Transformers documentation
TVP
TVP
Overview
The text-visual prompting (TVP) framework was proposed in the paper Text-Visual Prompting for Efficient 2D Temporal Video Grounding by Yimeng Zhang, Xin Chen, Jinghan Jia, Sijia Liu, Ke Ding.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
In this paper, we study the problem of temporal video grounding (TVG), which aims to predict the starting/ending time points of moments described by a text sentence within a long untrimmed video. Benefiting from fine-grained 3D visual features, the TVG techniques have achieved remarkable progress in recent years. However, the high complexity of 3D convolutional neural networks (CNNs) makes extracting dense 3D visual features time-consuming, which calls for intensive memory and computing resources. Towards efficient TVG, we propose a novel text-visual prompting (TVP) framework, which incorporates optimized perturbation patterns (that we call ‘prompts’) into both visual inputs and textual features of a TVG model. In sharp contrast to 3D CNNs, we show that TVP allows us to effectively co-train vision encoder and language encoder in a 2D TVG model and improves the performance of cross-modal feature fusion using only low-complexity sparse 2D visual features. Further, we propose a Temporal-Distance IoU (TDIoU) loss for efficient learning of TVG. Experiments on two benchmark datasets, Charades-STA and ActivityNet Captions datasets, empirically show that the proposed TVP significantly boosts the performance of 2D TVG (e.g., 9.79% improvement on Charades-STA and 30.77% improvement on ActivityNet Captions) and achieves 5× inference acceleration over TVG using 3D visual features.
This research addresses temporal video grounding (TVG), which is the process of pinpointing the start and end times of specific events in a long video, as described by a text sentence. Text-visual prompting (TVP), is proposed to enhance TVG. TVP involves integrating specially designed patterns, known as ‘prompts’, into both the visual (image-based) and textual (word-based) input components of a TVG model. These prompts provide additional spatial-temporal context, improving the model’s ability to accurately determine event timings in the video. The approach employs 2D visual inputs in place of 3D ones. Although 3D inputs offer more spatial-temporal detail, they are also more time-consuming to process. The use of 2D inputs with the prompting method aims to provide similar levels of context and accuracy more efficiently.
