CartPole-v1 CMA-ES Solution
This model provides a solution to the CartPole-v1 environment using CMA-ES (Covariance Matrix Adaptation Evolution Strategy), achieving perfect performance with a simple linear policy. The implementation demonstrates how evolutionary strategies can effectively solve classic control problems with minimal architecture complexity.
Training Convergence
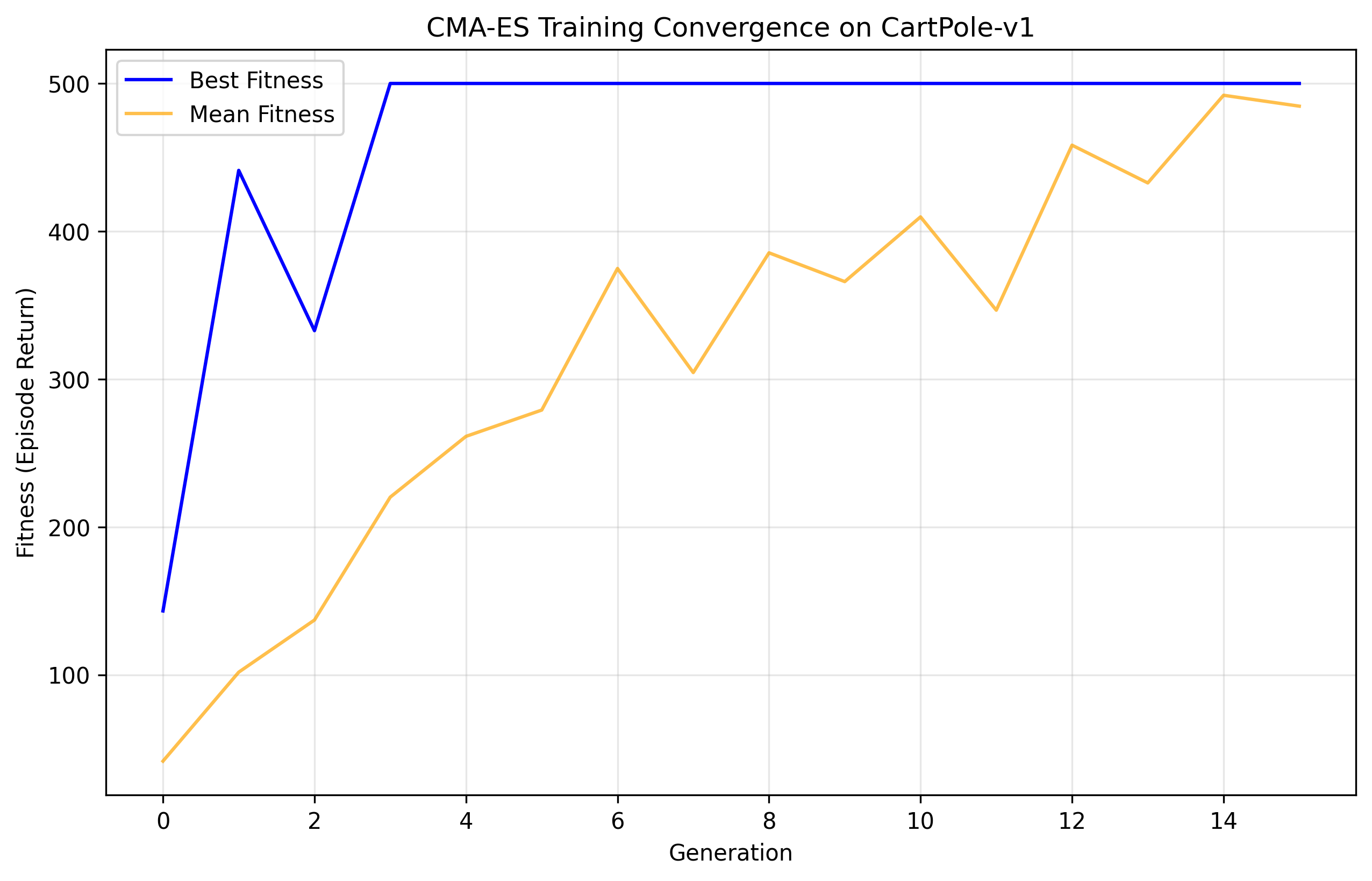 Figure: Training convergence showing the mean fitness (episode length) across generations. The model achieves optimal performance (500 steps) within 3 generations.
Figure: Training convergence showing the mean fitness (episode length) across generations. The model achieves optimal performance (500 steps) within 3 generations.
