Semantic Textual Similarity
Semantic Textual Similarity (STS) assigns a score on the similarity of two texts. In this example, we use the STSbenchmark as training data to fine-tune our network. See the following example scripts how to tune SentenceTransformer on STS data:
- training_stsbenchmark.py - This example shows how to create a SentenceTransformer model from scratch by using a pre-trained transformer model together with a pooling layer.
- training_stsbenchmark_continue_training.py - This example shows how to continue training on STS data for a previously created & trained SentenceTransformer model. In that example, we load a model trained on NLI data.
Training data
In STS, we have sentence pairs annotated together with a score indicating the similarity. For the STSbenchmark, the scores ranges from 0 (the content of the two sentences are competely different) up to 5 (the two sentences are identical in terms of their meaning). To train our network, we need to normalize these scores to a range of 0-1. This can simply be done by dividing the score by 5.
To store our training data, we create a list with InputExample objects. Each InputExample contains the sentence pair together with the label (score) that ranges between 0 - 1. A simplified version how the training data has to look like is the following:
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentencesDataset, InputExample, losses
model = SentenceTransformer('nli-distilroberta-base-v2')
train_examples = [InputExample(texts=['My first sentence', 'My second sentence'], label=0.8),
InputExample(texts=['Another pair', 'Unrelated sentence'], label=0.3)]
train_dataset = SentencesDataset(train_examples, model)
Loss Function
As loss function we use CosineSimilarityLoss.
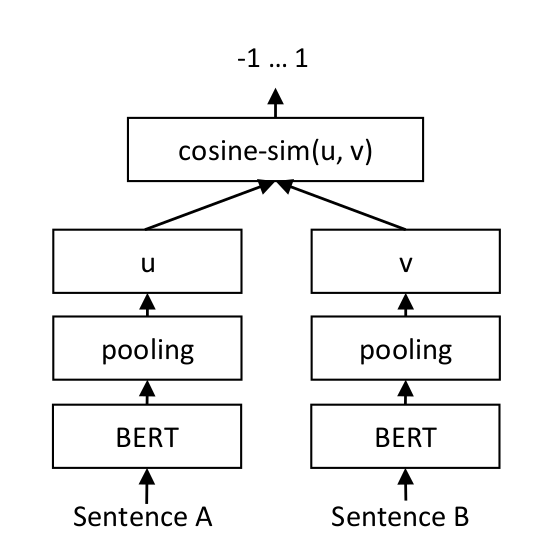
CosineSimilarityLoss trains the network with a siamese network structure (for details see: Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings using Siamese BERT-Networks)
For each sentence pair, we pass sentence A and sentence B through our network which yields the embeddings u und v. The similarity of these embeddings is computed using cosine similarity and the result is compared to the gold similarity score. This allows our network to be fine-tuned and to recognize the similarity of sentences.
This training in a siamese network structure is done automatically when we use CosineSimilarityLoss.