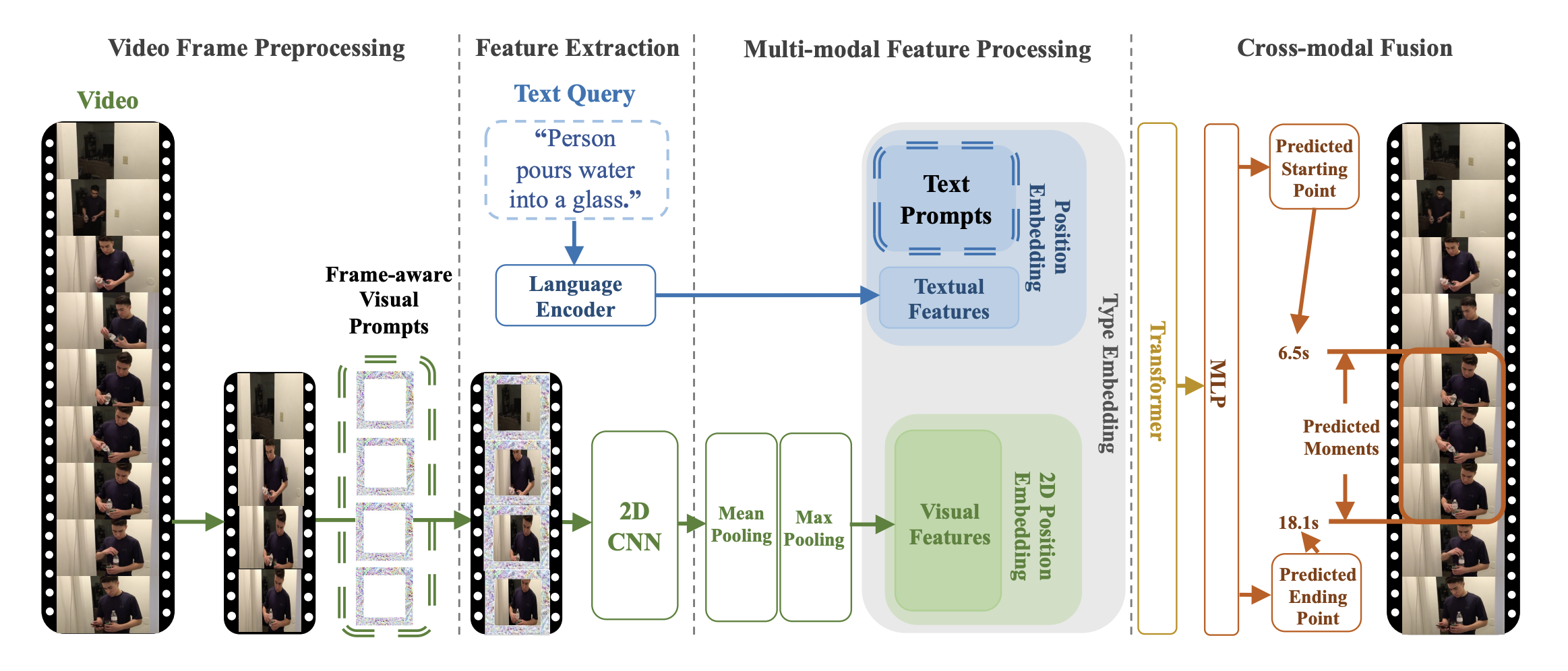 TVP architecture. Taken from the original paper.
TVP architecture. Taken from the original paper. This model was contributed by Jiqing Feng. The original code can be found here.
Usage tips and examples
Prompts are optimized perturbation patterns, which would be added to input video frames or text features. Universal set refers to using the same exact set of prompts for any input, this means that these prompts are added consistently to all video frames and text features, regardless of the input’s content.
TVP consists of a visual encoder and cross-modal encoder. A universal set of visual prompts and text prompts to be integrated into sampled video frames and textual features, respectively. Specially, a set of different visual prompts are applied to uniformly-sampled frames of one untrimmed video in order.
The goal of this model is to incorporate trainable prompts into both visual inputs and textual features to temporal video grounding(TVG) problems. In principle, one can apply any visual, cross-modal encoder in the proposed architecture.
The TvpProcessor wraps BertTokenizer and TvpImageProcessor into a single instance to both encode the text and prepare the images respectively.
The following example shows how to run temporal video grounding using TvpProcessor and TvpForVideoGrounding.
import av
import cv2
import numpy as np
import torch
from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
from transformers import AutoProcessor, TvpForVideoGrounding
def pyav_decode(container, sampling_rate, num_frames, clip_idx, num_clips, target_fps):
'''
Convert the video from its original fps to the target_fps and decode the video with PyAV decoder.
Args:
container (container): pyav container.
sampling_rate (int): frame sampling rate (interval between two sampled frames).
num_frames (int): number of frames to sample.
clip_idx (int): if clip_idx is -1, perform random temporal sampling.
If clip_idx is larger than -1, uniformly split the video to num_clips
clips, and select the clip_idx-th video clip.
num_clips (int): overall number of clips to uniformly sample from the given video.
target_fps (int): the input video may have different fps, convert it to
the target video fps before frame sampling.
Returns:
frames (tensor): decoded frames from the video. Return None if the no
video stream was found.
fps (float): the number of frames per second of the video.