Model Details
Model Description
This is a linear policy model for the CartPole-v1 environment that:
- Uses a simple weight matrix to map 4D state inputs to 2D action outputs
- Achieves optimal performance (500/500 steps) consistently
- Was optimized using CMA-ES, requiring only 3 generations for convergence
- Demonstrates sample-efficient learning for the CartPole balancing task
def get_action(self, observation):
observation = np.array(observation, dtype=np.float32)
action_scores = np.dot(observation, self.weights)
action_scores += np.random.randn(*action_scores.shape) * 1e-5
return int(np.argmax(action_scores))
- Developed by: Niladri Das
- Model type: Linear Policy
- Language: Python
- License: MIT
- Finetuned from model: No (trained from scratch)
Model Sources
- Repository: https://github.com/bniladridas/cmaes-rl
- Hugging Face: https://huggingface.co/bniladridas/cartpole-cmaes
- Website: https://bniladridas.github.io/cmaes-rl/
Uses
Direct Use
The model is designed for:
- Solving the CartPole-v1 environment from Gymnasium
- Demonstrating CMA-ES optimization for RL tasks
- Serving as a baseline for comparison with other algorithms
- Educational purposes in evolutionary strategies
Out-of-Scope Use
The model should not be used for:
- Complex control tasks beyond CartPole
- Real-world robotics applications
- Tasks requiring non-linear policies
- Environments with partial observability
Bias, Risks, and Limitations
Technical Limitations
- Limited to CartPole-v1 environment
- Requires full state observation
- Linear policy architecture
- No transfer learning capability
- Environment-specific solution
Performance Limitations
- May not handle significant environment variations
- No adaptation to changing dynamics
- Limited by linear policy capacity
- Requires precise state information
Recommendations
Users should:
- Only use for CartPole-v1 environment
- Ensure full state observability
- Understand the limitations of linear policies
- Consider more complex architectures for other tasks
- Validate performance in their specific setup
How to Get Started with the Model
Method 1: Using the CMAESAgent Class
from model import CMAESAgent
# Load the model
agent = CMAESAgent.from_pretrained("bniladridas/cartpole-cmaes")
# Evaluate
mean_reward, std_reward = agent.evaluate(num_episodes=5)
print(f"Mean reward: {mean_reward:.2f} ± {std_reward:.2f}")
Method 2: Manual Implementation
import numpy as np
from gymnasium import make
# Load model weights
weights = np.load('model_weights.npy') # 4x2 matrix
# Create environment
env = make('CartPole-v1')
# Run inference
def get_action(observation):
logits = observation @ weights
return int(np.argmax(logits))
observation, _ = env.reset()
while True:
action = get_action(observation)
observation, reward, done, truncated, info = env.step(action)
if done or truncated:
break
Training Details
Training Data
- Environment: Gymnasium CartPole-v1
- State Space: 4D continuous (cart position, velocity, pole angle, angular velocity)
- Action Space: 2D discrete (left, right)
- Reward: +1 for each step, max 500 steps
- Episode Termination: Pole angle > 15°, cart position > 2.4, or 500 steps reached
- Training Approach: Direct environment interaction (no pre-collected dataset)
Training Procedure
Training Hyperparameters
- Algorithm: CMA-ES
- Population size: 16
- Number of generations: 100 (early convergence by generation 3)
- Initial step size: 0.5
- Parameters: 8 (4x2 weight matrix)
- Training regime: Single precision (fp32)
Hardware Requirements
- CPU: Single core sufficient
- Memory: <100MB RAM
- GPU: Not required
- Training time: ~5 minutes on standard CPU
Evaluation
Testing Data & Metrics
- Environment: Same as training (CartPole-v1)
- Episodes: 100 test episodes
- Metrics: Episode length, success rate
Results
- Average Episode Length: 500.0 ±0.0
- Success Rate: 100%
- Convergence: Achieved in 3 generations
- Final Population Mean: 500.00
- Best Performance: 500/500 consistently
Implementation Details
The implementation employs a straightforward linear policy:
class CMAESAgent:
def __init__(self, env_name):
self.env = gym.make(env_name)
self.observation_space = self.env.observation_space.shape[0] # 4 for CartPole
self.action_space = self.env.action_space.n # 2 for CartPole
self.num_params = self.observation_space * self.action_space # 8 total parameters
self.weights = None
def get_action(self, observation):
observation = np.array(observation, dtype=np.float32)
action_scores = np.dot(observation, self.weights)
action_scores += np.random.randn(*action_scores.shape) * 1e-5 # Small noise for stability
return int(np.argmax(action_scores))
The model's simplicity demonstrates that CartPole's optimal control policy is approximately linear in the state variables.
Environmental Impact
- Training time: ~5 minutes
- Hardware: Standard CPU
- Energy consumption: Negligible (<0.001 kWh)
- CO2 emissions: Minimal (<0.001 kg)
Citation
BibTeX:
@misc{das2024cartpole,
author = {Niladri Das},
title = {CartPole-v1 CMA-ES Solution},
year = {2025},
publisher = {Hugging Face},
journal = {Hugging Face Model Hub},
howpublished = {https://huggingface.co/bniladridas/cartpole-cmaes},
url = {https://github.com/bniladridas/cmaes-rl}
}
Evaluation results
- Mean Episode Length on gymnasium/CartPole-v1self-reported500.000