correct output format as per the provided prompt in order to reproduce the benchmarks seen below.
Arena-Hard
| Reasoning Mode | Score |
|---|---|
| Reasoning Off | 88.3 |
MATH500
| Reasoning Mode | pass@1 |
|---|---|
| Reasoning Off | 74.0 |
| Reasoning On | 96.6 |
User Prompt Template:
"Below is a math question. I want you to reason through the steps and then give a final answer. Your final answer should be in \boxed{}.\nQuestion: {question}"
AIME25
| Reasoning Mode | pass@1 |
|---|---|
| Reasoning Off | 13.33 |
| Reasoning On | 58.4 |
User Prompt Template:
"Below is a math question. I want you to reason through the steps and then give a final answer. Your final answer should be in \boxed{}.\nQuestion: {question}"
GPQA
| Reasoning Mode | pass@1 |
|---|---|
| Reasoning Off | 50 |
| Reasoning On | 66.67 |
User Prompt Template:
"What is the correct answer to this question: {question}\nChoices:\nA. {option_A}\nB. {option_B}\nC. {option_C}\nD. {option_D}\nLet's think step by step, and put the final answer (should be a single letter A, B, C, or D) into a \boxed{}"
IFEval
| Reasoning Mode | Strict:Instruction |
|---|---|
| Reasoning Off | 89.21 |
BFCL V2 Live
| Reasoning Mode | Score |
|---|---|
| Reasoning Off | 73.7 |
User Prompt Template:
You are an expert in composing functions. You are given a question and a set of possible functions.
Based on the question, you will need to make one or more function/tool calls to achieve the purpose.
If none of the function can be used, point it out. If the given question lacks the parameters required by the function,
also point it out. You should only return the function call in tools call sections.
If you decide to invoke any of the function(s), you MUST put it in the format of <TOOLCALL>[func_name1(params_name1=params_value1, params_name2=params_value2...), func_name2(params)]</TOOLCALL>
You SHOULD NOT include any other text in the response.
Here is a list of functions in JSON format that you can invoke.
<AVAILABLE_TOOLS>{functions}</AVAILABLE_TOOLS>
{user_prompt}
MBPP 0-shot
| Reasoning Mode | pass@1 |
|---|---|
| Reasoning Off | 84.9 |
| Reasoning On | 91.3 |
User Prompt Template:
You are an exceptionally intelligent coding assistant that consistently delivers accurate and reliable responses to user instructions.
@@ Instruction
Here is the given problem and test examples:
{prompt}
Please use the python programming language to solve this problem.
Please make sure that your code includes the functions from the test samples and that the input and output formats of these functions match the test samples.
Please return all completed codes in one code block.
This code block should be in the following format:
```python
# Your codes here
```
MT-Bench
| Reasoning Mode | Score |
|---|---|
| Reasoning Off | 9.17 |
Ethical Considerations:
NVIDIA believes Trustworthy AI is a shared responsibility and we have established policies and practices to enable development for a wide array of AI applications. When downloaded or used in accordance with our terms of service, developers should work with their internal model team to ensure this model meets requirements for the relevant industry and use case and addresses unforeseen product misuse.
For more detailed information on ethical considerations for this model, please see the Model Card++ Explainability, Bias, Safety & Security, and Privacy Subcards.
Please report security vulnerabilities or NVIDIA AI Concerns here.
Citation
@misc{bercovich2025llamanemotronefficientreasoningmodels,
title={Llama-Nemotron: Efficient Reasoning Models},
author={Akhiad Bercovich and Itay Levy and Izik Golan and Mohammad Dabbah and Ran El-Yaniv and Omri Puny and Ido Galil and Zach Moshe and Tomer Ronen and Najeeb Nabwani and Ido Shahaf and Oren Tropp and Ehud Karpas and Ran Zilberstein and Jiaqi Zeng and Soumye Singhal and Alexander Bukharin and Yian Zhang and Tugrul Konuk and Gerald Shen and Ameya Sunil Mahabaleshwarkar and Bilal Kartal and Yoshi Suhara and Olivier Delalleau and Zijia Chen and Zhilin Wang and David Mosallanezhad and Adi Renduchintala and Haifeng Qian and Dima Rekesh and Fei Jia and Somshubra Majumdar and Vahid Noroozi and Wasi Uddin Ahmad and Sean Narenthiran and Aleksander Ficek and Mehrzad Samadi and Jocelyn Huang and Siddhartha Jain and Igor Gitman and Ivan Moshkov and Wei Du and Shubham Toshniwal and George Armstrong and Branislav Kisacanin and Matvei Novikov and Daria Gitman and Evelina Bakhturina and Jane Polak Scowcroft and John Kamalu and Dan Su and Kezhi Kong and Markus Kliegl and Rabeeh Karimi and Ying Lin and Sanjeev Satheesh and Jupinder Parmar and Pritam Gundecha and Brandon Norick and Joseph Jennings and Shrimai Prabhumoye and Syeda Nahida Akter and Mostofa Patwary and Abhinav Khattar and Deepak Narayanan and Roger Waleffe and Jimmy Zhang and Bor-Yiing Su and Guyue Huang and Terry Kong and Parth Chadha and Sahil Jain and Christine Harvey and Elad Segal and Jining Huang and Sergey Kashirsky and Robert McQueen and Izzy Putterman and George Lam and Arun Venkatesan and Sherry Wu and Vinh Nguyen and Manoj Kilaru and Andrew Wang and Anna Warno and Abhilash Somasamudramath and Sandip Bhaskar and Maka Dong and Nave Assaf and Shahar Mor and Omer Ullman Argov and Scot Junkin and Oleksandr Romanenko and Pedro Larroy and Monika Katariya and Marco Rovinelli and Viji Balas and Nicholas Edelman and Anahita Bhiwandiwalla and Muthu Subramaniam and Smita Ithape and Karthik Ramamoorthy and Yuting Wu and Suguna Varshini Velury and Omri Almog and Joyjit Daw and Denys Fridman and Erick Galinkin and Michael Evans and Katherine Luna and Leon Derczynski and Nikki Pope and Eileen Long and Seth Schneider and Guillermo Siman and Tomasz Grzegorzek and Pablo Ribalta and Monika Katariya and Joey Conway and Trisha Saar and Ann Guan and Krzysztof Pawelec and Shyamala Prayaga and Oleksii Kuchaiev and Boris Ginsburg and Oluwatobi Olabiyi and Kari Briski and Jonathan Cohen and Bryan Catanzaro and Jonah Alben and Yonatan Geifman and Eric Chung and Chris Alexiuk},
year={2025},
eprint={2505.00949},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.00949},
}
- Downloads last month
- 23,659