'''
video = container.streams.video[0]
fps = float(video.average_rate)
clip_size = sampling_rate * num_frames / target_fps * fps
delta = max(num_frames - clip_size, 0)
start_idx = delta * clip_idx / num_clips
end_idx = start_idx + clip_size - 1
timebase = video.duration / num_frames
video_start_pts = int(start_idx * timebase)
video_end_pts = int(end_idx * timebase)
seek_offset = max(video_start_pts - 1024, 0)
container.seek(seek_offset, any_frame=False, backward=True, stream=video)
frames = {}
for frame in container.decode(video=0):
if frame.pts < video_start_pts:
continue
frames[frame.pts] = frame
if frame.pts > video_end_pts:
break
frames = [frames[pts] for pts in sorted(frames)]
return frames, fps
def decode(container, sampling_rate, num_frames, clip_idx, num_clips, target_fps):
'''
Decode the video and perform temporal sampling.
Args:
container (container): pyav container.
sampling_rate (int): frame sampling rate (interval between two sampled frames).
num_frames (int): number of frames to sample.
clip_idx (int): if clip_idx is -1, perform random temporal sampling.
If clip_idx is larger than -1, uniformly split the video to num_clips
clips, and select the clip_idx-th video clip.
num_clips (int): overall number of clips to uniformly sample from the given video.
target_fps (int): the input video may have different fps, convert it to
the target video fps before frame sampling.
Returns:
frames (tensor): decoded frames from the video.
'''
assert clip_idx >= -2, "Not a valied clip_idx {}".format(clip_idx)
frames, fps = pyav_decode(container, sampling_rate, num_frames, clip_idx, num_clips, target_fps)
clip_size = sampling_rate * num_frames / target_fps * fps
index = np.linspace(0, clip_size - 1, num_frames)
index = np.clip(index, 0, len(frames) - 1).astype(np.int64)
frames = np.array([frames[idx].to_rgb().to_ndarray() for idx in index])
frames = frames.transpose(0, 3, 1, 2)
return frames
file = hf_hub_download(repo_id="Intel/tvp_demo", filename="AK2KG.mp4", repo_type="dataset")
model = TvpForVideoGrounding.from_pretrained("Intel/tvp-base")
decoder_kwargs = dict(
container=av.open(file, metadata_errors="ignore"),
sampling_rate=1,
num_frames=model.config.num_frames,
clip_idx=0,
num_clips=1,
target_fps=3,
)
raw_sampled_frms = decode(**decoder_kwargs)
text = "a person is sitting on a bed."
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("Intel/tvp-base")
model_inputs = processor(
text=[text], videos=list(raw_sampled_frms), return_tensors="pt", max_text_length=100#, size=size
)
model_inputs["pixel_values"] = model_inputs["pixel_values"].to(model.dtype)
output = model(**model_inputs)
def get_video_duration(filename):
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(filename)
if cap.isOpened():
rate = cap.get(5)
frame_num = cap.get(7)
duration = frame_num/rate
return duration
return -1
duration = get_video_duration(file)
start, end = processor.post_process_video_grounding(output.logits, duration)
print(f"The time slot of the video corresponding to the text \"{text}\" is from {start}s to {end}s")Tips:
- This implementation of TVP uses BertTokenizer to generate text embeddings and Resnet-50 model to compute visual embeddings.
- Checkpoints for pre-trained tvp-base is released.
- Please refer to Table 2 for TVP’s performance on Temporal Video Grounding task.
