Spaces:
Running
Running
Update README.md
Browse files
README.md
CHANGED
|
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ pinned: false
|
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
# InSTA: Towards Internet-Scale Training For Agents
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
-
 Gunnar Sigurdsson (2) Robinson Piramuthu (2) Ruslan Salakhutdinov (1)**
|
| 15 |
|
|
@@ -21,18 +21,18 @@ The predominant approach for training web navigation agents gathers human demons
|
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
## Section 4 - Internet-Scale Task Generation
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
-
, we improve Step Accuracy by up to +89.5% and +122.1% respectively for agents trained on mixtures of data from our pipeline, and human data. When training agents with all available human data from these benchmarks (right plot), agents trained on existing human data struggle to generalize to diverse real sites, and adding our data improves their generalization by +149.0% for WebLINX and +156.3% for Mind2Web.
|
|
|
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
# InSTA: Towards Internet-Scale Training For Agents
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
+

|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
**Brandon Trabucco (1) Gunnar Sigurdsson (2) Robinson Piramuthu (2) Ruslan Salakhutdinov (1)**
|
| 15 |
|
|
|
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
## Section 4 - Internet-Scale Task Generation
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
+

|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
**Task proposal and filtering for 150k live websites.** Starting from 1,000,000 websites, we employ a pretrained language model that marks sites as safe/unsafe for annotation, and assigns a realistic task that a hypothetical user might want to accomplish on each site. The task proposer rejects 85% of websites from the pipeline, resulting in 150k safe websites annotated with realistic tasks.
|
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
## Section 5 - Internet-Scale Agents
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
+
|
| 31 |
|
| 32 |
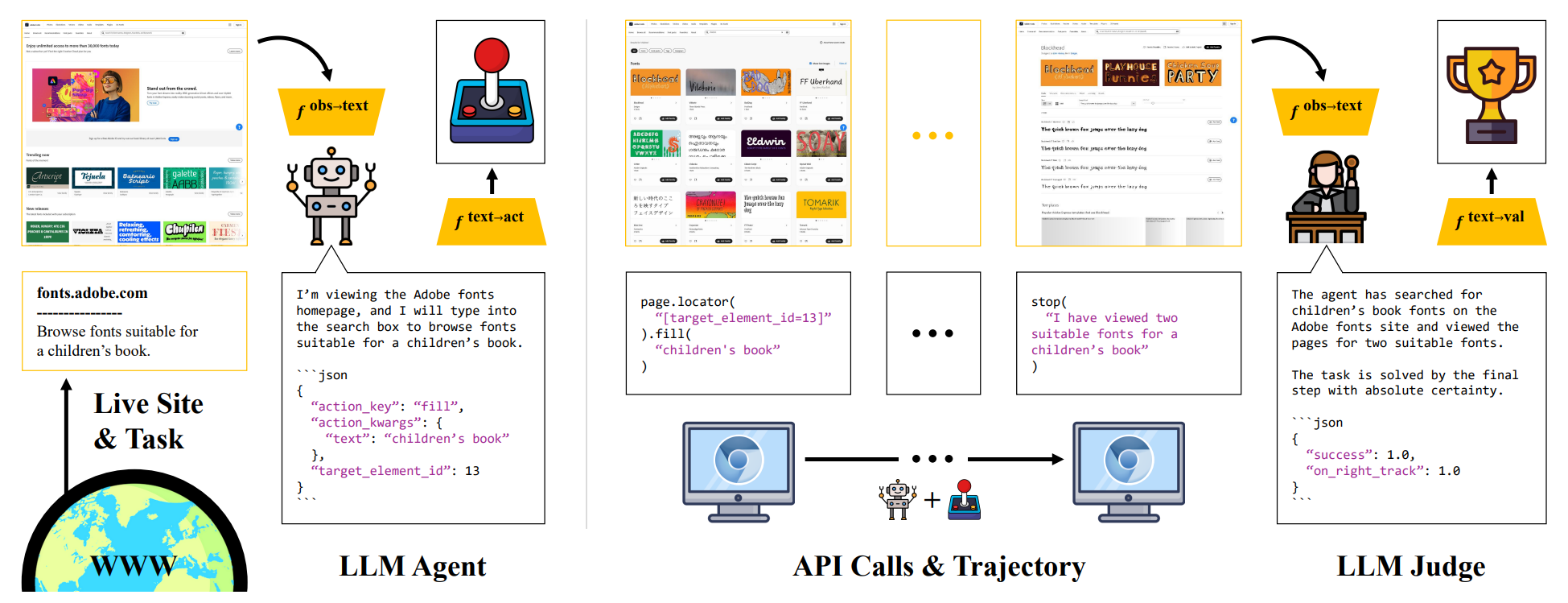
**Automatic evaluation for agents with language model judges.** Building on the large and diverse set of tasks generated by the pipeline, we employ pretrained language models to attempt and evaluate web navigation tasks. We dispatch language model agents to perform tasks by making calls to the Playwright API. We then employ language model judges to evaluate rollouts from agents.
