Rep-MTL: Unleashing the Power of Representation-level Task Saliency for Multi-Task Learning
Abstract
Rep-MTL enhances multi-task learning by leveraging representation-level saliency to promote task complementarity and mitigate negative transfer.
Despite the promise of Multi-Task Learning in leveraging complementary knowledge across tasks, existing multi-task optimization (MTO) techniques remain fixated on resolving conflicts via optimizer-centric loss scaling and gradient manipulation strategies, yet fail to deliver consistent gains. In this paper, we argue that the shared representation space, where task interactions naturally occur, offers rich information and potential for operations complementary to existing optimizers, especially for facilitating the inter-task complementarity, which is rarely explored in MTO. This intuition leads to Rep-MTL, which exploits the representation-level task saliency to quantify interactions between task-specific optimization and shared representation learning. By steering these saliencies through entropy-based penalization and sample-wise cross-task alignment, Rep-MTL aims to mitigate negative transfer by maintaining the effective training of individual tasks instead pure conflict-solving, while explicitly promoting complementary information sharing. Experiments are conducted on four challenging MTL benchmarks covering both task-shift and domain-shift scenarios. The results show that Rep-MTL, even paired with the basic equal weighting policy, achieves competitive performance gains with favorable efficiency. Beyond standard performance metrics, Power Law exponent analysis demonstrates Rep-MTL's efficacy in balancing task-specific learning and cross-task sharing. The project page is available at HERE.
Community
[ICCV 2025 Highlight] Rep-MTL: Unleashing the Power of Representation-level Task Saliency for Multi-Task Learning
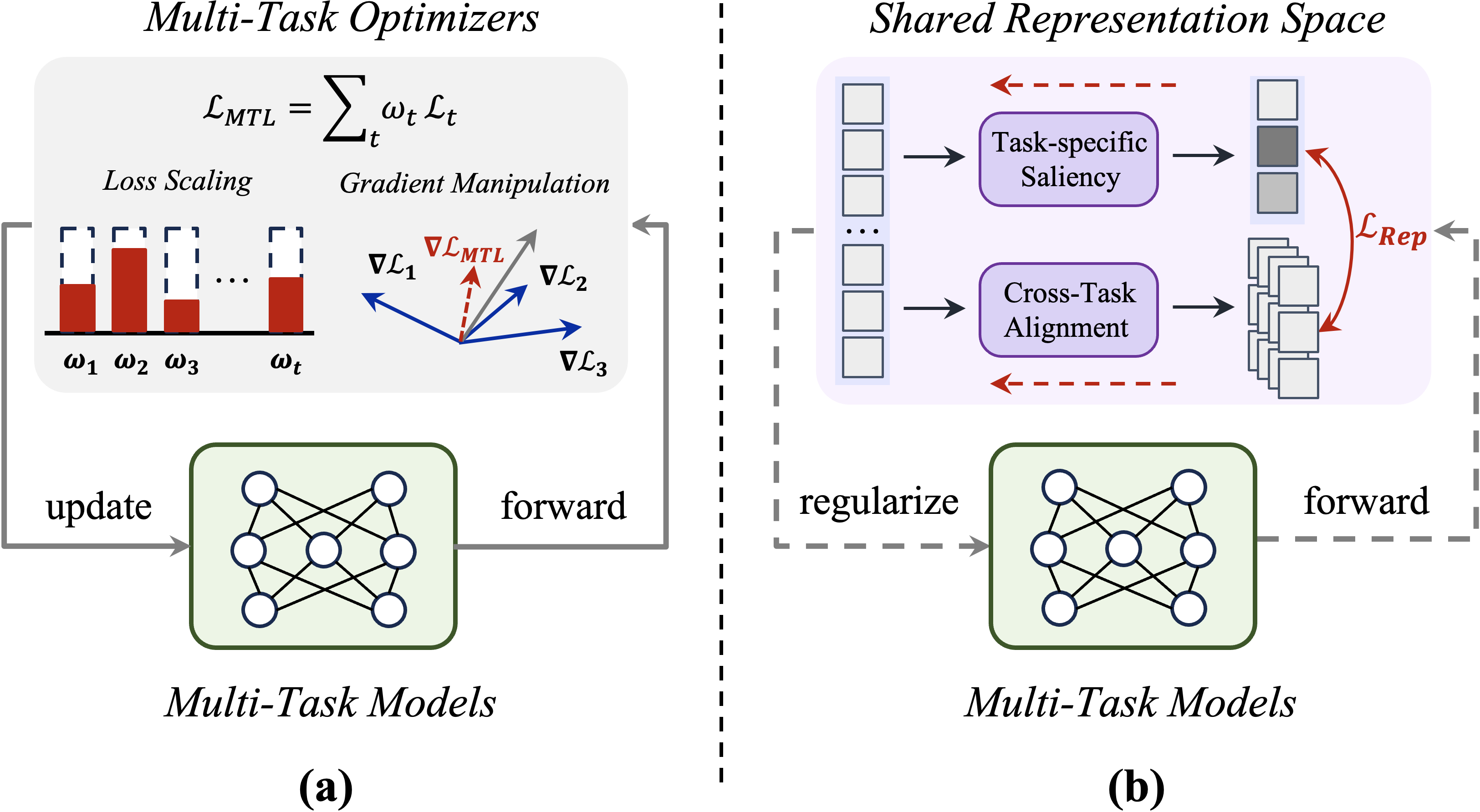
(a) Most existing multi-task optimization methods focus on addressing conflicts in parameter updates. (b) Rep-MTL instead leverages task saliency in shared representation space to explicitly facilitate cross-task information sharing while preserving task-specific signals via regularization, without modifications to either the underlying optimizers or model architectures.
arXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.21049
Project page: https://jacky1128.github.io/RepMTL/
GitHub: https://github.com/Jacky1128/Rep-MTL
This is an automated message from the Librarian Bot. I found the following papers similar to this paper.
The following papers were recommended by the Semantic Scholar API
- Multi-Task Dense Prediction Fine-Tuning with Mixture of Fine-Grained Experts (2025)
- SAMO: A Lightweight Sharpness-Aware Approach for Multi-Task Optimization with Joint Global-Local Perturbation (2025)
- Resolving Token-Space Gradient Conflicts: Token Space Manipulation for Transformer-Based Multi-Task Learning (2025)
- StableMTL: Repurposing Latent Diffusion Models for Multi-Task Learning from Partially Annotated Synthetic Datasets (2025)
- Merging Smarter, Generalizing Better: Enhancing Model Merging on OOD Data (2025)
- Controlled Data Rebalancing in Multi-Task Learning for Real-World Image Super-Resolution (2025)
- Gradient Similarity Surgery in Multi-Task Deep Learning (2025)
Please give a thumbs up to this comment if you found it helpful!
If you want recommendations for any Paper on Hugging Face checkout this Space
You can directly ask Librarian Bot for paper recommendations by tagging it in a comment:
@librarian-bot
recommend
arXiv explained breakdown of this paper 👉 https://arxivexplained.com/papers/rep-mtl-unleashing-the-power-of-representation-level-task-saliency-for-multi-task-learning
Models citing this paper 0
No model linking this paper
Datasets citing this paper 0
No dataset linking this paper
Spaces citing this paper 0
No Space linking this paper