TvpConfig
class transformers.TvpConfig
< source >( backbone_config = None backbone = None use_pretrained_backbone = False use_timm_backbone = False backbone_kwargs = None distance_loss_weight = 1.0 duration_loss_weight = 0.1 visual_prompter_type = 'framepad' visual_prompter_apply = 'replace' visual_prompt_size = 96 max_img_size = 448 num_frames = 48 vocab_size = 30522 hidden_size = 768 intermediate_size = 3072 num_hidden_layers = 12 num_attention_heads = 12 max_position_embeddings = 512 max_grid_col_position_embeddings = 100 max_grid_row_position_embeddings = 100 hidden_dropout_prob = 0.1 hidden_act = 'gelu' layer_norm_eps = 1e-12 initializer_range = 0.02 attention_probs_dropout_prob = 0.1 **kwargs )
Parameters
- backbone_config (
PretrainedConfigordict, optional) — The configuration of the backbone model. - backbone (
str, optional) — Name of backbone to use whenbackbone_configisNone. Ifuse_pretrained_backboneisTrue, this will load the corresponding pretrained weights from the timm or transformers library. Ifuse_pretrained_backboneisFalse, this loads the backbone’s config and uses that to initialize the backbone with random weights. - use_pretrained_backbone (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to use pretrained weights for the backbone. - use_timm_backbone (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to loadbackbonefrom the timm library. IfFalse, the backbone is loaded from the transformers library. - backbone_kwargs (
dict, optional) — Keyword arguments to be passed to AutoBackbone when loading from a checkpoint e.g.{'out_indices': (0, 1, 2, 3)}. Cannot be specified ifbackbone_configis set. - distance_loss_weight (
float, optional, defaults to 1.0) — The weight of distance loss. - duration_loss_weight (
float, optional, defaults to 0.1) — The weight of duration loss. - visual_prompter_type (
str, optional, defaults to"framepad") — Visual prompt type. The type of padding. Framepad means padding on each frame. Should be one of “framepad” or “framedownpad” - visual_prompter_apply (
str, optional, defaults to"replace") — The way of applying visual prompt. Replace means use the value of prompt to change the original value in visual inputs. Should be one of “replace”, or “add”, or “remove”. - visual_prompt_size (
int, optional, defaults to 96) — The size of visual prompt. - max_img_size (
int, optional, defaults to 448) — The maximum size of frame. - num_frames (
int, optional, defaults to 48) — The number of frames extracted from a video. - vocab_size (
int, optional, defaults to 30522) — Vocabulary size of the Tvp text model. Defines the number of different tokens that can be represented by theinputs_idspassed when calling TvpModel. - hidden_size (
int, optional, defaults to 768) — Dimensionality of the encoder layers. - intermediate_size (
int, optional, defaults to 3072) — Dimensionality of the “intermediate” (i.e., feed-forward) layer in the Transformer encoder. - num_hidden_layers (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Number of hidden layers in the Transformer encoder. - num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Number of attention heads for each attention layer in the Transformer encoder. - max_position_embeddings (
int, optional, defaults to 512) — The maximum sequence length that this model might ever be used with. Typically set this to something large just in case (e.g., 512 or 1024 or 2048). - max_grid_col_position_embeddings (
int, optional, defaults to 100) — The largest number of horizontal patches from a video frame. - max_grid_row_position_embeddings (
int, optional, defaults to 100) — The largest number of vertical patches from a video frame. - hidden_dropout_prob (
float, optional, defaults to 0.1) — The dropout probability of hidden layers. - hidden_act (
strorfunction, optional, defaults to"gelu") — The non-linear activation function (function or string) in the encoder and pooler. If string,"gelu","relu","selu"and"gelu_new"`"quick_gelu"are supported. - layer_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-12) — The epsilon used by the layer normalization layers. - initializer_range (
float, optional, defaults to 0.02) — The standard deviation of the truncated_normal_initializer for initializing all weight matrices. - attention_probs_dropout_prob (
float, optional, defaults to 0.1) — The dropout probability of attention layers.
This is the configuration class to store the configuration of a TvpModel. It is used to instantiate an Tvp model according to the specified arguments, defining the model architecture. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the Tvp Intel/tvp-base architecture.
Configuration objects inherit from PretrainedConfig and can be used to control the model outputs. Read the documentation from PretrainedConfig for more information.
from_backbone_config
< source >( backbone_config: PretrainedConfig **kwargs ) → TvpConfig
Parameters
- backbone_config (PretrainedConfig) — The backbone configuration.
Returns
An instance of a configuration object
Instantiate a TvpConfig (or a derived class) from a pre-trained backbone model configuration.
to_dict
< source >( ) → Dict[str, any]
Returns
Dict[str, any]
Dictionary of all the attributes that make up this configuration instance,
Serializes this instance to a Python dictionary. Override the default to_dict().