|
| 33 |
|
| 34 |
## Section 6 - Training Agents
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
+
|
| 37 |
|
| 38 |
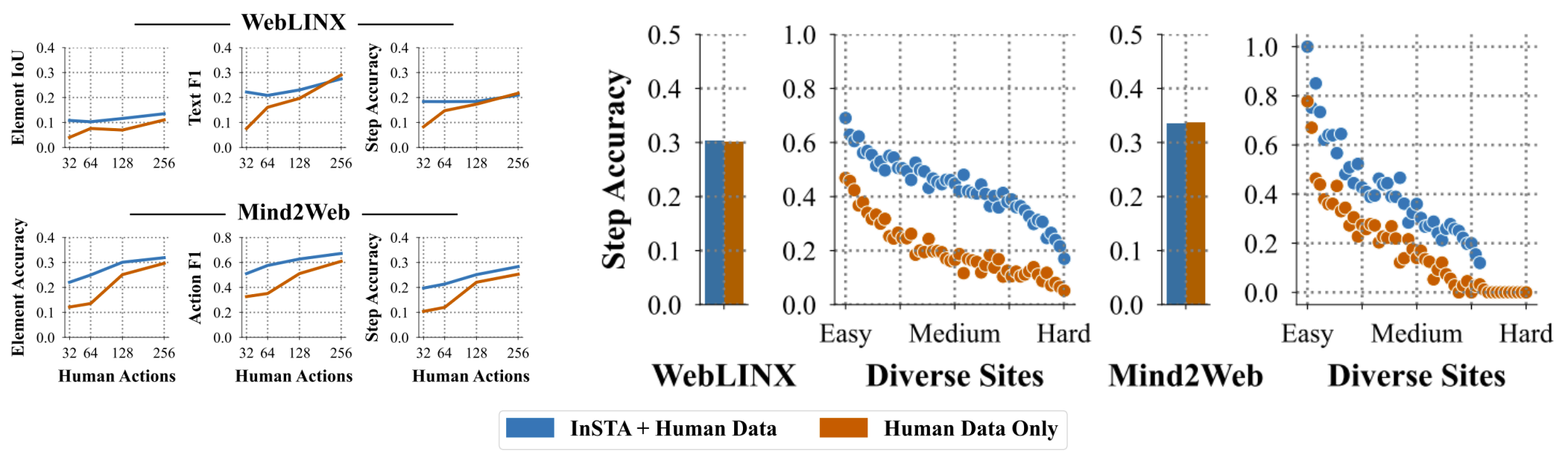
**Training agents with internet-scale data.** In data-limited settings derived from Mind2Web and WebLINX (left plot), we improve Step Accuracy by up to +89.5% and +122.1% respectively for agents trained on mixtures of data from our pipeline, and human data. When training agents with all available human data from these benchmarks (right plot), agents trained on existing human data struggle to generalize to diverse real sites, and adding our data improves their generalization by +149.0% for WebLINX and +156.3% for Mind2Web.
|