TvpImageProcessor
class transformers.TvpImageProcessor
< source >( do_resize: bool = True size: Dict = None resample: Resampling = <Resampling.BILINEAR: 2> do_center_crop: bool = True crop_size: Dict = None do_rescale: bool = True rescale_factor: Union = 0.00392156862745098 do_pad: bool = True pad_size: Dict = None constant_values: Union = 0 pad_mode: PaddingMode = <PaddingMode.CONSTANT: 'constant'> do_normalize: bool = True do_flip_channel_order: bool = True image_mean: Union = None image_std: Union = None **kwargs )
Parameters
- do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to resize the image’s (height, width) dimensions to the specifiedsize. Can be overridden by thedo_resizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - size (
Dict[str, int]optional, defaults to{"longest_edge" -- 448}): Size of the output image after resizing. The longest edge of the image will be resized tosize["longest_edge"]while maintaining the aspect ratio of the original image. Can be overriden bysizein thepreprocessmethod. - resample (
PILImageResampling, optional, defaults toResampling.BILINEAR) — Resampling filter to use if resizing the image. Can be overridden by theresampleparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - do_center_crop (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to center crop the image to the specifiedcrop_size. Can be overridden by thedo_center_cropparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - crop_size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults to{"height" -- 448, "width": 448}): Size of the image after applying the center crop. Can be overridden by thecrop_sizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to rescale the image by the specified scalerescale_factor. Can be overridden by thedo_rescaleparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - rescale_factor (
intorfloat, optional, defaults to1/255) — Defines the scale factor to use if rescaling the image. Can be overridden by therescale_factorparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - do_pad (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to pad the image. Can be overridden by thedo_padparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - pad_size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults to{"height" -- 448, "width": 448}): Size of the image after applying the padding. Can be overridden by thepad_sizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - constant_values (
Union[float, Iterable[float]], optional, defaults to 0) — The fill value to use when padding the image. - pad_mode (
PaddingMode, optional, defaults toPaddingMode.CONSTANT) — Use what kind of mode in padding. - do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to normalize the image. Can be overridden by thedo_normalizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - do_flip_channel_order (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to flip the color channels from RGB to BGR. Can be overridden by thedo_flip_channel_orderparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - image_mean (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toIMAGENET_STANDARD_MEAN) — Mean to use if normalizing the image. This is a float or list of floats the length of the number of channels in the image. Can be overridden by theimage_meanparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - image_std (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toIMAGENET_STANDARD_STD) — Standard deviation to use if normalizing the image. This is a float or list of floats the length of the number of channels in the image. Can be overridden by theimage_stdparameter in thepreprocessmethod.
Constructs a Tvp image processor.
preprocess
< source >( videos: Union do_resize: bool = None size: Dict = None resample: Resampling = None do_center_crop: bool = None crop_size: Dict = None do_rescale: bool = None rescale_factor: float = None do_pad: bool = None pad_size: Dict = None constant_values: Union = None pad_mode: PaddingMode = None do_normalize: bool = None do_flip_channel_order: bool = None image_mean: Union = None image_std: Union = None return_tensors: Union = None data_format: ChannelDimension = <ChannelDimension.FIRST: 'channels_first'> input_data_format: Union = None **kwargs )
Parameters
- videos (
ImageInputorList[ImageInput]orList[List[ImageInput]]) — Frames to preprocess. - do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_resize) — Whether to resize the image. - size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults toself.size) — Size of the image after applying resize. - resample (
PILImageResampling, optional, defaults toself.resample) — Resampling filter to use if resizing the image. This can be one of the enumPILImageResampling, Only has an effect ifdo_resizeis set toTrue. - do_center_crop (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_centre_crop) — Whether to centre crop the image. - crop_size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults toself.crop_size) — Size of the image after applying the centre crop. - do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_rescale) — Whether to rescale the image values between [0 - 1]. - rescale_factor (
float, optional, defaults toself.rescale_factor) — Rescale factor to rescale the image by ifdo_rescaleis set toTrue. - do_pad (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to pad the image. Can be overridden by thedo_padparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - pad_size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults to{"height" -- 448, "width": 448}): Size of the image after applying the padding. Can be overridden by thepad_sizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - constant_values (
Union[float, Iterable[float]], optional, defaults to 0) — The fill value to use when padding the image. - pad_mode (
PaddingMode, optional, defaults to “PaddingMode.CONSTANT”) — Use what kind of mode in padding. - do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_normalize) — Whether to normalize the image. - do_flip_channel_order (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_flip_channel_order) — Whether to flip the channel order of the image. - image_mean (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toself.image_mean) — Image mean. - image_std (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toself.image_std) — Image standard deviation. - return_tensors (
strorTensorType, optional) — The type of tensors to return. Can be one of:- Unset: Return a list of
np.ndarray. TensorType.TENSORFLOWor'tf': Return a batch of typetf.Tensor.TensorType.PYTORCHor'pt': Return a batch of typetorch.Tensor.TensorType.NUMPYor'np': Return a batch of typenp.ndarray.TensorType.JAXor'jax': Return a batch of typejax.numpy.ndarray.
- Unset: Return a list of
- data_format (
ChannelDimensionorstr, optional, defaults toChannelDimension.FIRST) — The channel dimension format for the output image. Can be one of:ChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format.ChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format.- Unset: Use the inferred channel dimension format of the input image.
- input_data_format (
ChannelDimensionorstr, optional) — The channel dimension format for the input image. If unset, the channel dimension format is inferred from the input image. Can be one of:"channels_first"orChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format."channels_last"orChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format."none"orChannelDimension.NONE: image in (height, width) format.
Preprocess an image or batch of images.
TvpProcessor
class transformers.TvpProcessor
< source >( image_processor = None tokenizer = None **kwargs )
Parameters
- image_processor (TvpImageProcessor, optional) — The image processor is a required input.
- tokenizer (BertTokenizerFast, optional) — The tokenizer is a required input.
Constructs an TVP processor which wraps a TVP image processor and a Bert tokenizer into a single processor.
TvpProcessor offers all the functionalities of TvpImageProcessor and BertTokenizerFast. See the
call() and decode() for more information.
__call__
< source >( text = None videos = None return_tensors = None **kwargs ) → BatchEncoding
Parameters
- text (
str,List[str],List[List[str]]) — The sequence or batch of sequences to be encoded. Each sequence can be a string or a list of strings (pretokenized string). If the sequences are provided as list of strings (pretokenized), you must setis_split_into_words=True(to lift the ambiguity with a batch of sequences). - videos (
List[PIL.Image.Image],List[np.ndarray],List[torch.Tensor],List[List[PIL.Image.Image]],List[List[np.ndarrray]], —List[List[torch.Tensor]]): The video or batch of videos to be prepared. Each video should be a list of frames, which can be either PIL images or NumPy arrays. In case of NumPy arrays/PyTorch tensors, each frame should be of shape (H, W, C), where H and W are frame height and width, and C is a number of channels. - return_tensors (
stror TensorType, optional) — If set, will return tensors of a particular framework. Acceptable values are:'tf': Return TensorFlowtf.constantobjects.'pt': Return PyTorchtorch.Tensorobjects.'np': Return NumPynp.ndarrayobjects.'jax': Return JAXjnp.ndarrayobjects.
Returns
A BatchEncoding with the following fields:
- input_ids — List of token ids to be fed to a model. Returned when
textis notNone. - attention_mask — List of indices specifying which tokens should be attended to by the model (when
return_attention_mask=Trueor if “attention_mask” is inself.model_input_namesand iftextis notNone). - pixel_values — Pixel values to be fed to a model. Returned when
videosis notNone.
Main method to prepare for the model one or several sequences(s) and image(s). This method forwards the text
and kwargs arguments to BertTokenizerFast’s call() if text is not None to encode
the text. To prepare the image(s), this method forwards the videos and kwargs arguments to
TvpImageProcessor’s call() if videos is not None. Please refer to the doctsring of
the above two methods for more information.
TvpModel
class transformers.TvpModel
< source >( config )
Parameters
- config (TvpConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
The bare Tvp Model transformer outputting BaseModelOutputWithPooling object without any specific head on top. This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
< source >( input_ids: Optional = None pixel_values: Optional = None attention_mask: Optional = None head_mask: Optional = None output_attentions: Optional = None output_hidden_states: Optional = None return_dict: Optional = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Indices can be obtained using AutoTokenizer. See PreTrainedTokenizer.encode() and PreTrainedTokenizer.call() for details. What are input IDs? - pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_frames, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using TvpImageProcessor. See TvpImageProcessor.call() for details. - attention_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked. What are attention masks?
- head_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
Returns
transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (<class 'transformers.models.tvp.configuration_tvp.TvpConfig'>) and inputs.
-
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model. -
pooler_output (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, hidden_size)) — Last layer hidden-state of the first token of the sequence (classification token) after further processing through the layers used for the auxiliary pretraining task. E.g. for BERT-family of models, this returns the classification token after processing through a linear layer and a tanh activation function. The linear layer weights are trained from the next sentence prediction (classification) objective during pretraining. -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs.
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The TvpModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
>>> import torch
>>> from transformers import AutoConfig, AutoTokenizer, TvpModel
>>> model = TvpModel.from_pretrained("Jiqing/tiny-random-tvp")
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("Jiqing/tiny-random-tvp")
>>> pixel_values = torch.rand(1, 1, 3, 448, 448)
>>> text_inputs = tokenizer("This is an example input", return_tensors="pt")
>>> output = model(text_inputs.input_ids, pixel_values, text_inputs.attention_mask)TvpForVideoGrounding
class transformers.TvpForVideoGrounding
< source >( config )
Parameters
- config (TvpConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
Tvp Model with a video grounding head on top computing IoU, distance, and duration loss.
This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
< source >( input_ids: Optional = None pixel_values: Optional = None attention_mask: Optional = None labels: Tuple = None head_mask: Optional = None output_attentions: Optional = None output_hidden_states: Optional = None return_dict: Optional = None ) → transformers.models.tvp.modeling_tvp.TvpVideoGroundingOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Indices can be obtained using AutoTokenizer. See PreTrainedTokenizer.encode() and PreTrainedTokenizer.call() for details. What are input IDs? - pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_frames, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using TvpImageProcessor. See TvpImageProcessor.call() for details. - attention_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked. What are attention masks?
- head_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple. - labels (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, 3), optional) — The labels contains duration, start time, and end time of the video corresponding to the text.
Returns
transformers.models.tvp.modeling_tvp.TvpVideoGroundingOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.tvp.modeling_tvp.TvpVideoGroundingOutput or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (<class 'transformers.models.tvp.configuration_tvp.TvpConfig'>) and inputs.
- loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenreturn_lossisTrue) — Temporal-Distance IoU loss for video grounding. - logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, 2)) — Contains start_time/duration and end_time/duration. It is the time slot of the videos corresponding to the input texts. - hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size). Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs. - attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).
The TvpForVideoGrounding forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
>>> import torch
>>> from transformers import AutoConfig, AutoTokenizer, TvpForVideoGrounding
>>> model = TvpForVideoGrounding.from_pretrained("Jiqing/tiny-random-tvp")
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("Jiqing/tiny-random-tvp")
>>> pixel_values = torch.rand(1, 1, 3, 448, 448)
>>> text_inputs = tokenizer("This is an example input", return_tensors="pt")
>>> output = model(text_inputs.input_ids, pixel_values, text_inputs.attention_mask)